Introduction to statistics for social sciences 1
Download as pptx, pdf5 likes523 views
Introduction to statistics for social sciences, Approaches, Use of Statistics, Limitations, and misuse of statistics
1 of 17
Downloaded 36 times
















Ad
Recommended
Introduction to Statistics



Introduction to StatisticsSaurav Shrestha This document provides an introduction to key concepts in statistics. It discusses various statistical measures such as measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode), measures of dispersion (range, standard deviation), correlation, and different types of correlation (simple, partial, multiple). It also outlines common statistical methods like scatter diagrams, Karl Pearson's method, and rank correlation method. The role of computer technology in statistics is mentioned.
Introduction to statistics for social sciences 1



Introduction to statistics for social sciences 1Minal Jadeja This document provides an introduction to statistics. It defines statistics as the collection, presentation, analysis, and interpretation of numerical data. Statistics can refer to either quantitative information or a method of dealing with quantitative or qualitative information. There are two main approaches in statistics - descriptive statistics, which deals with presenting data in tables or graphs to get a general picture of a sample, and inferential statistics, which involves techniques for making inferences about a whole population based on a sample. Some key uses and applications of statistics include showing how samples differ from normal distributions, facilitating comparisons, simplifying messages in data, helping to formulate and test hypotheses, and aiding in prediction and inference. However, there are also some limitations to consider with statistics, such
Data Analysis and Statistics



Data Analysis and StatisticsT.S. Lim This document provides an overview of data analysis and statistics concepts for a training session. It begins with an agenda outlining topics like descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, and independent vs dependent samples. Descriptive statistics concepts covered include measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode), measures of variability (range, standard deviation), and charts. Inferential statistics discusses estimating population parameters, hypothesis testing, and statistical tests like t-tests, ANOVA, and chi-squared. The document provides examples and online simulation tools. It concludes with some practical tips for data analysis like checking for errors, reviewing findings early, and consulting a statistician on analysis plans.
Statistics ppts



Statistics pptsPatelKapeesh The document provides information on the course content and practical components of a statistics course.
The theory section covers topics like introduction to statistics, measures of central tendency and dispersion, probability, normal distribution, correlation, regression, tests of significance, analysis of variance, and sampling methods.
The practical section involves applying concepts like graphical representation of data, measures of central tendency and dispersion, moments, correlation and regression analysis, t-tests, chi-square tests, and analysis of variance to real data. Reference books on agricultural statistics are also listed.
Correlationanalysis



CorrelationanalysisLibu Thomas Correlation analysis measures the relationship between two or more variables. The correlation coefficient ranges from -1 to 1, indicating the strength and direction of the linear relationship. A positive correlation means the variables increase together, while a negative correlation means they change in opposite directions. Correlation only measures association and does not imply causation. Common methods for calculating correlation include Pearson's correlation coefficient, Spearman's rank correlation coefficient, and scatter plots.
Descriptive statistics



Descriptive statisticsUniversity of Jaffna This document provides an overview of descriptive statistics. It discusses different types of descriptive statistics including measures of central tendency like mean, median and mode, and measures of variability. It also describes various ways of organizing and summarizing data, such as frequency distributions, histograms, stem-and-leaf plots and pie charts. The goal of descriptive statistics is to describe key characteristics of a data set in a simple and easy to understand way.
Estimation in statistics



Estimation in statisticsRabea Jamal This document discusses key concepts in statistical estimation including:
- Estimation involves using sample data to infer properties of the population by calculating point estimates and interval estimates.
- A point estimate is a single value that estimates an unknown population parameter, while an interval estimate provides a range of plausible values for the parameter.
- A confidence interval gives the probability that the interval calculated from the sample data contains the true population parameter. Common confidence intervals are 95% confidence intervals.
- Formulas for confidence intervals depend on whether the population standard deviation is known or unknown, and the sample size.
Regression analysis



Regression analysisTeachers Mitraa This document discusses regression analysis techniques. It defines regression as the tendency for estimated values to be close to actual values. Regression analysis investigates the relationship between variables, with the independent variable influencing the dependent variable. There are three main types of regression: linear regression which uses a linear equation to model the relationship between one independent and one dependent variable; logistic regression which predicts the probability of a binary outcome using multiple independent variables; and nonlinear regression which models any non-linear relationship between variables. The document provides examples of using linear and logistic regression and discusses their key assumptions and calculations.
Measures of central tendency



Measures of central tendencykurthDelossantos The document discusses different measures of central tendency:
- The mode is the most frequent score in a data set and is used for nominal data.
- The median is the middle score when data is arranged from lowest to highest and is not influenced by outliers.
- The mean is the average of all scores, calculated by summing all scores and dividing by the total number, and is preferred for interval/ratio scaled and non-skewed data.
statistic



statisticPwalmiki Basic statistics is the science of collecting, organizing, summarizing, and interpreting data. It allows researchers to gain insights from data through graphical or numerical summaries, regardless of the amount of data. Descriptive statistics can be used to describe single variables through frequencies, percentages, means, and standard deviations. Inferential statistics make inferences about phenomena through hypothesis testing, correlations, and predicting relationships between variables.
outliers



outliersARPAN PAUL. HERE I'VE GIVE THE DESCRIPTION ABOUT OUTLIERS AND IT'S TYPES WITH SOME EXAMPLE.
My Facebook handle _ https://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=100066529451772
Overall concept of statistics



Overall concept of statisticsASA university Bangladesh hello, friends. i'm humaira jahan. and this is my presentation on statistics. you can find a overall concept of statistics in this presentation. and i hope it will help you enough to know about statistics.
Basic Statistics & Data Analysis



Basic Statistics & Data AnalysisAjendra Sharma Statistics is the methodology used to interpret and draw conclusions from collected data. It provides methods for designing research studies, summarizing and exploring data, and making predictions about phenomena represented by the data. A population is the set of all individuals of interest, while a sample is a subset of individuals from the population used for measurements. Parameters describe characteristics of the entire population, while statistics describe characteristics of a sample and can be used to infer parameters. Basic descriptive statistics used to summarize samples include the mean, standard deviation, and variance, which measure central tendency, spread, and how far data points are from the mean, respectively. The goal of statistical data analysis is to gain understanding from data through defined steps.
Inferential statictis ready go



Inferential statictis ready goMmedsc Hahm This document discusses inferential statistics and different types of samples that can be drawn from a population. Inferential statistics involves making inferences about a population based on a sample. It consists of generalizing from samples to populations, estimating parameters, hypothesis testing, and determining relationships. Two main methods are estimation, which uses a sample to estimate a parameter and construct a confidence interval, and hypothesis testing, which involves assuming and testing a null hypothesis against collected data. Types of samples discussed are simple random samples, systematic samples, and stratified random samples.
Introduction to statistics



Introduction to statisticsSantosh Bhandari This document provides an introduction to statistics. It defines statistics as the scientific methods for collecting, organizing, summarizing, presenting and analyzing data to derive valid conclusions. Statistics is useful across many fields and careers as it helps make informed decisions based on data. The document outlines descriptive and inferential statistics, and notes that descriptive statistics simplifies complexity while inferential statistics allows for conclusions to be drawn. It also discusses types of data sources, including primary data collected directly and secondary data that has already been collected.
Introduction to Statistics



Introduction to Statisticsaan786 This document provides an introduction to statistics. It discusses why statistics is important and required for many programs. Reasons include the prevalence of numerical data in daily life, the use of statistical techniques to make decisions that affect people, and the need to understand how data is used to make informed decisions. The document also defines key statistical concepts such as population, parameter, sample, statistic, descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, variables, and different types of variables.
Statistical inference: Estimation



Statistical inference: EstimationParag Shah The ppt gives an idea about basic concept of Estimation. point and interval. Properties of good estimate is also covered. Confidence interval for single means, difference between two means, proportion and difference of two proportion for different sample sizes are included along with case studies.
Descriptive statistics



Descriptive statisticsAttaullah Khan What are descriptive Statistics, Types of statistics and its implications.
graphs, tables, variation, mean mode median, central tendency,
Data presentation 2



Data presentation 2Rawalpindi Medical College This document defines data and different types of data presentation. It discusses quantitative and qualitative data, and different scales for qualitative data. The document also covers different ways to present data scientifically, including through tables, graphs, charts and diagrams. Key types of visual presentation covered are bar charts, histograms, pie charts and line diagrams. Presentation should aim to clearly convey information in a concise and systematic manner.
Business statistics 



Business statistics Sajjad Chitrali This document provides an introduction to business statistics for a 4th semester BBA course. It defines statistics as the collection, analysis, and interpretation of numerical data. Descriptive statistics are used to summarize data through measures of central tendency, dispersion, graphs and tables. Inferential statistics allow generalization from samples to populations through estimation of parameters and hypothesis testing. The key terms of population, sample, parameter, and statistic are defined. Variables are characteristics that can take on different values and are classified as qualitative or quantitative. Quantitative variables are further divided into discrete and continuous types. Descriptive statistics simply describe data while inferential statistics make inferences about unknown population characteristics based on samples.
Descriptive statistics



Descriptive statisticsAileen Balbido 1. The document discusses descriptive statistics, which is the study of how to collect, organize, analyze, and interpret numerical data.
2. Descriptive statistics can be used to describe data through measures of central tendency like the mean, median, and mode as well as measures of variability like the range.
3. These statistical techniques help summarize and communicate patterns in data in a concise manner.
Business statistics what and why



Business statistics what and whydibasharmin This document provides an introduction to business statistics. It defines statistics as the science of collecting, organizing, analyzing, and interpreting numerical data. The document notes that statistics can refer to both quantitative information and the methods used to analyze that information. It describes the key stages of a statistical analysis: data collection, organization, presentation, analysis, and interpretation. The document also discusses whether statistics is a science or an art and the important functions of statistics like providing definiteness, enabling comparison, and aiding in prediction.
Introduction to statistics



Introduction to statisticsakbhanj Statistics can be defined in both a singular and plural sense. In the singular sense, it refers to statistical methods for collecting, analyzing, and interpreting numerical data. In the plural sense, it refers to the actual numerical facts or data collected. Statistics involves systematically collecting, organizing, presenting, analyzing, and interpreting numerical data to describe features and characteristics. It allows for comparing facts, establishing relationships, and facilitating policymaking and decision making. However, statistics only studies aggregates and averages, not individual cases, and results are true only on average. It also requires properly contextualizing and referencing results.
Measures of central tendency 



Measures of central tendency Jagdish Powar This document discusses measures of central tendency including mean, median, and mode. It provides definitions and formulas for calculating each measure from both grouped and ungrouped data. For mean, it is the sum of all values divided by the number of values. Median is the middle value when values are arranged in order. Mode is the most frequently occurring value. The document also discusses requirements for a good measure of central tendency and provides examples calculating the measures from sample medical data sets to illustrate their use and assess skewness.
Basic concepts of probability 



Basic concepts of probability Long Beach City College 1) The document introduces basic concepts of probability such as sample spaces, events, outcomes, and how to calculate classical and empirical probabilities.
2) It discusses approaches to determining probability including classical, empirical, and subjective probabilities. Simulations can also be used to estimate probabilities.
3) Examples are provided to illustrate calculating probabilities using classical and empirical approaches for single and compound events with different sample spaces.
Descriptive statistics



Descriptive statisticsDr Resu Neha Reddy Descriptive statistics, central tendency, measures of variability, measures of dispersion, skewness, kurtosis, range, standard deviation, mean, median, mode, variance, normal distribution
Point Estimation 



Point Estimation Pabna University of Science & Technology According to Wikipedia point estimation involves the use of sample data to calculate a single value (known as a point estimate since it identifies a point in some parameter space) which is to serve as a "best guess" or "best estimate" of an unknown population parameter (for example, the population means).
Descriptive Statistics



Descriptive StatisticsBhagya Silva This document discusses descriptive statistics and analysis. It provides definitions of key terms like data, variable, statistic, and parameter. It also describes common measures of central tendency like mean, median and mode. Additionally, it covers measures of variability such as range, variance and standard deviation. Various graphical and numerical methods for summarizing and presenting sample data are presented, including tables, charts and distributions.
Chapter#01 Introduction.ppt



Chapter#01 Introduction.pptMuntazirMehdi43 This document provides an introduction and overview of key concepts in statistics. It defines important statistical terms like population, sample, parameter, statistic, variable and constant. It distinguishes between discrete and continuous variables and quantitative and qualitative data. It describes the different meanings and definitions of statistics and outlines key characteristics of statistical data. It also discusses topics like collection of data, accuracy, significant figures and mathematical notation used in statistics.
Ad
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Measures of central tendency



Measures of central tendencykurthDelossantos The document discusses different measures of central tendency:
- The mode is the most frequent score in a data set and is used for nominal data.
- The median is the middle score when data is arranged from lowest to highest and is not influenced by outliers.
- The mean is the average of all scores, calculated by summing all scores and dividing by the total number, and is preferred for interval/ratio scaled and non-skewed data.
statistic



statisticPwalmiki Basic statistics is the science of collecting, organizing, summarizing, and interpreting data. It allows researchers to gain insights from data through graphical or numerical summaries, regardless of the amount of data. Descriptive statistics can be used to describe single variables through frequencies, percentages, means, and standard deviations. Inferential statistics make inferences about phenomena through hypothesis testing, correlations, and predicting relationships between variables.
outliers



outliersARPAN PAUL. HERE I'VE GIVE THE DESCRIPTION ABOUT OUTLIERS AND IT'S TYPES WITH SOME EXAMPLE.
My Facebook handle _ https://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=100066529451772
Overall concept of statistics



Overall concept of statisticsASA university Bangladesh hello, friends. i'm humaira jahan. and this is my presentation on statistics. you can find a overall concept of statistics in this presentation. and i hope it will help you enough to know about statistics.
Basic Statistics & Data Analysis



Basic Statistics & Data AnalysisAjendra Sharma Statistics is the methodology used to interpret and draw conclusions from collected data. It provides methods for designing research studies, summarizing and exploring data, and making predictions about phenomena represented by the data. A population is the set of all individuals of interest, while a sample is a subset of individuals from the population used for measurements. Parameters describe characteristics of the entire population, while statistics describe characteristics of a sample and can be used to infer parameters. Basic descriptive statistics used to summarize samples include the mean, standard deviation, and variance, which measure central tendency, spread, and how far data points are from the mean, respectively. The goal of statistical data analysis is to gain understanding from data through defined steps.
Inferential statictis ready go



Inferential statictis ready goMmedsc Hahm This document discusses inferential statistics and different types of samples that can be drawn from a population. Inferential statistics involves making inferences about a population based on a sample. It consists of generalizing from samples to populations, estimating parameters, hypothesis testing, and determining relationships. Two main methods are estimation, which uses a sample to estimate a parameter and construct a confidence interval, and hypothesis testing, which involves assuming and testing a null hypothesis against collected data. Types of samples discussed are simple random samples, systematic samples, and stratified random samples.
Introduction to statistics



Introduction to statisticsSantosh Bhandari This document provides an introduction to statistics. It defines statistics as the scientific methods for collecting, organizing, summarizing, presenting and analyzing data to derive valid conclusions. Statistics is useful across many fields and careers as it helps make informed decisions based on data. The document outlines descriptive and inferential statistics, and notes that descriptive statistics simplifies complexity while inferential statistics allows for conclusions to be drawn. It also discusses types of data sources, including primary data collected directly and secondary data that has already been collected.
Introduction to Statistics



Introduction to Statisticsaan786 This document provides an introduction to statistics. It discusses why statistics is important and required for many programs. Reasons include the prevalence of numerical data in daily life, the use of statistical techniques to make decisions that affect people, and the need to understand how data is used to make informed decisions. The document also defines key statistical concepts such as population, parameter, sample, statistic, descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, variables, and different types of variables.
Statistical inference: Estimation



Statistical inference: EstimationParag Shah The ppt gives an idea about basic concept of Estimation. point and interval. Properties of good estimate is also covered. Confidence interval for single means, difference between two means, proportion and difference of two proportion for different sample sizes are included along with case studies.
Descriptive statistics



Descriptive statisticsAttaullah Khan What are descriptive Statistics, Types of statistics and its implications.
graphs, tables, variation, mean mode median, central tendency,
Data presentation 2



Data presentation 2Rawalpindi Medical College This document defines data and different types of data presentation. It discusses quantitative and qualitative data, and different scales for qualitative data. The document also covers different ways to present data scientifically, including through tables, graphs, charts and diagrams. Key types of visual presentation covered are bar charts, histograms, pie charts and line diagrams. Presentation should aim to clearly convey information in a concise and systematic manner.
Business statistics 



Business statistics Sajjad Chitrali This document provides an introduction to business statistics for a 4th semester BBA course. It defines statistics as the collection, analysis, and interpretation of numerical data. Descriptive statistics are used to summarize data through measures of central tendency, dispersion, graphs and tables. Inferential statistics allow generalization from samples to populations through estimation of parameters and hypothesis testing. The key terms of population, sample, parameter, and statistic are defined. Variables are characteristics that can take on different values and are classified as qualitative or quantitative. Quantitative variables are further divided into discrete and continuous types. Descriptive statistics simply describe data while inferential statistics make inferences about unknown population characteristics based on samples.
Descriptive statistics



Descriptive statisticsAileen Balbido 1. The document discusses descriptive statistics, which is the study of how to collect, organize, analyze, and interpret numerical data.
2. Descriptive statistics can be used to describe data through measures of central tendency like the mean, median, and mode as well as measures of variability like the range.
3. These statistical techniques help summarize and communicate patterns in data in a concise manner.
Business statistics what and why



Business statistics what and whydibasharmin This document provides an introduction to business statistics. It defines statistics as the science of collecting, organizing, analyzing, and interpreting numerical data. The document notes that statistics can refer to both quantitative information and the methods used to analyze that information. It describes the key stages of a statistical analysis: data collection, organization, presentation, analysis, and interpretation. The document also discusses whether statistics is a science or an art and the important functions of statistics like providing definiteness, enabling comparison, and aiding in prediction.
Introduction to statistics



Introduction to statisticsakbhanj Statistics can be defined in both a singular and plural sense. In the singular sense, it refers to statistical methods for collecting, analyzing, and interpreting numerical data. In the plural sense, it refers to the actual numerical facts or data collected. Statistics involves systematically collecting, organizing, presenting, analyzing, and interpreting numerical data to describe features and characteristics. It allows for comparing facts, establishing relationships, and facilitating policymaking and decision making. However, statistics only studies aggregates and averages, not individual cases, and results are true only on average. It also requires properly contextualizing and referencing results.
Measures of central tendency 



Measures of central tendency Jagdish Powar This document discusses measures of central tendency including mean, median, and mode. It provides definitions and formulas for calculating each measure from both grouped and ungrouped data. For mean, it is the sum of all values divided by the number of values. Median is the middle value when values are arranged in order. Mode is the most frequently occurring value. The document also discusses requirements for a good measure of central tendency and provides examples calculating the measures from sample medical data sets to illustrate their use and assess skewness.
Basic concepts of probability 



Basic concepts of probability Long Beach City College 1) The document introduces basic concepts of probability such as sample spaces, events, outcomes, and how to calculate classical and empirical probabilities.
2) It discusses approaches to determining probability including classical, empirical, and subjective probabilities. Simulations can also be used to estimate probabilities.
3) Examples are provided to illustrate calculating probabilities using classical and empirical approaches for single and compound events with different sample spaces.
Descriptive statistics



Descriptive statisticsDr Resu Neha Reddy Descriptive statistics, central tendency, measures of variability, measures of dispersion, skewness, kurtosis, range, standard deviation, mean, median, mode, variance, normal distribution
Point Estimation 



Point Estimation Pabna University of Science & Technology According to Wikipedia point estimation involves the use of sample data to calculate a single value (known as a point estimate since it identifies a point in some parameter space) which is to serve as a "best guess" or "best estimate" of an unknown population parameter (for example, the population means).
Descriptive Statistics



Descriptive StatisticsBhagya Silva This document discusses descriptive statistics and analysis. It provides definitions of key terms like data, variable, statistic, and parameter. It also describes common measures of central tendency like mean, median and mode. Additionally, it covers measures of variability such as range, variance and standard deviation. Various graphical and numerical methods for summarizing and presenting sample data are presented, including tables, charts and distributions.
Similar to Introduction to statistics for social sciences 1 (20)
Chapter#01 Introduction.ppt



Chapter#01 Introduction.pptMuntazirMehdi43 This document provides an introduction and overview of key concepts in statistics. It defines important statistical terms like population, sample, parameter, statistic, variable and constant. It distinguishes between discrete and continuous variables and quantitative and qualitative data. It describes the different meanings and definitions of statistics and outlines key characteristics of statistical data. It also discusses topics like collection of data, accuracy, significant figures and mathematical notation used in statistics.
A power point presentation on statistics



A power point presentation on statisticsKriace Ward Statistics originated from Latin, Italian, and German words referring to organized states. Gottfried Achenwall is considered the "father of statistics" for coining the term to describe a specialized branch of knowledge. Modern statistics is defined as the science of judging collective phenomena through analysis and enumeration. While statistics can be an art and a science, its successful application depends on the skill of the statistician and their knowledge of the field being studied. Statistics are important across many domains from business, economics, and planning to the sciences. However, statistics also have limitations such as only studying aggregates, not individuals, and results being valid only on average and in the long run.
Data analysis presentation by Jameel Ahmed Qureshi



Data analysis presentation by Jameel Ahmed QureshiJameel Ahmed Qureshi Presentation is made by the student of M.phil Jameel Ahmed Qureshi Faculty of Education Elsa Kazi campus Hyderabad UoS Jamshoron, This presentation is an assignment assign by the Dr. Mumtaz Khwaja
Statistics Exericse 29



Statistics Exericse 29Melanie Erickson - Descriptive statistics are used to describe and summarize key characteristics of a data set.
- They include measures such as counts, means, ranges, and standard deviations.
- Descriptive statistics provide simple summaries about the sample and the measures, but do not make any claims about the population.
- The document provides examples of how descriptive statistics could be used to summarize caseload data from public defender offices.
Meaning and uses of statistics



Meaning and uses of statisticsRekhaChoudhary24 1. The document discusses the meaning, uses, functions, importance and limitations of statistics. It defines statistics as the collection, presentation, analysis and interpretation of numerical data.
2. Statistics has various uses across different fields such as policy planning, management, education, commerce and accounts. It helps present facts precisely and enables comparison, correlation, formulation and testing of hypotheses, and forecasting.
3. While statistics is important for planning, administration, economics and more, it also has limitations such as only studying aggregates, numerical data, and being an average. Statistics can also be misused if not used carefully by experts.
CHAPTER 1.pdf Probability and Statistics for Engineers



CHAPTER 1.pdf Probability and Statistics for Engineersbraveset14 Mainly concerned with the methods and techniques used in the collection,
organization, presentation, and analysis of a set of data without making any
conclusions or inferences.
Gathering data
Editing and classifying
Presenting data
Drawing diagrams and graphs
Calculating averages and measures of dispersions.
Remark: Descriptive statistics doesn‟t go beyond describing the data
themselves.
CHAPTER 1.pdfProbability and Statistics for Engineers



CHAPTER 1.pdfProbability and Statistics for Engineersbraveset14 Plural form
Numerical facts and figures collected for certain purposes
Aggregates of numerical expressed facts (figures) collected in a systematic
manner for a predetermined purpose
Singular form
Systematic collection and interpretation of numerical data to make a decision
The science of collecting, organizing, presenting, analyzing, and interpreting
numerical data to make decisions on the basis of such analysis
Bio stat



Bio statAbhishekDas15 This document provides an introduction and overview of biostatistics. It defines key biostatistics terms like population, sample, parameter, statistic, quantitative vs. qualitative data, levels of measurement, descriptive vs. inferential biostatistics, and common statistical notations. It also discusses sources of health information and how computerized health management information systems are used to collect, analyze and report data.
Types of Statistics Descriptive and Inferential Statistics



Types of Statistics Descriptive and Inferential StatisticsDr. Amjad Ali Arain Topic: Types of Statistics Descriptive and Inferential Statistics
Student Name: Bushra
Class: B.Ed. 2.5
Project Name: “Young Teachers' Professional Development (TPD)"
"Project Founder: Prof. Dr. Amjad Ali Arain
Faculty of Education, University of Sindh, Pakistan
Applied Statistics for E and B : Data and Statistics



Applied Statistics for E and B : Data and Statisticsvynagame198 Course in University about Applied Statistics for economics and business
Statistics Assignments 090427



Statistics Assignments 090427amykua Statistics are used by organizations to measure and analyze business performance. American Express uses statistics such as total returns to shareholders, numbers of cardholders by age group, and cardholder spending by age to analyze business units, identify targeted customer groups, and inform marketing campaigns. Statistics on labor force characteristics by gender help conclude that male monthly incomes are typically higher than females, though this does not necessarily mean males spend more.
Data Analysis 



Data Analysis Dr. Dawit Dibekulu The document provides an overview of data analysis concepts and methods for qualitative and quantitative data. It discusses topics such as descriptive statistics, measures of central tendency and spread. It also covers inferential statistics concepts like ANOVA, ANCOVA, regression, and correlation. Both the advantages and disadvantages of qualitative data analysis are presented. The document is a presentation on research methodology focusing on data analysis.
probability and statistics-4.pdf



probability and statistics-4.pdfhabtamu292245 It is ridiculous to hear that man from Peru complaining about America’s poverty. Peru has twice as much poverty
Statistics assignment



Statistics assignmentPragati Mehndiratta Statistics is a basic and important tool for professionals in all fields all over the worlds. This document provides the importance and scope of Statistics in major fields of study like a business, management, planning etc.
Chapter 1 introduction to statistics.



Chapter 1 introduction to statistics.OliviaNightingale2 a) Experimental
b) Observational
The study in a) manipulates one variable (giving one group a herb vs placebo) and observes the effect on another variable (respiratory tract infections), making it an experimental study.
The study in b) passively observes behaviors or events without manipulation, making it an observational study.
Stats notes



Stats notesPrabal Chakraborty Notes of BBA /B.Com as well as BCA. It will help average students to learn Business Statistics. It will help MBA and PGDM students in Quantitative Analysis.
Statistic Project Essay



Statistic Project EssayRobin Anderson This document discusses using statistics to analyze bottlenecks in a manufacturing process. It begins by introducing the purpose of using statistics to understand relationships between variables like population and country size. Later sections discuss using hypothesis testing to analyze sample data and determine if it represents the overall population parameters. Descriptive statistics are calculated on the sample data and a regression analysis is run to determine the relationship between population and sample size.
Ad
More from Minal Jadeja (6)
Charano ma gujarati presentation



Charano ma gujarati presentationMinal Jadeja Gujarat state textbook standard five Gujarati poem charnoma chalva no uchhale umang minaba jadeja
Vol4issue51



Vol4issue51Minal Jadeja The meeting date of C.T.E. is 19/12/2013. Dr. S.P. Shah will chair the meeting. Issues related to syllabus, examinations and new courses will be discussed. The meeting in Gandhinagar chaired by Dr. Shah discussed various academic matters.
On 17/12/2013, a meeting was held in Moti Bagh to discuss the formation of new committees of L.N.K.C.E. Dr. A.P. Shah could not attend due to illness. Issues related to syllabus and examinations were discussed. It was decided that regular meetings will be held and status reports presented.
L.N.K.C.E.
Vol4issue5



Vol4issue5Minal Jadeja The meeting date of CTE is 19/12/2013. Dr. S.P. Shah will chair the meeting. Important matters like new syllabus, results, and budget will be discussed. On 17/12/2013, a conference was held in Gandhinagar where Dr. S.P. Shah represented CTE. Many important CTE officials could not attend due to prior commitments. The officials discussed following up on pending matters. They also discussed streamlining the functioning of CTE and improving standards.
The EOTC conference of CTE college was held from 9/12/2013 to 14/12/2013. Students gained knowledge on subjects like environment, health, rural development through practical and theoretical learning
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
The History of Kashmir Karkota Dynasty NEP.pptx



The History of Kashmir Karkota Dynasty NEP.pptxArya Mahila P. G. College, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India. This slide is an exercise for the inquisitive students preparing for the competitive examinations of the undergraduate and postgraduate students. An attempt is being made to present the slide keeping in mind the New Education Policy (NEP). An attempt has been made to give the references of the facts at the end of the slide. If new facts are discovered in the near future, this slide will be revised.
This presentation is related to the brief History of Kashmir (Part-I) with special reference to Karkota Dynasty. In the seventh century a person named Durlabhvardhan founded the Karkot dynasty in Kashmir. He was a functionary of Baladitya, the last king of the Gonanda dynasty. This dynasty ruled Kashmir before the Karkot dynasty. He was a powerful king. Huansang tells us that in his time Taxila, Singhpur, Ursha, Punch and Rajputana were parts of the Kashmir state.
Kenan Fellows Participants, Projects 2025-26 Cohort



Kenan Fellows Participants, Projects 2025-26 CohortEducationNC These are the educators participating in the Kenan Fellows Program for Teacher Leadership at NC State University.
03#UNTAGGED. Generosity in architecture.



03#UNTAGGED. Generosity in architecture.MCH What makes space feel generous, and how architecture address this generosity in terms of atmosphere, metrics, and the implications of its scale? This edition of #Untagged explores these and other questions in its presentation of the 2024 edition of the Master in Collective Housing. The Master of Architecture in Collective Housing, MCH, is a postgraduate full-time international professional program of advanced architecture design in collective housing presented by Universidad Politécnica of Madrid (UPM) and Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH).
Yearbook MCH 2024. Master in Advanced Studies in Collective Housing UPM - ETH
How to Add Customer Note in Odoo 18 POS - Odoo Slides



How to Add Customer Note in Odoo 18 POS - Odoo SlidesCeline George In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to add customer note in Odoo 18 POS module. Customer Notes in Odoo 18 POS allow you to add specific instructions or information related to individual order lines or the entire order.
SCI BIZ TECH QUIZ (OPEN) PRELIMS XTASY 2025.pptx



SCI BIZ TECH QUIZ (OPEN) PRELIMS XTASY 2025.pptxRonisha Das SCI BIZ TECH QUIZ (OPEN) PRELIMS - XTASY 2025
How to Manage Upselling in Odoo 18 Sales



How to Manage Upselling in Odoo 18 SalesCeline George In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to manage upselling in Odoo 18 Sales module. Upselling in Odoo is a powerful sales technique that allows you to increase the average order value by suggesting additional or more premium products or services to your customers.
All About the 990 Unlocking Its Mysteries and Its Power.pdf



All About the 990 Unlocking Its Mysteries and Its Power.pdfTechSoup In this webinar, nonprofit CPA Gregg S. Bossen shares some of the mysteries of the 990, IRS requirements — which form to file (990N, 990EZ, 990PF, or 990), and what it says about your organization, and how to leverage it to make your organization shine.
Lecture 1 Introduction history and institutes of entomology_1.pptx



Lecture 1 Introduction history and institutes of entomology_1.pptxArshad Shaikh *Entomology* is the scientific study of insects, including their behavior, ecology, evolution, classification, and management.
Entomology continues to evolve, incorporating new technologies and approaches to understand and manage insect populations.
How to Create A Todo List In Todo of Odoo 18



How to Create A Todo List In Todo of Odoo 18Celine George In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to create a Todo List In Todo of Odoo 18. Odoo 18’s Todo module provides a simple yet powerful way to create and manage your to-do lists, ensuring that no task is overlooked.
APGAR SCORE BY sweety Tamanna Mahapatra MSc Pediatric



APGAR SCORE BY sweety Tamanna Mahapatra MSc PediatricSweetytamannaMohapat Learn about the APGAR SCORE , a simple yet effective method to evaluate a newborn's physical condition immediately after birth ....this presentation covers .....
what is apgar score ?
Components of apgar score.
Scoring system
Indications of apgar score........
Grade 3 - English - Printable Worksheet (PDF Format)



Grade 3 - English - Printable Worksheet (PDF Format)Sritoma Majumder Grade 3 - English - Printable Worksheet (PDF Format)
Ranking_Felicidade_2024_com_Educacao_Marketing Educacional_V2.pdf



Ranking_Felicidade_2024_com_Educacao_Marketing Educacional_V2.pdfRafael Villas B Marketing Educacional
Myopathies (muscle disorders) for undergraduate



Myopathies (muscle disorders) for undergraduateMohamed Rizk Khodair herediatary myopthies
myotonia
inflammatory myopthies
Redesigning Education as a Cognitive Ecosystem: Practical Insights into Emerg...



Redesigning Education as a Cognitive Ecosystem: Practical Insights into Emerg...Leonel Morgado Slides used at the Invited Talk at the Harvard - Education University of Hong Kong - Stanford Joint Symposium, "Emerging Technologies and Future Talents", 2025-05-10, Hong Kong, China.
Drive Supporter Growth from Awareness to Advocacy with TechSoup Marketing Ser...



Drive Supporter Growth from Awareness to Advocacy with TechSoup Marketing Ser...TechSoup Learn how to understand and optimize your audience experience with awareness of your impact.
Herbs Used in Cosmetic Formulations .pptx



Herbs Used in Cosmetic Formulations .pptxRAJU THENGE The content is for the educational purpose for Pharmacy and Cosmetic students.
Junction Field Effect Transistors (JFET)



Junction Field Effect Transistors (JFET)GS Virdi In this concise presentation, Dr. G.S. Virdi (Former Chief Scientist, CSIR-CEERI, Pilani) introduces the Junction Field-Effect Transistor (JFET)—a cornerstone of modern analog electronics. You’ll discover:
Why JFETs? Learn how their high input impedance and low noise solve the drawbacks of bipolar transistors.
JFET vs. MOSFET: Understand the core differences between JFET and MOSFET devices.
Internal Structure: See how source, drain, gate, and the depletion region form a controllable semiconductor channel.
Real-World Applications: Explore where JFETs power amplifiers, sensors, and precision circuits.
Perfect for electronics students, hobbyists, and practicing engineers looking for a clear, practical guide to JFET technology.
Lecture 4 INSECT CUTICLE and moulting.pptx



Lecture 4 INSECT CUTICLE and moulting.pptxArshad Shaikh The insect cuticle is a tough, external exoskeleton composed of chitin and proteins, providing protection and support. However, as insects grow, they need to shed this cuticle periodically through a process called moulting. During moulting, a new cuticle is prepared underneath, and the old one is shed, allowing the insect to grow, repair damaged cuticle, and change form. This process is crucial for insect development and growth, enabling them to transition from one stage to another, such as from larva to pupa or adult.
LDMMIA Reiki News Ed3 Vol1 For Team and Guests



LDMMIA Reiki News Ed3 Vol1 For Team and GuestsLDM Mia eStudios Happy May and Taurus Season.
♥☽✷♥We have a large viewing audience for Presentations. So far my Free Workshop Presentations are doing excellent on views. I just started weeks ago within May. I am also sponsoring Alison within my blog and courses upcoming. See our Temple office for ongoing weekly updates.
https://ldmchapels.weebly.com
♥☽About: I am Adult EDU Vocational, Ordained, Certified and Experienced. Course genres are personal development for holistic health, healing, and self care/self serve.
Lecture 2 CLASSIFICATION OF PHYLUM ARTHROPODA UPTO CLASSES & POSITION OF_1.pptx



Lecture 2 CLASSIFICATION OF PHYLUM ARTHROPODA UPTO CLASSES & POSITION OF_1.pptxArshad Shaikh *Phylum Arthropoda* includes animals with jointed appendages, segmented bodies, and exoskeletons. It's divided into subphyla like Chelicerata (spiders), Crustacea (crabs), Hexapoda (insects), and Myriapoda (millipedes, centipedes). This phylum is one of the most diverse groups of animals.
The History of Kashmir Karkota Dynasty NEP.pptx



The History of Kashmir Karkota Dynasty NEP.pptxArya Mahila P. G. College, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India.
Introduction to statistics for social sciences 1
- 1. Introduction to Statistics By Dr. Minalba B. Jadeja M.Sc. M.Ed. M.Phil. Ph.D. NET, GSET
- 2. 2 ⊸ The word statistics conveys a variety of meaning to people in different walks of life. ⊸ The word statistics comes from the Italian words Statista = "statesman" Or ⊸ Latin Word ‘Status’ = State Or ⊸ The German word Statistik = "Collection of data involving the State" INTRODUCTION
- 3. ⊸ The word Statistics today refers to : ⊸ either quantitative information or a method of dealing with quantitative or qualitative information. ⊸ Statistical Science or Statistics 3
- 5. 5 Three different context of Statistics Numerical Data Numerical Facts Collection of Data and Facts Use of Theory, Methods, and Procedures in analyzing interpreting collected data
- 6. 6 ⊸ DEFINITION ⊸ “Statistics is defined as collection, Presentation, analysis and interpretation of numerical data”. Croxton & cowden ⊸ Statistics is a science of probability and Inference Boudington
- 7. 7 ⊸ Statistics is a Science of averages ⊸ Statistics is a science of measurement in Social Sciences ⊸ Statistics is the sciences and art of dealing with figure and facts.
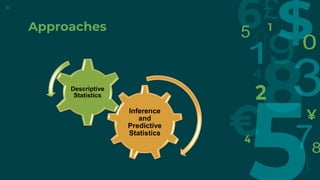
- 9. Approaches ⊸ Descriptive Statistics – It deals with the presentation of numerical facts, or data, in either tables or graphs form. It give techniques to get general picture of sample. Example :- Mean , Median , Mode, Standard Deviation etc… 9
- 10. Approaches ⊸ Inferential Statistics – It involves techniques for making inferences about the whole population on the basis of observations obtained from samples. Examples :- t test, F test etc… 10
- 11. USE & APPLICATION OF STATISTICS ⊸ It shows how sample differs from normal distribution ⊸ It facilitates comparisons ⊸ It simplifies the message of figure ⊸ It helps in formulating and testing hypothesis ⊸ It help in prediction ⊸ It helps in inference
- 12. Limitations and Statistics ⊸ To ascribe unrealistic data by misuse of an average ⊸ To compare unrelated and irrelevant data in order to mislead people 12
- 13. Students marks out of 100 ( passing marks 35) :- Average :- 42 13 Roll No Marks 1 30 2 25 3 25 4 30 5 30 6 25 7 35 8 25 9 96 10 99 Actually 7 Students failed but for advertisement only average will be presented
- 14. Limitations and Statistics ⊸ Students scores 99 marks out of 100 ⊸ But the actual situation is differ 14
- 15. Limitations and Statistics ⊸ To commit an error of generalizing the conclusion on the basis of small samples ⊸ In the above mentioned example the result of only brilliant class is displayed for advertisement of the school 15
- 16. Limitations and Statistics ⊸ To predict changes in two variables without taking cognizance of causal relationship between them ⊸ To mislead people by making unnecessary and clumsy presentation of statistical data 16
- 17. Thanks! 17
Editor's Notes
- #3: Student :- subject Business men :- 5 star Politician :- trees 10000 Gruhini :- average






