Advanced Statistics with Computer Application
- 1. Advanced Statistics with Computer Application GROUP 1 MPA 1Y1-1 Advanced Statistics with Computer Application Marivic De Gracia, Azenith Gonzalgo-Pua, Jaime Anne Larracas, Djeriel Estrella, Florence Villpando-Mendoza, and Lyka Merilles
- 2. Introduction of Statistics and Importance of Statistics Frequency Distribution and their Graphic Presentation Collection and Presentation of Data Outline Measure of Central Tendency
- 3. STATISTICS It is a branch of mathematics that deals with collecting, analyzing, interpreting, organizing and presenting data. It is a powerful tool used to make sense of large amounts of information, drawing conclusions, making predictions, and informing decisions based on data.
- 4. Uses of Statistics Economics Weather Forecast Medicine Social sciences Decision making
- 5. Importance of Statistics It is essential for analyzing and interpreting data, providing the tools needed to make informed decisions based on empirical evidence. It helps people make informed decisions. Governments, organizations, and businesses all collect statistics to help them track progress, measure performance, analyze problems, and prioritize.
- 6. • Data Driven Decision Making • Understanding and Managing Uncertainty • Scientific Research and Innovation • Social Understanding and Policy Development • Quality Control and Improvement • Education and Learning • Personal Decision Making • Global Development and Sustainability If Statistics is effectively utilized ....
- 8. DATA Refers to any facts or figures that are collated with the intention of being presented, interpreted, and analyzed.
- 9. Qualitative Quantitative Data may be: Data that describes characteristics or qualities. Data that is quantified or measured. Usually deals with language Usually deals with numbers. is descriptive. It includes things like color, texture, and taste. is numerical. It includes things like height, rate, and speed.
- 10. TYPES OF QUANTITATIVE DATA Discrete Data The data that have fixed value is called discrete data, discrete data can easily be counted Continuous Data The data that has no fixed value and has a range of data is called continuous data. It can be measured
- 11. Identify each of the following pieces of data about the girl pictured to the right as either qualitative or quantitative: 1. Pink pants 2. Short hair 3.Five feet, three inches tall 4.Twenty years old 5.Outgoing personality CHECK FOR UNDERSTANDING
- 12. Identify each of the following pieces of data about the girl pictured to the right as either qualitative or quantitative: 1. Pink pants = qualitative 2. Short hair = qualitative 3.Five feet, three inches tall = quantitative 4.Twenty two years old = quantitative 5.Outgoing personality = qualitative CHECK FOR UNDERSTANDING
- 13. SOURCES OF DATA Primary Data is a type of information that is obtained directly from the first- hand source through experiments, surveys or observations. Secondary Data is data collected by someone other than the actual user. It means that the information is already available, and someone analyses it.
- 15. Surveys and Questionnaires Description: A method of gathering information from a sample of people, typically by asking them a series of questions. Application: Useful for collecting a large amount of data quickly from a diverse group. Experiments Description: A method where variables are controlled and manipulated to observe their effect on other variables. Application: Commonly used in scientific research to test hypotheses.
- 16. Observational Studies Description: A method of collecting data by observing subjects in their natural environment without interference. Application: Useful when manipulation of variables is not possible or ethical Interviews Description: A method involving direct, face-to-face, or telephonic interaction to gather detailed information. Application: Useful for collecting in-depth qualitative data.
- 17. Focus Group Description: A method where a small group of people discuss a topic, guided by a moderator, to gather opinions and attitudes. Application: Useful for exploring complex issues and generating ideas. Existing Records and Database Description: A method that involves using pre-existing data from sources like government databases, business records, or academic research. Application: Cost-effective and time-saving, but may require careful evaluation of data reliability.
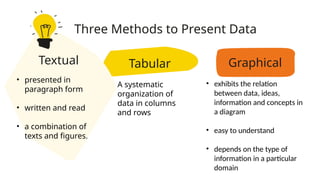
- 19. Graphical • exhibits the relation between data, ideas, information and concepts in a diagram • easy to understand • depends on the type of information in a particular domain Tabular • A systematic organization of data in columns and rows Three Methods to Present Data Textual • presented in paragraph form • written and read • a combination of texts and figures.
- 20. Using Graphs to Represent Data S TAT I S T I CS
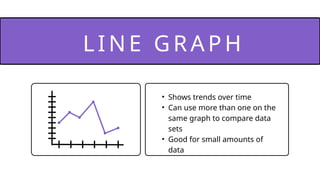
- 21. LI NE GRA P H • Shows trends over time • Can use more than one on the same graph to compare data sets • Good for small amounts of data
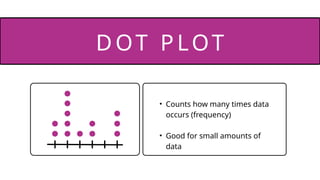
- 22. • Counts how many times data occurs (frequency) • Good for small amounts of data DOT P LOT
- 23. BAR GR AP H • Used to compare groups. • Used rectangular bars to present the frequency or value of data. • Bars can be vertical or horizontal.
- 24. • Used to depict parts of a whole. • A Circular chart divided into sectors, with each sector representing a proportion of the whole. P IE CHA RT
- 25. • Can use more than one to compare data on the same graph • Good for large amounts of data B O X & W H I S K E R P L OT
- 26. • Counts how many times data occurs between set ranges • Good for large amounts of data HI STO GR AM
- 27. • Used images or symbols to represent data . • Each symbol represents a specific quality, making it easy to visualize and compare. P I C T O G R A P H
- 28. SCAT T ER P LOT • Great for analyzing correlation between two variables • Good for large amounts of data
- 29. Statistics provide single values to represent data sets, but graphs are another tool for analyzing data. Graphs represent data visually, and serve to make trends in data more clear. ANALYZING GRAPHS
- 30. The same researcher is finished with her experiment on the effects of music on plant growth. She has calculated the average amount of growth done by each group of plants (Group One: 4 in., Group Two: 2 in., Group Three: 5 in.). What type of graph would be best for this data set? CHECK FOR UNDERSTANDING
- 31. ...she has calculated the average amount of growth done by each group of plants (Group One: 4 in., Group Two: 2 in., Group Three: 5 in.). What type of graph would be best for this data set? CHECK FOR UNDERSTANDING A bar graph would be best for this data set because she is comparing groups of plants.