Introduction to Statistics Presentation(2).pptx
- 1. What is statistics? Statistics is defined as the science of decision making with calculated risks in the face of uncertainty. Statistics can be defined as the collection, presentation and interpretation of data.
- 2. Origin and History of Statistics The History of statistics can be said to start around 1749 although, over time, there have been changes to the interpretation of the word statistics. In early times, the meaning was restricted to information about states. By the 18th century, the term "statistics" designated the systematic collection of demographic and economic data by states In the early 19th century, collection intensified, and the meaning of "statistics" broadened to include the discipline concerned with the collection, summary, and analysis of data. Today, data are collected, and statistics are computed and widely distributed in government, business, most of the sciences and sports etc.,…
- 3. Scope and Importance of Statistics 1. Statistics and planning: Statistics is indispensable into planning in the modern age which is termed as “the age of planning”. Almost all over the world the govt. are re-storing to planning for economic development. 2. Statistics and economics: Statistical data and techniques of statistical analysis have to immensely useful involving economical problem. Such as wages, price, time series analysis, demand analysis. 3. Statistics and business: Statistics is a responsible tool for production control. Business executive are relying more and more on statistical techniques for studying the much and desire of the valued customers. 4. Statistics and industry: In industry statistics is widely used for quality control. In production engineering to find out whether the product is confirming to the specifications or not. Statistical tools, such as inspection plan, control chart etc. 5. Statistics and mathematics: Statistics are intimately related recent advancements in statistical technique are the outcome of wide applications of mathematics. 6. Statistics and modern science: In medical science the statistical tools for collection, presentation and analysis of observed facts relating to causes and incidence of dieses and the result of application various drugs and medicine are of great importance. 7. Statistics, psychology and education: In education and physiology statistics has found wide application such as, determining or to determine the reliability and validity to a test, factor analysis etc. 8. Statistics and war: In war the theory of decision function can be a great assistance to the military and personal to plan “maximum destruction with minimum effort.”
- 4. Statistics in business and management 1. Marketing: Statistical analysis are frequently used in providing information for making decision in the field of marketing it is necessary first to find out what can be sold and the to evolve suitable strategy, so that the goods which to the ultimate consumer. A skill full analysis of data on production purchasing power, man power, habits of competitors, habits of consumer, transportation cost should be consider to take any attempt to establish a new market. 2. Production: In the field of production statistical data and method play a very important role. The decision about what to produce? How to produce? When to produce? For whom to produce is based largely on statistical analysis. 3. Banking: Banking institute have found if increasingly to establish research department within their organization for the purpose of gathering and analysis information, not only regarding their own business but also regarding general economic situation and every segment of business in which they may have interest. 4. Investment: Statistics greatly assists investors in making clear and valued judgment in his investment decision in selecting securities which are safe and have the best prospects of yielding a good income. 5. Purchase: the purchase department in discharging their function makes use of statistical data to frame suitable purchase policies such as what to buy? What quantity to buy? What time to buy? Where to buy? Whom to buy? 6. Control: The management control process combines statistical and accounting method in making the overall budget for the coming year including sales, materials, labor and other costs and net profits and capital requirement.
- 5. Functions of Statistics To present facts in definite form Precision to the facts Comparisons Formulation and testing of Hypothesis Forecasting Policy making It enlarges Knowledge To measure Uncertainty
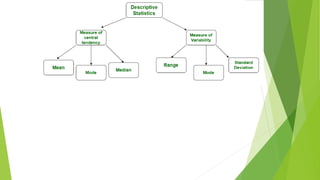
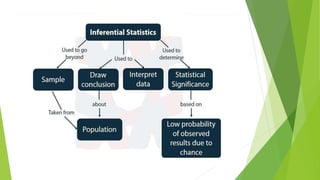
- 6. Branches of statistics In general, there are two branches of statistics, and they are (i)Descriptive statistics (ii)Inferential statistics Descriptive Statistics Descriptive statistics deals with the collection and presentation of data. This is usually the first part of a statistical analysis. It is usually not as simple as it sounds, and the statistician needs to be aware of designing experiments, choosing the right focus group and avoid biases that are so easy to creep into the experiment. Inferential Statistics Inferential statistics, as the name suggests, involves drawing the right conclusions from the statistical analysis that has been performed using descriptive statistics. In the end, it is the inferences that make studies important, and this aspect is dealt with in inferential statistics.
- 10. Computers and Statistics Computational statistics, or statistical computing, is the interface between statistics and computer science. What is Statistical Analysis Software? Statistical analysis software products are specialized programs designed to allow users to perform complex statistical analysis. These products typically provide tools for the organization, interpretation, and presentation of selected data sets. Statistical solutions typically package these data management capabilities with features specific to statistical analysis. Statistical analysis capabilities refer to capabilities that support analysis methodologies such as regression analysis, predictive analytics, and statistical modelling, among many others.
- 11. Top 7 Statistical Analysis Software’s as on date. SPSS ( IBM)-Statistical package for social sciences R-Software( R Foundation) MATLAB ( The MathWorks) Microsoft Excel SAS ( Statistical Analysis Software) GraphPad Prism Minitab Conclusion: There are a range of different software tools available, and each offers something slightly different to the user – what you choose will depend on a range of factors, including your research question, knowledge of statistics, and experience of coding.
- 12. Limitations of Statistics Statistics laws are true on average. Statistics are aggregates of facts. So single observation is not a statistics, it deals with groups and aggregates only. Statistical methods are best applicable on quantitative data. Statistical methods cannot be applied to heterogeneous data. If sufficient care is not exercised in collecting, analyzing and interpretation the data, statistical results might be misleading. Only a person who has an expert knowledge of statistics can handle statistical data efficiently. Some errors are possible in statistical decisions. Particularly the inferential statistics involves certain errors. We do not know whether an error has been committed or not.