Biostatistics pt 1
- 1. IMPORTANCE OF STATISTICS Dr. Bipul Borthakur (Professor) Dept of Orthopaedics, SMCH
- 2. Introduction Statistics is a field of study concerned with collection, organisation, summarisation and analysis of data and the drawing of inferences about a body when only a part of data are observed. In other words, it is the scientific methodology of decision making from collected data or information.
- 3. Types of Statistics DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS Organisation and summarisation of data, i.e. numerical or graphics summaries of data. Example- Charts, graphs, tables, summary etc. INFERENTIAL STATISTICS Making inferences about samples drawn from population Allows conclusion to be drawn about the data set and predictions that can be made about relationships found between different variables. Example- Chi square test, T-test, Anova test
- 4. Variables Simple variable • has only one main component • example- weight, height Composite variable • has more than one component • example- body mass index Dependent variable • one variable depends upon or is a consequence of other variable. • example- health status of country Independent variable • variable that is antecedent to or the cause of the dependent variable • example- age, gender
- 5. Variables Latent variable • the variable which cannot be measured directly but assumed to be related to a no. of observations • example- bright student, efficient worker. Random variable • when value cannot be predicted in advance • example- tossing a coin Attribute- • qualitative character of an event is referred to as attribute. • example- sex, religion,
- 6. Data Data are facts expressed in numerical terms Information • When data set undergoes through statistical processing, it becomes information. Intelligence • It is for the decision or policy makers based on transformation of the information.
- 7. Classification of data Data can be classified in various ways. Continuous & Discrete data Continuous is data for which an unlimited no. of possible values exist. Example is height and weight Discrete data is data for which limited no. of variable exist. Example- no. of players in a cricket team. Qualitative & quantitative data Qualitative data- which can’t be measured, but can be expressed in frequency, example- sex, religion. Quantitative data- characteristic and the frequency of a variable can be measured, example- height, weight. Primary & secondary data Primary data- collected by researcher themselves, example- census data, field survey Secondary data- which has been collected by someone else and are used by another researcher.
- 8. Hard & soft data Hard data- usually displayed on continuous scale as a digital readout or computer print out, taken from modern mechanical instruments. Soft data- any subjective measurement which has more potential for bias or variability on the part of the observer. Example- pain of a cancer patient.
- 9. Presentation of data Data can be presented in two ways Diagrammatic Tabular
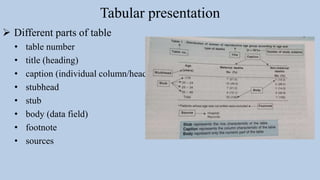
- 10. Tabular presentation Different parts of table • table number • title (heading) • caption (individual column/heads/boxhead) • stubhead • stub • body (data field) • footnote • sources
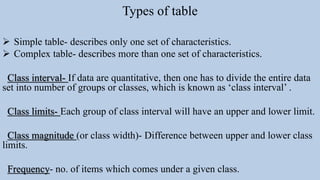
- 11. Types of table Simple table- describes only one set of characteristics. Complex table- describes more than one set of characteristics. Class interval- If data are quantitative, then one has to divide the entire data set into number of groups or classes, which is known as ‘class interval’ . Class limits- Each group of class interval will have an upper and lower limit. Class magnitude (or class width)- Difference between upper and lower class limits. Frequency- no. of items which comes under a given class.
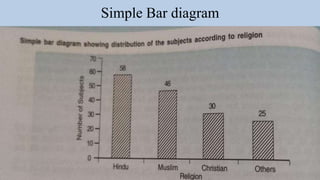
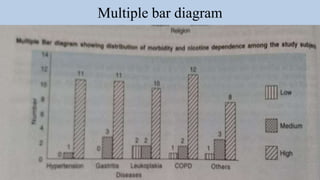
- 12. Graphic representation Diagrams for qualitative/categorial/discrete data Bar diagram: • Different categories are indicated on one axis and frequency of data in each category is indicated on the other axis and categories are compared by length of bars. • Three different types of bar diagram- simple, multiple and component bar diagram. Pie diagram • It is used to represent division of whole into segments by using wedge-shaped portions of a circle for comparison. • Degrees of angle denote the frequency and area of sector. Pictogram • Small pictures or symbols are used to represent the diagram that conveys some statistical information.
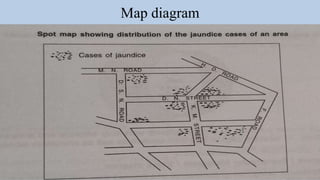
- 13. Map diagram • This consists of a map of an area with location of each case of an event. Venn diagram • This shows the degree of overlap and exclusively for two or more characteristics or factors within a sample, or population, or for a characteristic among two or more samples.
- 17. Pie diagram
- 18. Pictogram
- 19. Map diagram
- 20. Venn diagram
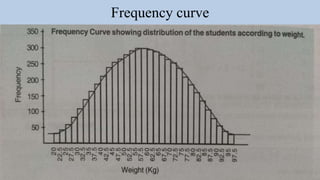
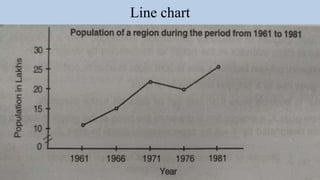
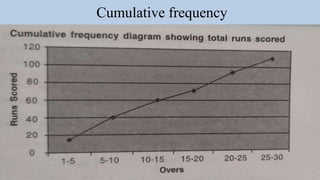
- 21. Quantitative data Histogram Frequency polygon Frequency curve Line chart Cumulative frequency Scatter diagram Box plot Stem and Leaf plot/Stem plot Spider Chart
- 22. Histogram
- 24. Frequency curve
- 25. Line chart
- 27. Scatter diagram
- 28. Box plot
- 29. Stem and Leaf plot/Stem plot
- 30. Spider chart
- 31. Scales of measurements Four different measurement scales Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio
- 32. Nominal scale It provides a convenient way of keeping track of people, objects and events. Data are divided into qualitative categories or groups Example- Hindu/Muslim/ Christian, Blood group A/B/AB/O
- 33. Ordinal scale This scale places events in a meaningful order i.e. observations are ordered or ranked on the basis of specific characteristics. Example- Acute respiratory infection may be classified as no pneumonia, pneumonia, severe pneumonia
- 34. Interval scale Similar to ordinal scale, here data are placed in meaningful order and in addition they have definite interval between them. Example- In Celsius scale, difference between 100 degree and degree.
- 35. Ratio scale This scale has some properties as an interval scale; nut because it has an absolute zero, meaningful ratios do exist. Example- weight in grams or pounds, time in seconds or days.
- 36. THANK YOU “sukhaduḥkhe same kṛtvā lābhālābhau jayājayau tato yuddhāya yujyasva naivaṃ pāpamavāpsyasi” “Holding pleasure and pain, gain and loss, victory and defeat as alike, gird yourself up for the battle. Thus, you shall not incur any sin.”