Introduction to statistics
- 1. Introduction to Statistics Pooja Yadav, Research Scholar Curaj, Ajmer Satyender Yadav Research Scholar, UCCMS, MLSU, Udaipur
- 2. Topics to be covered Introduction to statistics. Types of statistics. Data measurement. Levels of measurement. Important statistical terms.
- 3. INTRODUCTION • The word statistics conveys a variety of meaning to people in different walks of life. The word statistics comes from the Italian words Statista meaning STATEMENT The German word Statistik meaning POLITICAL STATE Statistics is a branch of scientific methods used in dealing with phenomena that can be described numerically either by count or by measurement.
- 4. INTRODUCTION • Statistics refers to dealing with quantitative information. A branch of mathematics which deals with gathering, organizing, analyzing, and interpreting numerical data. • Statistics is the sciences and art of dealing with figure and facts. • Father of statistics is GOTTFRIED ARCHENWALL.
- 5. DEFINITIONS Definitions – • Webster’s Third New International Dictionary gives a comprehensive definition of statistics as a science dealing with the collection, analysis, interpretation and presentation of numerical data. • According to W.I. King – “The science of statistics is the method of judging collection, natural or social phenomena from the results obtained from the analysis or enumeration or collection of estimates.”
- 6. FEATURES OF STATISTICS 1. It is aggregated of facts. 2. Numerically expressed (Quantitative). 3. Affected to a marked extent by multiplicity of causes. 4. Estimated according to reasonable standard of accuracy. 5. Collecting data in a systematic manner. 6. Statistics are collected for a predetermined purpose, well defined & specific. 7. Should be placed in relation to each other. 8. Data can’t be expressed in qualitative form.
- 7. STATEMENT • All Statistics are numerical statements (data) but all numerical statements (data) are not statistics. • E.g. Ram has 100 Rs. In his pocket is not statistics. The average age of 5th class is 10 yrs. is a statistical concept.
- 8. TYPES OF STATISTICS Descriptive statistics Inferential statistics Statistics can be divided into two branches: Descriptive statistics and Inferential statistics.
- 9. DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS Descriptive statistics- Descriptive statistics results from gathering data from a body, group, or population and reaching conclusions only about that particular group or population. For example- If an instructor produces statistics to summarize a class’s examination effort and uses those statistics to reach conclusions about that class only, the statistics are descriptive.
- 10. INFERENTIAL STATISTICS Inferential statistics- Sample is collected from the group or population and statistics is used to reach conclusions about the group or population from which the sample was taken, this statistics is called inferential statistics. For example- Testing of new drug on a small sample of patients to reach the conclusions about the drug and make inferences about the population.
- 11. INFERENTIAL STATISTICS • Two major types of inferential statistics are: Parametric Statistics Non-Parametric Statistics
- 12. INFERENTIAL STATISTICS • Parametric Statistics: Certain assumptions are made about the distribution of the data. Only Interval and Ratio data are used in parametric statistics . • Non-Parametric Statistics: When there is no assumptions made about the distribution of the data. Only Nominal and Ordinal data are used in non-parametric statistics .
- 13. DATA MEASUREMENT Scaling is an extension of the concept of measurement. It is said the result of measurement is a scale comprises of set of numerals on which an object score is placed using a certain rule of assignment. According to Adward • “Scaling is a procedure for the assignment of numbers to a property of objects in order to impart some of characteristics of numbers to the properties in question”.
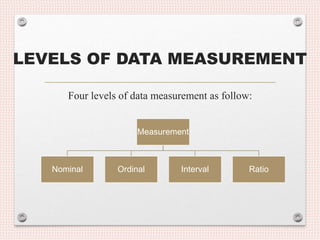
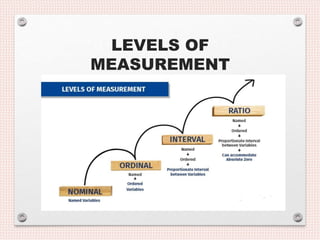
- 14. LEVELS OF DATA MEASUREMENT Four levels of data measurement as follow: Measurement Nominal Ordinal Interval Ratio
- 16. NOMINAL LEVEL • Nominal Level :- The lowest level of data measurement is the nominal level. Nominal level data measurement is used to define data as numbers, alphabets or symbols without any quantitative value. Numbers representing nominal level data can be used only to classify or categorize. Examples: Employee identification numbers. The numbers are used to differentiate employees and not to make a value statement about them.
- 17. ORDINAL LEVEL • Ordinal Level :- Ordinal level data measurement is higher than the nominal level. Ordinal level measurement can be used to rank, order or give preference to the objects. For example: Using ordinal data, a supervisor can evaluate three employees by ranking their productivity with the numbers 1 to 3.
- 18. INTERVAL LEVEL • Interval Level :- Interval level data measurement is the next to the highest level of data in which the distances between consecutive numbers have meaning and the data are always numerical. The distances represented by the differences between consecutive numbers are equal; i.e. interval data have equal intervals. For example, when we measure temperature (in Fahrenheit), the distance from 30-40 is same as distance from 70-80
- 19. RATIO LEVEL Ratio Level :- Ratio level data measurement is the highest level of data measurement. Ratio data have the same properties as interval data, but ratio data have an absolute zero and the ratio of two numbers is meaningful. The value of zero can not be arbitrarily assigned because it represent a fixed point. Examples of ratio data are height, weight, time, volume etc. Note: Ratio scale is also the part of interval scale. Interval scale ranges from negative to positive while the ratio scale starts from positive i.e. zero “0”.
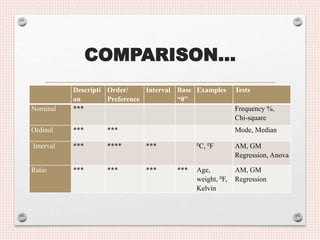
- 20. COMPARISON… Descripti on Order/ Preference Interval Base “0” Examples Tests Nominal *** Frequency %, Chi-square Ordinal *** *** Mode, Median Interval *** **** *** 0C, 0F AM, GM Regression, Anova Ratio *** *** *** *** Age, weight, 0F, Kelvin AM, GM Regression
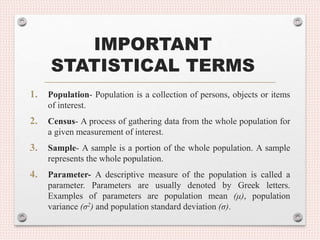
- 21. IMPORTANT STATISTICAL TERMS 1. Population- Population is a collection of persons, objects or items of interest. 2. Census- A process of gathering data from the whole population for a given measurement of interest. 3. Sample- A sample is a portion of the whole population. A sample represents the whole population. 4. Parameter- A descriptive measure of the population is called a parameter. Parameters are usually denoted by Greek letters. Examples of parameters are population mean (μ), population variance (σ2) and population standard deviation (σ).
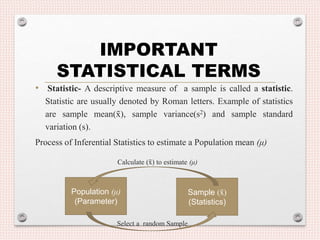
- 22. • Statistic- A descriptive measure of a sample is called a statistic. Statistic are usually denoted by Roman letters. Example of statistics are sample mean(x̄ ), sample variance(s2) and sample standard variation (s). Process of Inferential Statistics to estimate a Population mean (μ) Calculate (x̄ ) to estimate (μ) Select a random Sample Population (μ) (Parameter) Sample (x̄ ) (Statistics) IMPORTANT STATISTICAL TERMS
- 23. For any query, doubt and help please mail us at: pujayadav026@gmail.com yadavsatyender724@gmail.com