chapter one business mathematical statistics.pptx
- 2. Introduction Statistics is concerned with scientific method of collecting, organizing, analyzing, summarizing and presenting data, so as to comprehend the essential features and relationship of the data. It can be defined as “the study of the methods of collecting and analysis of data to draw a helpful conclusion.
- 3. Major steps in statistical analysis are; • Data collection • Data Organization • Data analysis • Data presentation and interpretation of data, • Drawing of inferences body of data when only a small part of the data is observed.
- 4. Importance of Statistics Discover knowledge Base for decision making Understand circumstances Support ideas and arguments etc
- 5. Business Statistics Business Statistics -Statistics is the study of how to collect, organizes, analyze, and interpret numerical information from data. Business statistics is statistics as applied to the Business and economic.
- 6. Uses of Business Statistics Provide methods of organizing information Assessment of market status Commercial program evaluation Resource allocation Magnitude of association (Strong vs. weak association between cause and effect)
- 7. Role of Statisticians in Business Guide the design of an experiment Guide the design of prior to data collection Decide which information to gather Analyze data using proper statistical procedures Make the best summary Present and interpret the results for decision making
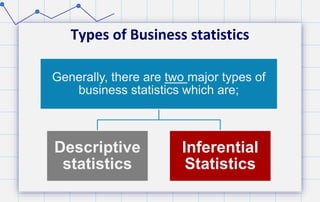
- 8. Types of Business statistics Generally, there are two major types of business statistics which are; Descriptive statistics Inferential Statistics
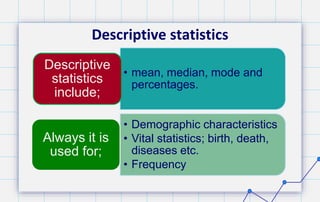
- 9. Descriptive Statistics Descriptive statistics is involves the collection, organization, summarization and presentation of data in order to describe the various facts about the data This describes and summarizes the data through tables or charts in order to bring out the important facts about the data
- 10. Descriptive statistics • mean, median, mode and percentages. Descriptive statistics include; • Demographic characteristics • Vital statistics; birth, death, diseases etc. • Frequency Always it is used for;
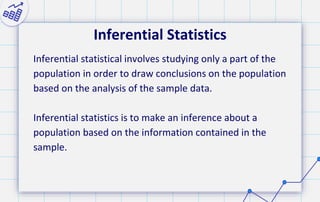
- 11. Inferential Statistics Inferential statistical involves studying only a part of the population in order to draw conclusions on the population based on the analysis of the sample data. Inferential statistics is to make an inference about a population based on the information contained in the sample.
- 12. Inferential Statistics Inferential statistics are used for; Hypothesis Testing Determining Relationships among Variables Making Predictions
- 13. Characteristics of Inferential Statistics Uses samples from larger populations Draw conclusions from sample data Conclusions apply to whole population Estimate a population value Test a hypothesis State probability of error
- 14. Population and Sample Population: Population refers to any collection of objects. Collection of items that have something shared or common and we wish to draw conclusions at a particular time E.g., All hospitals, all hotels, all students, all pregnant women, all health worker.
- 15. Population and Sample Sample Sample refers to a portion or part of the population of interest Sample is a single item that was selected from the whole population or representative part from population E.g., 100 health workers selected from all health workers, 10 hotels selected from all hospital, 100 students selected to represent all the students
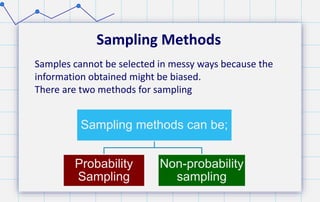
- 16. Sampling Methods Sampling methods can be; Probability Sampling Non-probability sampling Samples cannot be selected in messy ways because the information obtained might be biased. There are two methods for sampling
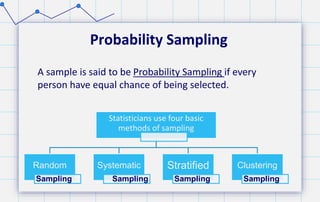
- 17. Probability Sampling Statisticians use four basic methods of sampling Random Sampling Systematic Sampling Stratified Sampling Clustering Sampling A sample is said to be Probability Sampling if every person have equal chance of being selected.
- 18. Random sampling Also known as simple random sampling; is to select sample by using chance methods or random numbers. For example; number each subject in the population. Then place numbered cards in a bowl, mix them thoroughly, and select as many cards as needed
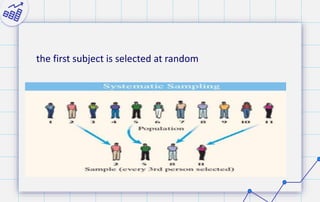
- 19. Systematic Sampling Researchers obtain systematic samples by numbering each subject of the population and then selecting every Kth subject. For example, suppose there were 11 employees in the population and a sample of 4 employees were needed. Since 11 /4 = 2.75 = almost 3, then k=3, and every 3rd subject would be selected
- 20. the first subject is selected at random
- 21. Stratified Samples Stratified sampling is by dividing the population into groups (called strata) according to some characteristic that is important to the study, then sampling from each group. Samples within the strata should be randomly selected.
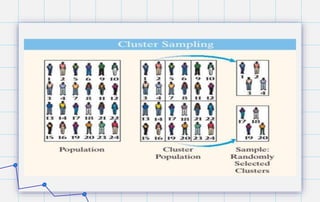
- 22. Cluster Sampling Here the population is divided into groups called clusters by some means such as geographic area or schools in a large school district, etc. Then the researcher randomly selects some of these clusters and uses all members of the selected clusters as the subjects of the samples
- 24. Non-probability Sampling Non-probability sampling can be divided into; Four Judgment Sampling Quota Sampling Convenience Sampling Multistage Sampling Snowball Sampling A sample is said to be non-probability sampling if every person does not have equal chance of being selected
- 25. Judgment Sampling A sample is said to be judgment sample when it is selected deliberately by the researcher by taking some factors into consideration. This technique is useful only when dealing with small populations
- 26. Quota Sampling In quota sampling, the population is subdivided into heterogeneous parts and judgment sub samples are taken from each part in percentage proportion of the parts in the population
- 27. Convenience Sampling A convenience sampling is simply uses results or data that are conveniently and readily obtained. Convenience sample is obtained by selecting convenient population units
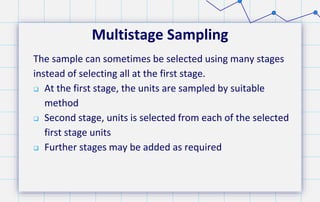
- 28. Multistage Sampling The sample can sometimes be selected using many stages instead of selecting all at the first stage. At the first stage, the units are sampled by suitable method Second stage, units is selected from each of the selected first stage units Further stages may be added as required
- 29. Snowball Sampling is a non-probability method of recruiting participants by referrals from existing ones. Snowball sampling can be a useful way to conduct research about people with specific traits who might otherwise be difficult to identify (e.g., people with a rare disease).
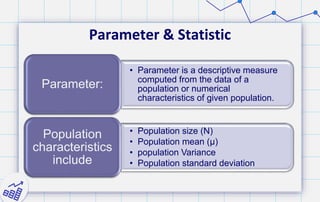
- 30. Parameter & Statistic • Parameter is a descriptive measure computed from the data of a population or numerical characteristics of given population. Parameter: • Population size (N) • Population mean (μ) • population Variance • Population standard deviation Population characteristics include
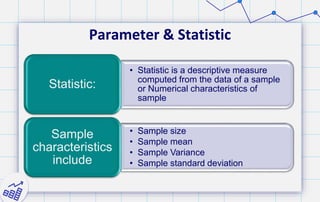
- 31. Parameter & Statistic • Statistic is a descriptive measure computed from the data of a sample or Numerical characteristics of sample Statistic: • Sample size • Sample mean • Sample Variance • Sample standard deviation Sample characteristics include