Statistics Presentation week 7
Download as ppt, pdf2 likes2,539 views
Here are the steps to solve this problem: 1) State the null (H0) and alternative (Ha) hypotheses: H0: μ = 60 Ha: μ < 60 2) Set the significance level: α = 0.05 3) Find the critical value for a one-tailed test: Zc = -1.65 4) Calculate the test statistic: Z = (58 - 60)/√(40) = -2 5) Make a decision: Since Z = -2 < -1.65, reject H0. 6) State your conclusion: At the 5% significance level, there is sufficient evidence to conclude that the mean battery life is less
1 of 30
Downloaded 90 times


















Ad
Recommended
Estimators for structural equation models of Likert scale data



Estimators for structural equation models of Likert scale dataNick Stauner - The document compares different estimation methods (ML, WLS, ULS, DWLS, GLS) for confirmatory factor analysis with ordinal/Likert scale data.
- WLS estimates deviated most from the target values, while ML, ULS, and DWLS estimates were roughly equal. WLS estimates were the least accurate.
- For non-normal data, fit statistics from ML and GLS were biased, while ULS and DWLS were considered the most robust and liberal estimators.
Quantitative Data Analysis: Hypothesis Testing



Quantitative Data Analysis: Hypothesis TestingMurni Mohd Yusof This document provides an overview of quantitative data analysis techniques for hypothesis testing, including types of errors, statistical power, and tests for single and multiple sample means. It also discusses regression analysis, issues of multicollinearity, and other multivariate tests such as discriminant analysis, logistic regression, and canonical correlation.
Logistic regression



Logistic regressionDrZahid Khan This document provides an overview of logistic regression. It begins by defining logistic regression as a specialized form of regression used when the dependent variable is dichotomous while the independent variables can be of any type. It notes logistic regression allows prediction of discrete variables from continuous and discrete predictors without assumptions about variable distributions. The document then discusses why logistic regression is used when assumptions of other regressions like normality and equal variance are violated. It also outlines how to perform and interpret logistic regression including assessing model fit. Finally, it provides an example research question and hypotheses about predicting solar panel adoption using household income and mortgage as predictors.
Proportion test using Chi square



Proportion test using Chi squareParag Shah SPSS does not have Z test for proportions, So, we use Chi-Square test for proportion tests. Test for single proportion and Test for proportions of two samples
Bivariate data



Bivariate datajulienorman80065 - MAP testing will take place this week, with detailed information available in announcements
- Next week, students will begin working on their end-of-year projects
- This document provides information about bivariate data, scatter plots, and lines of best fit for a statistics and probability lesson
Normality



NormalityDr. Nithin Nair (PT) This document discusses normality testing of data. It defines the normal curve and lists the steps for testing normality in SPSS. These include checking skewness and kurtosis values and the Shapiro-Wilk test p-value. The document demonstrates how to perform normality testing in SPSS and interpret the outputs, which include skewness, kurtosis, histograms, Q-Q plots and box plots. The summary should report whether the sample data were found to be normally or not normally distributed based on these tests.
The median test



The median testMajesty Ortiz I. The median test is used to determine if two independent groups have been drawn from populations with the same median. It requires at least ordinal scale data.
II. The combined median of both groups is calculated. Scores from each group are then split based on whether they are above or below the combined median. These frequencies are entered into a 2x2 contingency table.
III. The median test statistic (chi-square) is calculated and compared to a critical value based on the significance level and degrees of freedom to determine whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis that the two groups have the same median.
Spearman Rank Correlation Presentation



Spearman Rank Correlation Presentationcae_021 The document discusses Spearman's rank correlation coefficient, a nonparametric measure of statistical dependence between two variables. It assumes values between -1 and 1, with -1 indicating a perfect negative correlation and 1 a perfect positive correlation. The steps involve converting values to ranks, calculating the differences between ranks, and determining if there is a statistically significant correlation based on the test statistic and critical values. An example calculates Spearman's rho using rankings of cricket teams in test and one day international matches.
Mann Whitney U test



Mann Whitney U testDr. Ankit Gaur This presentation contains information about Mann Whitney U test, what is it, when to use it and how to use it. I have also put an example so that it may help you to easily understand it.
Lesson 24 testing the hypothesis



Lesson 24 testing the hypothesismjlobetos This document discusses hypothesis testing and its importance in research. It defines statistical significance as a relationship between variables that is not due to chance. A hypothesis is a statement assumed to be true that must be tested. There are two types of hypotheses: the null hypothesis states there is no relationship, while the alternative hypothesis states there is a relationship. The document outlines the steps in hypothesis testing, including stating hypotheses, choosing a statistical test, determining significance levels, computing test values, and deciding whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis based on a comparison of critical and calculated values. It also discusses types I and II errors and parametric vs. non-parametric tests.
SCATTER PLOTS



SCATTER PLOTSONE Virtual Services Illustrate the nature of bivariate data;
Construct a scatter plot;
Describe shapes (form), trend (direction), and variation (strength) based on the scatter plot; and
Estimate strength of association between the variables based on a scatter plot.
Visit the website for other Services: https://cristinamontenegro92.wixsite.com/onevs
Inferential Statistics



Inferential StatisticsUniversity of Jaffna This document provides an overview of inferential statistics. It defines inferential statistics as using samples to draw conclusions about populations and make predictions. It discusses key concepts like hypothesis testing, null and alternative hypotheses, type I and type II errors, significance levels, power, and effect size. Common inferential tests like t-tests, ANOVA, and meta-analyses are also introduced. The document emphasizes that inferential statistics allow researchers to generalize from samples to populations and test hypotheses about relationships between variables.
SAMPLING and SAMPLING DISTRIBUTION



SAMPLING and SAMPLING DISTRIBUTIONRia Micor This document provides information about sampling and sampling distributions. It discusses how to calculate the mean, variance, and standard deviation of sample means and their sampling distributions. Students are instructed to form groups and collect sample data from their group members to calculate these statistics. They are given examples of data on candy prices and asked to determine values like the sample mean, variance and standard deviation of the sampling distribution from the sample mean.
Independent sample t test



Independent sample t testShajar Khan The document describes how to conduct an independent samples t-test. It explains that the t-test is used to compare differences between separate groups. An example is provided where participants are randomly assigned to either a pizza or beer diet for a week, and their weight gain is measured. Calculations are shown to find the variance, mean, and t-value for each group. The results indicate participants on the beer diet gained significantly more weight than those on the pizza diet, t(8) = 4.47, p < .05. Instructions are also provided for conducting this analysis in SPSS.
Advance Statistics - Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test



Advance Statistics - Wilcoxon Signed Rank TestJoshua Batalla The Wilcoxon signed-rank test is a non-parametric test used to compare two related samples, such as repeated measurements on a single sample, to assess whether their population mean ranks differ. It can be used as a non-parametric alternative to the paired Student's t-test when the population cannot be assumed to be normally distributed. The test involves ranking the differences between pairs of observations and comparing the sum of the ranks of the positive differences to what would be expected if there was no effect. The document provides information on the requirements, formula, and an example application of the Wilcoxon signed-rank test.
Binary Logistic Regression



Binary Logistic RegressionSeth Anandaram Jaipuria College If dependent variable is binary and independent variables are categorical , we use Binary Logistic Regression
Testing for normality



Testing for normalityDr. Ankita Srivastava This document discusses methods for testing whether a data set is normally distributed. It describes both graphical and statistical tests for normality, including Q-Q plots and the Kolmogorov-Smirnov, Shapiro-Wilk, and Lilliefors tests. It then provides a detailed example of how to perform the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for normality on a set of height data.
Correlational research



Correlational researchAzura Zaki Correlational research investigates relationships between two variables without manipulating either variable. It can be used for explanatory purposes to help explain behaviors, or for prediction purposes to predict outcomes. Common correlational techniques include scatter plots, regression analysis, multiple regression, and factor analysis. Threats to internal validity like subject characteristics, location, instrumentation, and mortality must be evaluated. The basic steps in correlational research are problem selection, sampling, instrumentation, design, data collection, and evaluating threats to validity.
4. parameter and statistic



4. parameter and statisticONE Virtual Services Distinguish between Parameter and Statistic.
Calculate sample variance and sample standard deviation.
Visit the website for more services: https://cristinamontenegro92.wixsite.com/onevs
Simple Linear Regression (simplified)



Simple Linear Regression (simplified)Haoran Zhang A set of slides to illustrate the idea of simple linear regression. Could be used as introductory materials before teaching linear regression.
Mann Whitney U Test | Statistics



Mann Whitney U Test | StatisticsTransweb Global Inc The Mann Witney U Test in statistics is related to a testing without considering any assumption as to the parameters of frequently distributed of a valueless hypothesis. It is similar to the value selected randomly from one sample, can be higher than or lesser than a value selected randomly from a second sample. Copy the link given below and paste it in new browser window to get more information on Mann Whitney U Test:- http://www.transtutors.com/homework-help/statistics/mann-whitney-u-test.aspx
Data analysis with spss anova



Data analysis with spss anovaSurjeet Randhir Singh Dhaka This document provides information on conducting a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) using SPSS. It uses an example where a farmer tests the effect of different fertilizers (biological, chemical, none) on the weight of parsley plants. The summary is:
The document walks through running a one-way ANOVA in SPSS to analyze the weights of parsley plants that received different fertilizers. The ANOVA results show that fertilizer significantly affects weight. A post hoc test finds a significant difference between plants that received chemical fertilizer versus no fertilizer. The document also briefly describes two-way ANOVAs for analyzing the effects of two independent variables.
Statistical inference



Statistical inferenceJags Jagdish This document discusses statistical inference, which involves drawing conclusions about an unknown population based on a sample. There are two main types of statistical inference: parameter estimation and hypothesis testing. Parameter estimation involves obtaining numerical values of population parameters from a sample, like estimating the percentage of people aware of a product. Hypothesis testing involves making judgments about assumptions regarding population parameters based on sample data. The document also discusses point estimation, interval estimation, standard error, and provides examples of calculating confidence intervals.
Regression analysis



Regression analysisTeachers Mitraa This document discusses regression analysis techniques. It defines regression as the tendency for estimated values to be close to actual values. Regression analysis investigates the relationship between variables, with the independent variable influencing the dependent variable. There are three main types of regression: linear regression which uses a linear equation to model the relationship between one independent and one dependent variable; logistic regression which predicts the probability of a binary outcome using multiple independent variables; and nonlinear regression which models any non-linear relationship between variables. The document provides examples of using linear and logistic regression and discusses their key assumptions and calculations.
Inferential statistics powerpoint



Inferential statistics powerpointkellula This document provides an introduction to inferential statistics, including key terms like test statistic, critical value, degrees of freedom, p-value, and significance. It explains that inferential statistics allow inferences to be made about populations based on samples through probability and significance testing. Different levels of measurement are discussed, including nominal, ordinal, and interval data. Common inferential tests like the Mann-Whitney U, Chi-squared, and Wilcoxon T tests are mentioned. The process of conducting inferential tests is outlined, from collecting and analyzing data to comparing test statistics to critical values to determine significance. Type 1 and Type 2 errors in significance testing are also defined.
Linear Regression Using SPSS



Linear Regression Using SPSSDr Athar Khan Linear regression analysis predicts the value of a dependent variable based on the value of an independent variable. It requires continuous variables, a linear relationship between variables, no outliers, independent observations, homoscedasticity, and normally distributed residuals. The analysis identifies whether changes in the independent variable reliably predict changes in the dependent variable.
Basis of statistical inference



Basis of statistical inferencezahidacademy Statistical inference involves using probability concepts to draw conclusions about populations based on samples. It includes point and range estimation to estimate population values, as well as hypothesis testing to test hypotheses about populations. Hypothesis testing involves making a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis before collecting sample data. Common hypotheses include claims of no difference or significant differences. Statistical tests like z-tests, t-tests, and chi-square tests are used to either accept or reject the null hypothesis based on the sample data and a significance level, typically 5%. P-values indicate the probability of observing the sample results by chance. Type 1 and type 2 errors can occur when making inferences about hypotheses.
Introduction to ANOVAs



Introduction to ANOVAsflorentinoz ANOVA (analysis of variance) is used to determine if different treatment groups differ significantly on some measure. It compares the variance between groups to the variance within groups. If the between-group variance is large relative to the within-group variance, it suggests the treatment had an effect. The analysis calculates an F-ratio, with larger values indicating it is less likely the groups differ due to chance. Researchers use statistical tables to determine the probability (p-value) that the F-ratio occurred by chance if there was actually no effect.
Hypothesis Testing



Hypothesis TestingJeremy Lane This document provides an introduction to hypothesis testing using the normal distribution to test claims about population means. It defines key terminology used in hypothesis testing such as the null and alternative hypotheses, test statistic, p-value, critical region, significance level, and critical value. It also outlines the four-step process for conducting a hypothesis test which includes stating the question, planning by specifying distributions and hypotheses, solving to calculate test statistics and p-values, and concluding whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis. Examples are provided for left-sided, right-sided, and two-sided hypothesis tests.
Lect w6 hypothesis_testing



Lect w6 hypothesis_testingRione Drevale This document summarizes key concepts in hypothesis testing including:
1. The four main steps: stating hypotheses, setting criteria, computing test statistics, and making a decision.
2. Common test statistics like z-test and t-test and how to compute them.
3. Key terms like type I and type II errors, significance levels, p-values, and how they relate to rejecting or failing to reject the null hypothesis.
4. Examples of hypothesis testing for means, proportions, and paired differences.
Ad
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Mann Whitney U test



Mann Whitney U testDr. Ankit Gaur This presentation contains information about Mann Whitney U test, what is it, when to use it and how to use it. I have also put an example so that it may help you to easily understand it.
Lesson 24 testing the hypothesis



Lesson 24 testing the hypothesismjlobetos This document discusses hypothesis testing and its importance in research. It defines statistical significance as a relationship between variables that is not due to chance. A hypothesis is a statement assumed to be true that must be tested. There are two types of hypotheses: the null hypothesis states there is no relationship, while the alternative hypothesis states there is a relationship. The document outlines the steps in hypothesis testing, including stating hypotheses, choosing a statistical test, determining significance levels, computing test values, and deciding whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis based on a comparison of critical and calculated values. It also discusses types I and II errors and parametric vs. non-parametric tests.
SCATTER PLOTS



SCATTER PLOTSONE Virtual Services Illustrate the nature of bivariate data;
Construct a scatter plot;
Describe shapes (form), trend (direction), and variation (strength) based on the scatter plot; and
Estimate strength of association between the variables based on a scatter plot.
Visit the website for other Services: https://cristinamontenegro92.wixsite.com/onevs
Inferential Statistics



Inferential StatisticsUniversity of Jaffna This document provides an overview of inferential statistics. It defines inferential statistics as using samples to draw conclusions about populations and make predictions. It discusses key concepts like hypothesis testing, null and alternative hypotheses, type I and type II errors, significance levels, power, and effect size. Common inferential tests like t-tests, ANOVA, and meta-analyses are also introduced. The document emphasizes that inferential statistics allow researchers to generalize from samples to populations and test hypotheses about relationships between variables.
SAMPLING and SAMPLING DISTRIBUTION



SAMPLING and SAMPLING DISTRIBUTIONRia Micor This document provides information about sampling and sampling distributions. It discusses how to calculate the mean, variance, and standard deviation of sample means and their sampling distributions. Students are instructed to form groups and collect sample data from their group members to calculate these statistics. They are given examples of data on candy prices and asked to determine values like the sample mean, variance and standard deviation of the sampling distribution from the sample mean.
Independent sample t test



Independent sample t testShajar Khan The document describes how to conduct an independent samples t-test. It explains that the t-test is used to compare differences between separate groups. An example is provided where participants are randomly assigned to either a pizza or beer diet for a week, and their weight gain is measured. Calculations are shown to find the variance, mean, and t-value for each group. The results indicate participants on the beer diet gained significantly more weight than those on the pizza diet, t(8) = 4.47, p < .05. Instructions are also provided for conducting this analysis in SPSS.
Advance Statistics - Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test



Advance Statistics - Wilcoxon Signed Rank TestJoshua Batalla The Wilcoxon signed-rank test is a non-parametric test used to compare two related samples, such as repeated measurements on a single sample, to assess whether their population mean ranks differ. It can be used as a non-parametric alternative to the paired Student's t-test when the population cannot be assumed to be normally distributed. The test involves ranking the differences between pairs of observations and comparing the sum of the ranks of the positive differences to what would be expected if there was no effect. The document provides information on the requirements, formula, and an example application of the Wilcoxon signed-rank test.
Binary Logistic Regression



Binary Logistic RegressionSeth Anandaram Jaipuria College If dependent variable is binary and independent variables are categorical , we use Binary Logistic Regression
Testing for normality



Testing for normalityDr. Ankita Srivastava This document discusses methods for testing whether a data set is normally distributed. It describes both graphical and statistical tests for normality, including Q-Q plots and the Kolmogorov-Smirnov, Shapiro-Wilk, and Lilliefors tests. It then provides a detailed example of how to perform the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for normality on a set of height data.
Correlational research



Correlational researchAzura Zaki Correlational research investigates relationships between two variables without manipulating either variable. It can be used for explanatory purposes to help explain behaviors, or for prediction purposes to predict outcomes. Common correlational techniques include scatter plots, regression analysis, multiple regression, and factor analysis. Threats to internal validity like subject characteristics, location, instrumentation, and mortality must be evaluated. The basic steps in correlational research are problem selection, sampling, instrumentation, design, data collection, and evaluating threats to validity.
4. parameter and statistic



4. parameter and statisticONE Virtual Services Distinguish between Parameter and Statistic.
Calculate sample variance and sample standard deviation.
Visit the website for more services: https://cristinamontenegro92.wixsite.com/onevs
Simple Linear Regression (simplified)



Simple Linear Regression (simplified)Haoran Zhang A set of slides to illustrate the idea of simple linear regression. Could be used as introductory materials before teaching linear regression.
Mann Whitney U Test | Statistics



Mann Whitney U Test | StatisticsTransweb Global Inc The Mann Witney U Test in statistics is related to a testing without considering any assumption as to the parameters of frequently distributed of a valueless hypothesis. It is similar to the value selected randomly from one sample, can be higher than or lesser than a value selected randomly from a second sample. Copy the link given below and paste it in new browser window to get more information on Mann Whitney U Test:- http://www.transtutors.com/homework-help/statistics/mann-whitney-u-test.aspx
Data analysis with spss anova



Data analysis with spss anovaSurjeet Randhir Singh Dhaka This document provides information on conducting a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) using SPSS. It uses an example where a farmer tests the effect of different fertilizers (biological, chemical, none) on the weight of parsley plants. The summary is:
The document walks through running a one-way ANOVA in SPSS to analyze the weights of parsley plants that received different fertilizers. The ANOVA results show that fertilizer significantly affects weight. A post hoc test finds a significant difference between plants that received chemical fertilizer versus no fertilizer. The document also briefly describes two-way ANOVAs for analyzing the effects of two independent variables.
Statistical inference



Statistical inferenceJags Jagdish This document discusses statistical inference, which involves drawing conclusions about an unknown population based on a sample. There are two main types of statistical inference: parameter estimation and hypothesis testing. Parameter estimation involves obtaining numerical values of population parameters from a sample, like estimating the percentage of people aware of a product. Hypothesis testing involves making judgments about assumptions regarding population parameters based on sample data. The document also discusses point estimation, interval estimation, standard error, and provides examples of calculating confidence intervals.
Regression analysis



Regression analysisTeachers Mitraa This document discusses regression analysis techniques. It defines regression as the tendency for estimated values to be close to actual values. Regression analysis investigates the relationship between variables, with the independent variable influencing the dependent variable. There are three main types of regression: linear regression which uses a linear equation to model the relationship between one independent and one dependent variable; logistic regression which predicts the probability of a binary outcome using multiple independent variables; and nonlinear regression which models any non-linear relationship between variables. The document provides examples of using linear and logistic regression and discusses their key assumptions and calculations.
Inferential statistics powerpoint



Inferential statistics powerpointkellula This document provides an introduction to inferential statistics, including key terms like test statistic, critical value, degrees of freedom, p-value, and significance. It explains that inferential statistics allow inferences to be made about populations based on samples through probability and significance testing. Different levels of measurement are discussed, including nominal, ordinal, and interval data. Common inferential tests like the Mann-Whitney U, Chi-squared, and Wilcoxon T tests are mentioned. The process of conducting inferential tests is outlined, from collecting and analyzing data to comparing test statistics to critical values to determine significance. Type 1 and Type 2 errors in significance testing are also defined.
Linear Regression Using SPSS



Linear Regression Using SPSSDr Athar Khan Linear regression analysis predicts the value of a dependent variable based on the value of an independent variable. It requires continuous variables, a linear relationship between variables, no outliers, independent observations, homoscedasticity, and normally distributed residuals. The analysis identifies whether changes in the independent variable reliably predict changes in the dependent variable.
Basis of statistical inference



Basis of statistical inferencezahidacademy Statistical inference involves using probability concepts to draw conclusions about populations based on samples. It includes point and range estimation to estimate population values, as well as hypothesis testing to test hypotheses about populations. Hypothesis testing involves making a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis before collecting sample data. Common hypotheses include claims of no difference or significant differences. Statistical tests like z-tests, t-tests, and chi-square tests are used to either accept or reject the null hypothesis based on the sample data and a significance level, typically 5%. P-values indicate the probability of observing the sample results by chance. Type 1 and type 2 errors can occur when making inferences about hypotheses.
Introduction to ANOVAs



Introduction to ANOVAsflorentinoz ANOVA (analysis of variance) is used to determine if different treatment groups differ significantly on some measure. It compares the variance between groups to the variance within groups. If the between-group variance is large relative to the within-group variance, it suggests the treatment had an effect. The analysis calculates an F-ratio, with larger values indicating it is less likely the groups differ due to chance. Researchers use statistical tables to determine the probability (p-value) that the F-ratio occurred by chance if there was actually no effect.
Viewers also liked (15)
Hypothesis Testing



Hypothesis TestingJeremy Lane This document provides an introduction to hypothesis testing using the normal distribution to test claims about population means. It defines key terminology used in hypothesis testing such as the null and alternative hypotheses, test statistic, p-value, critical region, significance level, and critical value. It also outlines the four-step process for conducting a hypothesis test which includes stating the question, planning by specifying distributions and hypotheses, solving to calculate test statistics and p-values, and concluding whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis. Examples are provided for left-sided, right-sided, and two-sided hypothesis tests.
Lect w6 hypothesis_testing



Lect w6 hypothesis_testingRione Drevale This document summarizes key concepts in hypothesis testing including:
1. The four main steps: stating hypotheses, setting criteria, computing test statistics, and making a decision.
2. Common test statistics like z-test and t-test and how to compute them.
3. Key terms like type I and type II errors, significance levels, p-values, and how they relate to rejecting or failing to reject the null hypothesis.
4. Examples of hypothesis testing for means, proportions, and paired differences.
Statistics Presentation week 6



Statistics Presentation week 6krookroo The document discusses the normal distribution and how to calculate probabilities and z-scores. It provides examples of finding the probability that a value falls within a certain range of the mean based on the standard deviation. It also shows how to calculate z-scores and find the corresponding value given the mean and standard deviation.
Discrete & Continuous Data



Discrete & Continuous DataBitsy Griffin This document discusses two types of data: continuous and discrete. Continuous data involves measurements like temperature, length, or area where data points can be connected and any value of x will produce a y value. Discrete data involves counts of objects like numbers of shirts or books, where data points are not connected and not every x value produces a y value.
discrete and continuous data



discrete and continuous dataSkills for Life, Suffolk New college The document discusses different ways of representing discrete and continuous data using tables, charts, and graphs. It provides an example of discrete data from "Dave's Car Wash" showing the number and types of cars washed on a Sunday. This data is displayed in a table and frequency chart showing that 20 of the 60 cars washed were white. It then shows this same data represented using a pie chart and bar graph to illustrate different visual representations of the discrete data. The document also provides an example of continuous data recording the volume of water in a filling bath over time, and includes a line graph to represent this continuous data variation.
Exercise 5:Continuous and Discrete Variable



Exercise 5:Continuous and Discrete VariableAndrilyn Alcantara This document contains an exercise to determine whether 20 given variables are continuous or discrete. The variables include things like temperature, length, weight, time, sales numbers, prices, data counts, and percentages, which would need to be evaluated individually to classify them as having continuous or discrete possible values. The purpose is to practice distinguishing between variables that can take on any value within a range from those that are restricted to individual points or counts.
Discrete And Continuous Simulation



Discrete And Continuous SimulationNguyen Chien This document discusses different types of simulation models. It describes:
1) Static vs dynamic models, with dynamic models changing over time and static models as snapshots.
2) Deterministic vs stochastic vs chaotic models, depending on how predictable the behavior is.
3) Discrete vs continuous models, with discrete changing at countable points and continuous changing continuously.
4) Aggregate vs individual models, with aggregate models taking a more distant view and individual models a closer view of decisions.
parametric test of difference z test f test one-way_two-way_anova 



parametric test of difference z test f test one-way_two-way_anova Tess Anoza The document provides information about z-tests and F-tests. It defines what a z-test and F-test are, explains why and how they are used, and discusses the z-test for one sample and two sample groups as well as the F-test. For the z-test, it provides the formula, steps to use it for one and two sample groups, and an example problem. For the F-test, it defines what it is, when it is used, provides the formula and steps to compute the F-value including using an ANOVA table. It also provides an example problem to demonstrate solving the F-value.
Sampling distribution



Sampling distributionNilanjan Bhaumik This document discusses sampling and sampling distributions. It begins by explaining why sampling is preferable to a census in terms of time, cost and practicality. It then defines the sampling frame as the listing of items that make up the population. Different types of samples are described, including probability and non-probability samples. Probability samples include simple random, systematic, stratified, and cluster samples. Key aspects of each type are defined. The document also discusses sampling distributions and how the distribution of sample statistics such as means and proportions can be approximated as normal even if the population is not normal, due to the central limit theorem. It provides examples of how to calculate probabilities and intervals for sampling distributions.
Variables



Variablesshoffma5 This document discusses key concepts in research variables including:
1) Independent variables are those that influence or explain variation in the dependent variable, while dependent variables are outcomes measured.
2) Variables can be categorical (taking a small set of values) or continuous (quantitative and measured on a scale).
3) Scales of measurement include nominal (labels), ordinal (ordered ranks), interval (equal intervals), and ratio (true zero point).
4) Identifying the independent and dependent variables and their properties (categorical vs. continuous, scale of measurement) is important for research questions.
Research Design



Research Designgaurav22 The document discusses different aspects of research design including what research design is, its key components, and types of research design. It defines research design as the arrangement of conditions for collecting and analyzing data to combine relevance to the research purpose with efficient procedures. The main components of research design discussed are sampling design, observational design, statistical design, and operational design. It also outlines features of a good research design and key concepts like dependent and independent variables, extraneous variables, control, and research hypotheses. Finally, it discusses research design for exploratory, descriptive, diagnostic, and hypothesis-testing research studies.
Hypothesis



HypothesisMichael Gezae This document provides an overview of hypotheses for a presentation. It begins with learning outcomes which are to explain the meaning and significance of hypotheses, identify types of hypotheses, and illustrate why hypotheses are needed.
The presentation will cover the scientific method, meaning and types of variables, characteristics of good hypotheses, categories of hypotheses including null and alternative, and how to form and test hypotheses. Hypotheses are defined as educated guesses that relate variables and guide research. They must be testable, falsifiable, and contribute to theory. Hypotheses can be categorized by their formulation as null or alternative, by direction as directional or non-directional, and by their derivation as inductive or deductive.
Hypothesis testing ppt final



Hypothesis testing ppt finalpiyushdhaker This document provides an overview of hypothesis testing in inferential statistics. It defines a hypothesis as a statement or assumption about relationships between variables or tentative explanations for events. There are two main types of hypotheses: the null hypothesis (H0), which is the default position that is tested, and the alternative hypothesis (Ha or H1). Steps in hypothesis testing include establishing the null and alternative hypotheses, selecting a suitable test of significance or test statistic based on sample characteristics, formulating a decision rule to either accept or reject the null hypothesis based on where the test statistic value falls, and understanding the potential for errors. Key criteria for constructing hypotheses and selecting appropriate statistical tests are also outlined.
Test of hypothesis



Test of hypothesisvikramlawand The document discusses hypothesis testing in research. It defines a hypothesis as a proposition that can be tested scientifically. The key points are:
- A hypothesis aims to explain a phenomenon and can be tested objectively. Common hypotheses compare two groups or variables.
- Statistical hypothesis testing involves a null hypothesis (H0) and alternative hypothesis (Ha). H0 is the initial assumption being tested, while Ha is what would be accepted if H0 is rejected.
- Type I errors incorrectly reject a true null hypothesis. Type II errors fail to reject a false null hypothesis. Hypothesis tests aim to control the probability of type I errors.
- The significance level is the probability of a type I error,
Hypothesis testing; z test, t-test. f-test



Hypothesis testing; z test, t-test. f-testShakehand with Life Hypothesis is usually considered as the principal instrument in research and quality control. Its main function is to suggest new experiments and observations. In fact, many experiments are carried out with the deliberate object of testing hypothesis. Decision makers often face situations wherein they are interested in testing hypothesis on the basis of available information and then take decisions on the basis of such testing. In Six –Sigma methodology, hypothesis testing is a tool of substance and used in analysis phase of the six sigma project so that improvement can be done in right direction
Ad
Similar to Statistics Presentation week 7 (20)
Hypothesis testing



Hypothesis testingLorelyn Turtosa-Dumaug This document discusses hypothesis testing. It defines key terms like the null hypothesis (Ho), alternative hypothesis (H1), type 1 and type 2 errors, significance level, test statistics, critical values, rejection regions, and one-tailed vs two-tailed tests. It provides examples of how to formulate hypotheses, determine appropriate test statistics, establish critical regions, and make conclusions based on computed test values for both known and unknown population variances with one and two sample tests concerning means.
STATISTICS: Hypothesis Testing



STATISTICS: Hypothesis Testingjundumaug1 This document discusses hypothesis testing, including:
1) The objectives are to formulate statistical hypotheses, discuss types of errors, establish decision rules, and choose appropriate tests.
2) Key symbols and concepts are defined, such as the null and alternative hypotheses, Type I and Type II errors, test statistics like z and t, means, variances, sample sizes, and significance levels.
3) The two types of errors in hypothesis testing are discussed. Hypothesis tests can result in correct decisions or two types of errors when the null hypothesis is true or false.
4) Steps in hypothesis testing are outlined, including formulating hypotheses, specifying a significance level, choosing a test statistic, establishing a
Critical Value and The P Value



Critical Value and The P ValuePharmacy Universe The document defines key concepts in hypothesis testing such as critical value, significance level, p-value, type I and type II errors, and power. It states that the critical value divides the normal distribution into regions for rejecting or failing to reject the null hypothesis. The significance level corresponds to the critical region. A p-value less than 0.05 indicates the result is statistically significant. Type I error occurs when the null hypothesis is rejected when it is true, while type II error is failing to reject a false null hypothesis. Power is defined as 1 - β, where β is the probability of a type II error.
Testing of hypothesis



Testing of hypothesisRuchiJainRuchiJain The document discusses testing of hypotheses. It defines a hypothesis as a tentative prediction about the relationship between variables. Good hypotheses are precise, testable, and consistent with known facts. Hypothesis testing involves formulating a null hypothesis (Ho) and an alternative hypothesis (H1). A significance level such as 5% is chosen. If the test statistic falls within the critical region, Ho is rejected. Type I error rejects a true Ho, while Type II error accepts a false Ho. Power refers to correctly rejecting a false Ho. The testing process determines test statistics, critical regions, and interprets results to draw conclusions.
Tests of significance



Tests of significanceShubhanshu Gupta This document provides an overview of statistical inference and hypothesis testing. It discusses key concepts such as the null and alternative hypotheses, type I and type II errors, one-tailed and two-tailed tests, test statistics, p-values, confidence intervals, and parametric vs non-parametric tests. Specific statistical tests covered include the t-test, z-test, ANOVA, chi-square test, and correlation analyses. The document also addresses how sample size affects test power and significance.
Unit 2 Testing of Hypothesis - Hypothesis - Null, Alternative, Type 1 and 2 a...



Unit 2 Testing of Hypothesis - Hypothesis - Null, Alternative, Type 1 and 2 a...Ravinandan A P Hypothesis - Null Hypothesis, Alternative Hypothesis,
Type 1 Error and Type 2 Error
Level of significance
P value
hypothesis-tesing.pdf



hypothesis-tesing.pdfSandeep Phogat Hypothesis testing involves making an assumption about an unknown population parameter, called the null hypothesis (H0). A hypothesis is tested by collecting a sample from the population and comparing sample statistics to the null hypothesis. If the sample statistic is sufficiently different from the null hypothesis, the null hypothesis is rejected. There are two types of errors that can occur - type 1 errors occur when a true null hypothesis is rejected, and type 2 errors occur when a false null hypothesis is not rejected. Hypothesis tests can be one-tailed, testing if the sample statistic is greater than or less than the null hypothesis, or two-tailed, testing if it is significantly different in either direction.
Hypothesis_Testing.ppt



Hypothesis_Testing.pptssuserac2a40 1) Hypothesis testing involves making an educated guess about a population parameter and designing a study to analyze sample data to determine if the population characteristic is likely or unlikely.
2) The null hypothesis states what is assumed to be true about the population parameter, while the alternative hypothesis is what would be accepted if the null is rejected. Type I and Type II errors occur when the wrong conclusion is reached.
3) Key aspects of hypothesis testing include defining the test statistic, rejection region, significance level, and whether a one-tailed or two-tailed test is appropriate based on the alternative hypothesis.
Top schools in delhi ncr



Top schools in delhi ncrEdhole.com The document discusses hypothesis testing, including:
- The null hypothesis is initially assumed to be true, and data is examined to determine if there is strong enough evidence in favor of the alternative hypothesis to reject the null.
- There are two types of errors - type I errors where a true null hypothesis is incorrectly rejected, and type II errors where a false null hypothesis is not rejected. The significance level determines the likelihood of type I errors.
- Hypothesis tests can be conducted using either the rejection region approach which defines critical values, or the p-value approach which directly calculates the probability of obtaining the sample results if the null is true.
Testing of hypothesis



Testing of hypothesisJags Jagdish Hypothesis testing involves making an assumption about an unknown population parameter, called the null hypothesis (H0). A hypothesis is tested by collecting a sample from the population and comparing sample statistics to the hypothesized parameter value. If the sample value differs significantly from the hypothesized value based on a predetermined significance level, then the null hypothesis is rejected. There are two types of errors that can occur - type 1 errors occur when a true null hypothesis is rejected, and type 2 errors occur when a false null hypothesis is not rejected. Hypothesis tests can be one-tailed, testing if the sample value is greater than or less than the hypothesized value, or two-tailed, testing if the sample value is significantly different from the hypothesized value.
Testing of hypothesis



Testing of hypothesisSanjay Basukala This document discusses the process of testing hypotheses. It begins by defining hypothesis testing as a way to make decisions about population characteristics based on sample data, which involves some risk of error. The key steps are outlined as:
1) Formulating the null and alternative hypotheses, with the null hypothesis stating no difference or relationship.
2) Computing a test statistic based on the sample data and selecting a significance level, usually 5%.
3) Comparing the test statistic to critical values to either reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Examples are provided to demonstrate hypothesis testing for a single mean, comparing two means, and testing a claim about population characteristics using sample data and statistics.
Hypothesis testing



Hypothesis testingKaimrc_Rss_Jd This document discusses hypothesis testing, which involves drawing inferences about a population based on a sample from that population. It outlines the key elements of a hypothesis test, including the null and alternative hypotheses, test statistics, critical regions, significance levels, critical values, and p-values. Type I and Type II errors are explained, where a Type I error involves rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true, and a Type II error involves failing to reject the null when it is false. The power of a hypothesis test is defined as the probability of correctly rejecting the null hypothesis when it is false. Controlling type I and II errors involves considering the significance level, sample size, and population parameters in the null and alternative hypotheses.
Econometrics chapter 5-two-variable-regression-interval-estimation-



Econometrics chapter 5-two-variable-regression-interval-estimation-Alamin Milton - The document discusses hypothesis testing using regression analysis, focusing on the confidence interval approach and test of significance approach.
- It provides an example using wage and education data to test the hypothesis that the slope coefficient is equal to 0.5. Both the confidence interval approach and t-test approach are used to reject the null hypothesis.
- One-tailed and two-tailed hypothesis tests are explained. Additional topics covered include choosing the significance level, statistical versus practical significance, and reporting the results of regression analysis.
Biostatistics Made Ridiculously Simple by Dr. Aryan (Medical Booklet Series b...



Biostatistics Made Ridiculously Simple by Dr. Aryan (Medical Booklet Series b...Dr. Aryan (Anish Dhakal) Basic concepts in biostatistics that need to be understood very well which many students find difficult and overwhelming. Best wishes.
hypothesis.pptx



hypothesis.pptxPrakharMishra925441 Hypothesis testing involves setting up a null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis, determining a significance level, calculating a test statistic, identifying the critical region, computing the test statistic value based on a sample, and making a decision to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis. The z-test is used when the sample size is large and the population standard deviation is known, while the t-test is used for small samples when the population standard deviation is unknown. Both tests involve calculating a test statistic and comparing it to critical values to determine if there is sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis. Limitations include that the tests only indicate differences and not the reasons for them, and inferences are based on probabilities rather than certainty.
More Statistics



More Statisticsmandrewmartin The document discusses various statistical concepts related to hypothesis testing, including:
- Types I and II errors that can occur when testing hypotheses
- How the probability of committing errors depends on factors like the sample size and how far the population parameter is from the hypothesized value
- The concept of critical regions and how they are used to determine if a null hypothesis can be rejected
- The difference between discrete and continuous probability distributions and examples of each
- How an observed test statistic is calculated and compared to a critical value to determine whether to reject or not reject the null hypothesis
Testing Hypothesis



Testing HypothesisAzmi Mohd Tamil This document provides an overview of basic hypothesis testing concepts. It defines key terms like the null hypothesis, type I and type II errors, significance levels, and p-values. It explains how hypothesis tests are used to determine if there is a statistically significant difference between two groups, with the goal of rejecting or failing to reject the null hypothesis. Examples are given around comparing the effectiveness of two drugs and testing if reindeer can fly. Both parametric and non-parametric statistical tests are introduced.
Unit 3



Unit 3Rai University This document discusses hypothesis testing and the t-test. It covers:
1) The basics of hypothesis testing including null and alternative hypotheses, types of hypotheses, and types of errors.
2) The t-test, which is used for small samples from a normally distributed population. It relies on the t-distribution and the degree of freedom.
3) Applications of the t-test including testing the significance of a single mean, difference between two means, and paired t-tests.
4) When sample sizes are large, the normal distribution can be used instead in Z-tests for similar applications.
Biostatistics Made Ridiculously Simple by Dr. Aryan (Medical Booklet Series b...



Biostatistics Made Ridiculously Simple by Dr. Aryan (Medical Booklet Series b...Dr. Aryan (Anish Dhakal)
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
Canadian book publishing: Insights from the latest salary survey - Tech Forum...



Canadian book publishing: Insights from the latest salary survey - Tech Forum...BookNet Canada Join us for a presentation in partnership with the Association of Canadian Publishers (ACP) as they share results from the recently conducted Canadian Book Publishing Industry Salary Survey. This comprehensive survey provides key insights into average salaries across departments, roles, and demographic metrics. Members of ACP’s Diversity and Inclusion Committee will join us to unpack what the findings mean in the context of justice, equity, diversity, and inclusion in the industry.
Results of the 2024 Canadian Book Publishing Industry Salary Survey: https://publishers.ca/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/ACP_Salary_Survey_FINAL-2.pdf
Link to presentation recording and transcript: https://bnctechforum.ca/sessions/canadian-book-publishing-insights-from-the-latest-salary-survey/
Presented by BookNet Canada and the Association of Canadian Publishers on May 1, 2025 with support from the Department of Canadian Heritage.
Connect and Protect: Networks and Network Security



Connect and Protect: Networks and Network SecurityVICTOR MAESTRE RAMIREZ Connect and Protect: Networks and Network Security
TrsLabs Consultants - DeFi, WEb3, Token Listing



TrsLabs Consultants - DeFi, WEb3, Token ListingTrs Labs Enter the world of web3 with experienced strategic partner.
Open your business to new opportunities.
Webinar - Top 5 Backup Mistakes MSPs and Businesses Make .pptx



Webinar - Top 5 Backup Mistakes MSPs and Businesses Make .pptxMSP360 Data loss can be devastating — especially when you discover it while trying to recover. All too often, it happens due to mistakes in your backup strategy. Whether you work for an MSP or within an organization, your company is susceptible to common backup mistakes that leave data vulnerable, productivity in question, and compliance at risk.
Join 4-time Microsoft MVP Nick Cavalancia as he breaks down the top five backup mistakes businesses and MSPs make—and, more importantly, explains how to prevent them.
The Future of Cisco Cloud Security: Innovations and AI Integration



The Future of Cisco Cloud Security: Innovations and AI IntegrationRe-solution Data Ltd Stay ahead with Re-Solution Data Ltd and Cisco cloud security, featuring the latest innovations and AI integration. Our solutions leverage cutting-edge technology to deliver proactive defense and simplified operations. Experience the future of security with our expert guidance and support.
Viam product demo_ Deploying and scaling AI with hardware.pdf



Viam product demo_ Deploying and scaling AI with hardware.pdfcamilalamoratta Building AI-powered products that interact with the physical world often means navigating complex integration challenges, especially on resource-constrained devices.
You'll learn:
- How Viam's platform bridges the gap between AI, data, and physical devices
- A step-by-step walkthrough of computer vision running at the edge
- Practical approaches to common integration hurdles
- How teams are scaling hardware + software solutions together
Whether you're a developer, engineering manager, or product builder, this demo will show you a faster path to creating intelligent machines and systems.
Resources:
- Documentation: https://on.viam.com/docs
- Community: https://discord.com/invite/viam
- Hands-on: https://on.viam.com/codelabs
- Future Events: https://on.viam.com/updates-upcoming-events
- Request personalized demo: https://on.viam.com/request-demo
fennec fox optimization algorithm for optimal solution



fennec fox optimization algorithm for optimal solutionshallal2 Imagine you have a group of fennec foxes searching for the best spot to find food (the optimal solution to a problem). Each fox represents a possible solution and carries a unique "strategy" (set of parameters) to find food. These strategies are organized in a table (matrix X), where each row is a fox, and each column is a parameter they adjust, like digging depth or speed.
Bepents tech services - a premier cybersecurity consulting firm



Bepents tech services - a premier cybersecurity consulting firmBenard76 Introduction
Bepents Tech Services is a premier cybersecurity consulting firm dedicated to protecting digital infrastructure, data, and business continuity. We partner with organizations of all sizes to defend against today’s evolving cyber threats through expert testing, strategic advisory, and managed services.
🔎 Why You Need us
Cyberattacks are no longer a question of “if”—they are a question of “when.” Businesses of all sizes are under constant threat from ransomware, data breaches, phishing attacks, insider threats, and targeted exploits. While most companies focus on growth and operations, security is often overlooked—until it’s too late.
At Bepents Tech, we bridge that gap by being your trusted cybersecurity partner.
🚨 Real-World Threats. Real-Time Defense.
Sophisticated Attackers: Hackers now use advanced tools and techniques to evade detection. Off-the-shelf antivirus isn’t enough.
Human Error: Over 90% of breaches involve employee mistakes. We help build a "human firewall" through training and simulations.
Exposed APIs & Apps: Modern businesses rely heavily on web and mobile apps. We find hidden vulnerabilities before attackers do.
Cloud Misconfigurations: Cloud platforms like AWS and Azure are powerful but complex—and one misstep can expose your entire infrastructure.
💡 What Sets Us Apart
Hands-On Experts: Our team includes certified ethical hackers (OSCP, CEH), cloud architects, red teamers, and security engineers with real-world breach response experience.
Custom, Not Cookie-Cutter: We don’t offer generic solutions. Every engagement is tailored to your environment, risk profile, and industry.
End-to-End Support: From proactive testing to incident response, we support your full cybersecurity lifecycle.
Business-Aligned Security: We help you balance protection with performance—so security becomes a business enabler, not a roadblock.
📊 Risk is Expensive. Prevention is Profitable.
A single data breach costs businesses an average of $4.45 million (IBM, 2023).
Regulatory fines, loss of trust, downtime, and legal exposure can cripple your reputation.
Investing in cybersecurity isn’t just a technical decision—it’s a business strategy.
🔐 When You Choose Bepents Tech, You Get:
Peace of Mind – We monitor, detect, and respond before damage occurs.
Resilience – Your systems, apps, cloud, and team will be ready to withstand real attacks.
Confidence – You’ll meet compliance mandates and pass audits without stress.
Expert Guidance – Our team becomes an extension of yours, keeping you ahead of the threat curve.
Security isn’t a product. It’s a partnership.
Let Bepents tech be your shield in a world full of cyber threats.
🌍 Our Clientele
At Bepents Tech Services, we’ve earned the trust of organizations across industries by delivering high-impact cybersecurity, performance engineering, and strategic consulting. From regulatory bodies to tech startups, law firms, and global consultancies, we tailor our solutions to each client's unique needs.
Web and Graphics Designing Training in Rajpura



Web and Graphics Designing Training in RajpuraErginous Technology Web & Graphics Designing Training at Erginous Technologies in Rajpura offers practical, hands-on learning for students, graduates, and professionals aiming for a creative career. The 6-week and 6-month industrial training programs blend creativity with technical skills to prepare you for real-world opportunities in design.
The course covers Graphic Designing tools like Photoshop, Illustrator, and CorelDRAW, along with logo, banner, and branding design. In Web Designing, you’ll learn HTML5, CSS3, JavaScript basics, responsive design, Bootstrap, Figma, and Adobe XD.
Erginous emphasizes 100% practical training, live projects, portfolio building, expert guidance, certification, and placement support. Graduates can explore roles like Web Designer, Graphic Designer, UI/UX Designer, or Freelancer.
For more info, visit erginous.co.in , message us on Instagram at erginoustechnologies, or call directly at +91-89684-38190 . Start your journey toward a creative and successful design career today!
The No-Code Way to Build a Marketing Team with One AI Agent (Download the n8n...



The No-Code Way to Build a Marketing Team with One AI Agent (Download the n8n...SOFTTECHHUB The No-Code Way to Build a Marketing Team with One AI Agent (Download the n8n Template Free)
TrsLabs - Fintech Product & Business Consulting



TrsLabs - Fintech Product & Business ConsultingTrs Labs Hybrid Growth Mandate Model with TrsLabs
Strategic Investments, Inorganic Growth, Business Model Pivoting are critical activities that business don't do/change everyday. In cases like this, it may benefit your business to choose a temporary external consultant.
An unbiased plan driven by clearcut deliverables, market dynamics and without the influence of your internal office equations empower business leaders to make right choices.
Getting things done within a budget within a timeframe is key to Growing Business - No matter whether you are a start-up or a big company
Talk to us & Unlock the competitive advantage
Unlocking Generative AI in your Web Apps



Unlocking Generative AI in your Web AppsMaximiliano Firtman Slides for the session delivered at Devoxx UK 2025 - Londo.
Discover how to seamlessly integrate AI LLM models into your website using cutting-edge techniques like new client-side APIs and cloud services. Learn how to execute AI models in the front-end without incurring cloud fees by leveraging Chrome's Gemini Nano model using the window.ai inference API, or utilizing WebNN, WebGPU, and WebAssembly for open-source models.
This session dives into API integration, token management, secure prompting, and practical demos to get you started with AI on the web.
Unlock the power of AI on the web while having fun along the way!
Vaibhav Gupta BAML: AI work flows without Hallucinations



Vaibhav Gupta BAML: AI work flows without Hallucinationsjohn409870 Shipping Agents
Vaibhav Gupta
Cofounder @ Boundary
in/vaigup
boundaryml/baml
Imagine if every API call you made
failed only 5% of the time
boundaryml/baml
Imagine if every LLM call you made
failed only 5% of the time
boundaryml/baml
Imagine if every LLM call you made
failed only 5% of the time
boundaryml/baml
Fault tolerant systems are hard
but now everything must be
fault tolerant
boundaryml/baml
We need to change how we
think about these systems
Aaron Villalpando
Cofounder @ Boundary
Boundary
Combinator
boundaryml/baml
We used to write websites like this:
boundaryml/baml
But now we do this:
boundaryml/baml
Problems web dev had:
boundaryml/baml
Problems web dev had:
Strings. Strings everywhere.
boundaryml/baml
Problems web dev had:
Strings. Strings everywhere.
State management was impossible.
boundaryml/baml
Problems web dev had:
Strings. Strings everywhere.
State management was impossible.
Dynamic components? forget about it.
boundaryml/baml
Problems web dev had:
Strings. Strings everywhere.
State management was impossible.
Dynamic components? forget about it.
Reuse components? Good luck.
boundaryml/baml
Problems web dev had:
Strings. Strings everywhere.
State management was impossible.
Dynamic components? forget about it.
Reuse components? Good luck.
Iteration loops took minutes.
boundaryml/baml
Problems web dev had:
Strings. Strings everywhere.
State management was impossible.
Dynamic components? forget about it.
Reuse components? Good luck.
Iteration loops took minutes.
Low engineering rigor
boundaryml/baml
React added engineering rigor
boundaryml/baml
The syntax we use changes how we
think about problems
boundaryml/baml
We used to write agents like this:
boundaryml/baml
Problems agents have:
boundaryml/baml
Problems agents have:
Strings. Strings everywhere.
Context management is impossible.
Changing one thing breaks another.
New models come out all the time.
Iteration loops take minutes.
boundaryml/baml
Problems agents have:
Strings. Strings everywhere.
Context management is impossible.
Changing one thing breaks another.
New models come out all the time.
Iteration loops take minutes.
Low engineering rigor
boundaryml/baml
Agents need
the expressiveness of English,
but the structure of code
F*** You, Show Me The Prompt.
boundaryml/baml
<show don’t tell>
Less prompting +
More engineering
=
Reliability +
Maintainability
BAML
Sam
Greg Antonio
Chris
turned down
openai to join
ex-founder, one
of the earliest
BAML users
MIT PhD
20+ years in
compilers
made his own
database, 400k+
youtube views
Vaibhav Gupta
in/vaigup
vbv@boundaryml.com
boundaryml/baml
Thank you!
The Microsoft Excel Parts Presentation.pdf



The Microsoft Excel Parts Presentation.pdfYvonneRoseEranista This is an overview of the different parts of the Microsoft Excel.
Heap, Types of Heap, Insertion and Deletion



Heap, Types of Heap, Insertion and DeletionJaydeep Kale This pdf will explain what is heap, its type, insertion and deletion in heap and Heap sort
How analogue intelligence complements AI



How analogue intelligence complements AIPaul Rowe
Artificial Intelligence is providing benefits in many areas of work within the heritage sector, from image analysis, to ideas generation, and new research tools. However, it is more critical than ever for people, with analogue intelligence, to ensure the integrity and ethical use of AI. Including real people can improve the use of AI by identifying potential biases, cross-checking results, refining workflows, and providing contextual relevance to AI-driven results.
News about the impact of AI often paints a rosy picture. In practice, there are many potential pitfalls. This presentation discusses these issues and looks at the role of analogue intelligence and analogue interfaces in providing the best results to our audiences. How do we deal with factually incorrect results? How do we get content generated that better reflects the diversity of our communities? What roles are there for physical, in-person experiences in the digital world?
Statistics Presentation week 7
- 1. STATISTICS & PROBABILITY Hypothesis Testing
- 2. What is a Hypothesis? I assume the mean • an assumption about GPA of this class the population is 3.5! parameter • an educated guess about the population parameter
- 3. Hypotheses Testing: This is the process of making an inference or generalization on population parameters based on the results of the study on samples. Reject? Accept? Statistical Hypotheses: It is a guess or prediction made by the researcher regarding the possible outcome of the study.
- 4. Hypotheses Testing is deciding between what is REALITY and what is COINCIDENCE!
- 5. Types of Statistical Hypotheses Null Hypothesis (Ho): is always hoped to be rejected Always contains “=“ sign Alternative Hypothesis (Ha): •Challenges Ho •Never contains “=“ sign •Uses “< or > or ≠ “ •It generally represents the idea which the researcher wants to prove.
- 6. The Null Hypothesis: Ho Ex. Ho: The average GPA of this class is 3.5 µ = 3.5 H0: The Alternative Hypothesis: Ha Ha: The average GPA of this class is a) higher than 3.5 (Ha: µ > 3.5) b) lower than 3.5 (Ha: µ < 3.5) c) not equal to 3.5 (Ha: µ ≠ 3.5)
- 7. Types of Hypotheses Tests 1. One-tailed left directional test – this is used if Ha uses < symbol Critical value is α = 0.05 obtained Acceptance from the table region Area = 0.05 Rejection region
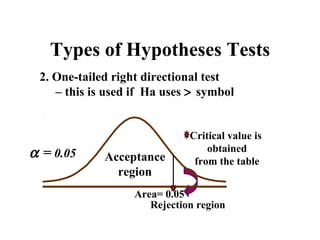
- 8. Types of Hypotheses Tests 2. One-tailed right directional test – this is used if Ha uses > symbol Critical value is α = 0.05 Acceptance obtained from the table region Area= 0.05 Rejection region
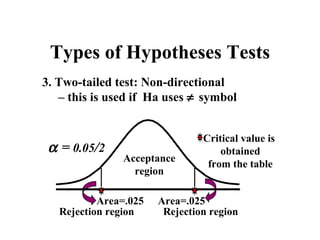
- 9. Types of Hypotheses Tests 3. Two-tailed test: Non-directional – this is used if Ha uses ≠ symbol Critical value is α = 0.05/2 obtained Acceptance from the table region Area=.025 Area=.025 Rejection region Rejection region
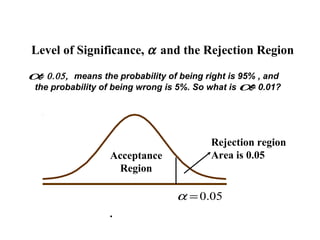
- 10. Level of Significance, α and the Rejection Region α 0.05, = means the probability of being right is 95% , and the probability of being wrong is 5%. So what is α 0.01? = Rejection region Acceptance Area is 0.05 Region α = 0.05 .
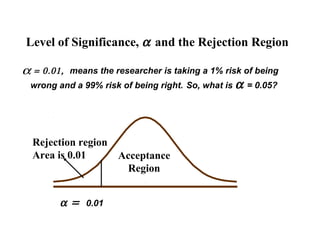
- 11. Level of Significance, α and the Rejection Region α= 0.01, means the researcher is taking a 1% risk of being wrong and a 99% risk of being right. So, what is α = 0.05? Rejection region Area is 0.01 Acceptance Region α = 0.01
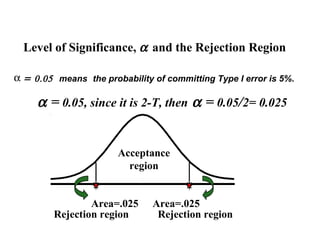
- 12. Level of Significance, α and the Rejection Region α = 0.05 means the probability of committing Type I error is 5%. α = 0.05, since it is 2-T, then α = 0.05/2= 0.025 Acceptance region Area=.025 Area=.025 Rejection region Rejection region
- 13. Level of Significance, α and the Rejection Region To summarize: α = 0.05, means the probability of being right is 95% and the probability of being wrong is 5%. So what is α 0.01? = α= 0.01, means the researcher is taking a 1% risk of being wrong and a 99% risk of being right. So, what is α = 0.05? α = 0.05 means the probability of committing Type I error is 5%. α So what is = 0.01?
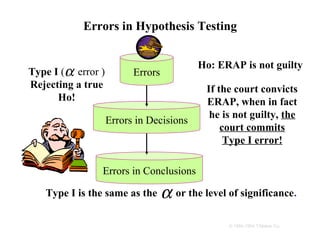
- 14. Errors in Hypothesis Testing Ho: ERAP is not guilty Type I (α error ) Errors Rejecting a true If the court convicts Ho! ERAP, when in fact he is not guilty, the Errors in Decisions court commits Type I error! Errors in Conclusions Type I is the same as the α or the level of significance. © 1984-1994 T/Maker Co.
- 15. Errors in Hypothesis Testing Type II (β error ) Errors Accepting a false Ho: ERAP is not guilty Ho! If the court acquits Errors in Decisions ERAP, when in fact he is guilty, the court commits Type II error! Errors in Conclusions
- 16. Decisions made regarding Ho (Reject Ho/Do not reject Ho) If we reject Ho, it means it is wrong! If we do not reject Ho, it doesn’t mean it is correct, we just don’t have enough evidence to reject it! © 1984-1994 T/Maker Co.
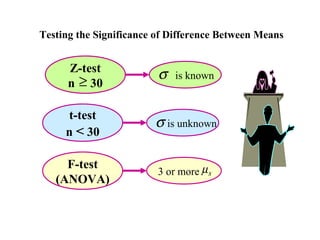
- 17. Testing the Significance of Difference Between Means Z-test σ is known n ≥ 30 t-test σ is unknown n < 30 F-test 3 or more µ s (ANOVA)
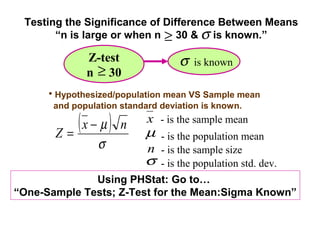
- 18. Testing the Significance of Difference Between Means “n is large or when n ≥ 30 & σ is known.” Z-test σ is known n ≥ 30 • Hypothesized/population mean VS Sample mean and population standard deviation is known. Z= (x − µ ) n x - is the sample mean µ - is the population mean σ n - is the sample size σ - is the population std. dev. Using PHStat: Go to… “One-Sample Tests; Z-Test for the Mean:Sigma Known”
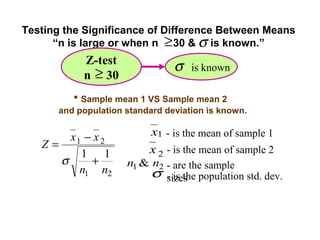
- 19. Testing the Significance of Difference Between Means “n is large or when n ≥ 30 & σ is known.” Z-test σ is known n ≥ 30 • Sample mean 1 VS Sample mean 2 and population standard deviation is known. x1 − x 2 x1 - is the mean of sample 1 Z= x 2 - is the mean of sample 2 1 1 σ + n1 & n2 - are the sample n1 n2 σ - is the population std. dev. sizes
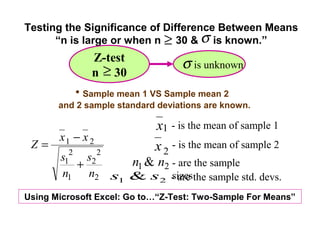
- 20. Testing the Significance of Difference Between Means “n is large or when n ≥ 30 & σ is known.” Z-test σ is unknown n ≥ 30 • Sample mean 1 VS Sample mean 2 and 2 sample standard deviations are known. x1 - is the mean of sample 1 x1 − x 2 Z= x 2 - is the mean of sample 2 s12 s2 2 n1 & n2 - are the sample + n1 n2 s1 & s2 - are the sample std. devs. sizes Using Microsoft Excel: Go to…“Z-Test: Two-Sample For Means”
- 21. The Critical Value Approach in Testing the Significance of Difference Between Means The 5-step solution Step 1. Formulate Ho and Ha Step 2. Set the level of significance α , usually it is given in the problem. Step 3. Formulate the decision rule (when to reject Ho); Find the critical value/P-value. Step 4. Make your decision. Step 5. Formulate your conclusion.
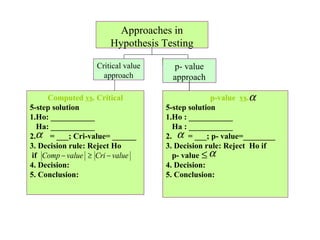
- 22. Approaches in Hypothesis Testing Critical value p- value approach approach Computed vs. Critical p-valueα vs.α α ≤ 5-step solution 5-step solution 1.Ho: ___________ 1.Ho : ___________ Ha: ___________ Ha : ___________ 2.α = ___; Cri-value= ______ 2. α = ___; p- value=________ α 3. Decision rule: Reject Ho 3. Decision rule: Reject Ho if if Comp − value ≥ Cri − value p- value ≤ α ≤α 4. Decision: α 4. Decision: 5. Conclusion: 5. Conclusion:
- 23. Finding Critical Values: One-Tailed What Is Z Given α = 0.05? .45 .05 Α= α = .05 Z 4 5 Z=1.65 Critical value 1.5 .4382 .4394 1.6 .4495 .4505
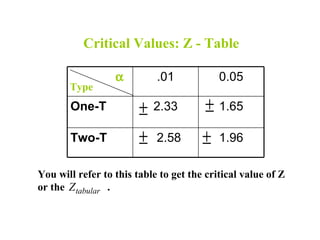
- 24. Critical Values: Z - Table α .01 0.05 Type One-T ± 2.33 ± 1.65 Two-T ± 2.58 ± 1.96 You will refer to this table to get the critical value of Z or the Z tabular .
- 25. CRITERION: 1. One-tailed test (right directional) “Reject H0 if Zc ≥ Zt “ 2. One-tailed test (left directional) “Reject H0 if Zc ≤ Zt 3. Two-tailed test (Zc = +) “Reject H0 if Zc ≥ Zt “ 4. Two-tailed test (Zc = -) ‘Reject H0 if Zc ≤ Zt “
- 26. EXERCISES: 1. Past records showed that the average final examination grade of students in Statistics was 70 with standard deviation of 8.0. A random sample of 100 students was taken and found to have a mean final examination grade of 71.8. Is this an indication that the sample grade is better than the rest of the students? Test at 0.05 level of significance.
- 27. 2. A certain type of battery is known to have a mean life of 60 hours. In random sample of 40 batteries, the mean life was found to be 58 hours with a standard deviation of 4.5 hours. Does it indicate that the mean lifetime of such battery has been reduced? Test at 0.01 level of significance.
- 28. 3. The manager of a rent-a-car business wants to know whether the true average numbers of cars rented a day is 25 with a standard deviation of 6.9 rentals. A random sample of 30 days was taken and found to have an average of 22.8 rentals. Is there a significance between the mean and the sample mean? Test at 0.05 level of significance.
- 29. 4. Advertisements claim that the average nicotine content of a certain kind of cigarette is 0.30 milligram. Suspecting that this figure is too low, a consumer protection service takes a random sample of 50 of these cigarette from different production slots and find that their nicotine content has a mean of 0.33 milligram with a standard deviation of 0.18 milligram. Use the 0.05 level of significance to test the null hypothesis µ = 0.30 against the alternative hypothesis µ < 0.30.
- 30. 5. An experiment was planned to compare the mean time (in days) required to recover from common cold for person given a daily doze of 4 mgs. of vitamin C versus those who were not given a vitamin supplement. Suppose that 35 adults were randomly selected for each treatment category and that the mean recovery times and standard deviations for the 2 groups were as follows: n X δ W/ vit. C 35 5.8 1.2 W/o vit. C 35 6.9 5.8 Suppose your research objective is to show that the use of vit. C increases the mean time required to recover from common cold. Test using α = 0.05.





