SUVIDHA CHAPLOT Business Statistics_ Data-Driven Decision Making.pptx
- 1. Business Statistics: Data-Driven Decision Making •BY- SUVIDHA CHAPLOT
- 2. CONTENTS 01 Introduction to Business Statistics 02 Descriptive Statistics: Summarizing Data 03 Data Presentation & Visualization 04 Sampling Techniques 05 Statistical Inference 06 Correlation and Regression
- 3. 01 Introduction to Business Statistics
- 4. Why Statistics Matter in Business 01 03 02 Key Statistical Concepts Descriptive statistics, sampling, statistical inference, correlation, and regression are fundamental for business operations and decision-making. Informed Decisions Statistics provides tools for data analysis and interpretation, leading to informed decisions; essential for navigating complex business environments. Unit Overview We will explore essential statistical methods, equipping businesses with the ability to apply them effectively.
- 5. The Power of Data Analysis Data-Driven Insights Statistics enables businesses to extract meaningful insights from data; this helps to identify trends, patterns, and relationships. Improving Business Outcomes Analyzing data leads to optimized strategies, improved operations, and enhanced decision-making for better business outcomes. Staying Competitive In today's data-rich environment, statistical analysis is crucial for staying competitive and adapting to market changes.
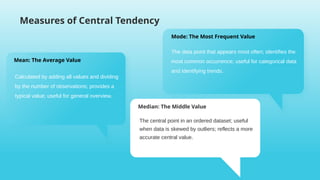
- 7. Measures of Central Tendency Mode: The Most Frequent Value The data point that appears most often; identifies the most common occurrence; useful for categorical data and identifying trends. Mean: The Average Value Calculated by adding all values and dividing by the number of observations; provides a typical value; useful for general overview. Median: The Middle Value The central point in an ordered dataset; useful when data is skewed by outliers; reflects a more accurate central value.
- 8. Measures of Dispersion The difference between the highest and lowest values; offers a simple view of data spread; sensitive to extreme values. Range: Quick Spread Assessment Average of squared differences from the mean; indicates data variability; more complex but comprehensive measure of spread. Variance: Measuring Data Deviation Square root of variance; expresses variability in original data units; easier to interpret in the context of the data. Standard Deviation: Interpretable Dispersion
- 9. Presenting Data Visually Importance of Visualization Visual aids enhance understanding and make complex data more accessible and easier to interpret for decision-makers. Enhancing Data Clarity Well-designed visuals can reveal patterns and insights that might be missed in raw data; improving communication effectiveness. Accessibility and Engagement Visual presentations can engage a wider audience and simplify complex information, leading to better understanding and decision-making.
- 10. Types of Data Quantitative Data: Measurable Metrics Numeric data that can be measured and quantified; includes sales figures, revenue, and employee performance metrics. Qualitative Data: Categorical Insights Non-numeric data categorized into groups; examples include customer preferences, product types, and geographical regions.
- 12. 有赞云发展历程 Pie Charts: Proportions of a Whole Circular charts divided into slices; represents proportions of a whole; best for showing relative percentages of categories. Histograms: Distribution of Quantitative Data Displays data distribution across intervals or bins; helps identify skewness and outliers; essential for understanding data patterns. Bar Charts: Representing Categories Rectangular bars representing categorical data; bar length corresponds to the category's frequency or value for quick comparisons. Frequency Distributions: Tabular Representation Tabular data showing outcomes' frequency; visualized as histograms; provides a clear count of how often each value occurs. Cumulative Frequency Curves Curves showing accumulated frequencies as data increases; determines observations below a value; great for complex analysis. Graphical Methods
- 14. Random Sampling Equal Chance of Selection Every individual has an equal chance; minimizes bias; foundational for unbiased data collection and representation. Reducing Selection Bias Helps avoid systematic errors; ensures sample fairly represents population; improves the reliability of statistical inference. Foundation for Unbiased Analysis Provides a solid base for reliable conclusions; essential for trustworthy results; helps to make valid data-driven decisions.
- 15. Stratified Sampling 01 Dividing into Subgroups (Strata) Population divided into subgroups; random samples taken from each subgroup; ensures representation across all segments. 02 Ensuring Segment Representation Guarantees each segment in the population is represented; provides a more accurate and comprehensive view for analysis. 03 Comprehensive Population View Useful in highly varied populations; helps to uncover insights that might be missed using simpler sampling methods.
- 16. Systematic Sampling Selecting Every Nth Item Selecting every nth item from a list after a random start; simple method; potential bias if there's order in the data. Simplicity and Efficiency Efficient sampling; quick to implement; suited to situations where a list is readily available and manageable. Potential for Bias If data has recurring patterns, sampling can lead to inaccurate results; critical to be aware of potential bias.
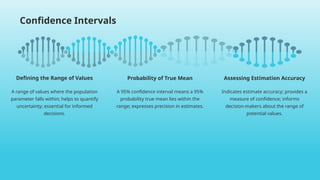
- 18. Confidence Intervals A range of values where the population parameter falls within; helps to quantify uncertainty; essential for informed decisions. Defining the Range of Values A 95% confidence interval means a 95% probability true mean lies within the range; expresses precision in estimates. Probability of True Mean Indicates estimate accuracy; provides a measure of confidence; informs decision-makers about the range of potential values. Assessing Estimation Accuracy
- 19. Hypothesis Testing Involves formulating null (no effect) and alternative (effect tested) hypotheses; guides statistical testing & interpretations. Null & Alternative Hypotheses Used to test assumptions about a population; a structured method to validate claims; provides data-driven validation. Testing Assumptions Used to determine whether evidence supports rejecting or accepting the null hypothesis; fundamental for informed decision-making. Data-Driven Decisions
- 20. Common Hypothesis Tests 01 T-Test: Comparing Two Means Compares means of two groups; determines if significant difference exists; useful for assessing group-based changes. 02 Chi-Square Test: Categorical Data For categorical data; assesses if observed frequencies match expected frequencies; evaluates independence between variables. 03 Z-Test: Comparing Sample to Population Compares sample data to a population; variance is known; useful to see if new data deviates significantly from known data.
- 22. Correlation 03 02 01 1 Measuring Variable relationships Measures strength and direction between two variables; use to understand the nature of associations; essential for insight. 2 Pearson Correlation Coefficient Ranges from -1 to +1; quantifies relationship; 0 indicates no relationship; the most practical form measure for correlation. 3 Identifying Key Relationships Relationship understanding lets businesses pinpoint key factors; improve strategies; use information to enhance outcomes.
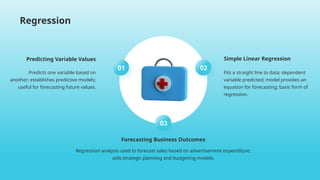
- 23. Predicting Variable Values Predicts one variable based on another; establishes predictive models; useful for forecasting future values. Forecasting Business Outcomes Regression analysis used to forecast sales based on advertisement expenditure; aids strategic planning and budgeting models. Fits a straight line to data; dependent variable predicted; model provides an equation for forecasting; basic form of regression. Simple Linear Regression Regression 02 03 01
- 24. 07 Case Studies and Applications
- 25. Real-World Examples 01 Applying Statistical Methods Showcasing business statistic applications; demonstrates practical relevance; increases understanding of methods' potential. 03 Data-Driven Success Stories Presents successes from data-backed strategies; reinforces data role; promotes adoption of statistics to gain business results. 02 Solving Business Problems Discuss how statistical techniques resolve issues; highlight real-world impact; emphasizes usefulness for decision-making.
- 26. Optimizing Business Strategies Aligning Strategy with Insights Discuss aligning strategies with data-driven insights; showcases transformation; strengthens data's influence on corporate strategy. 01 Case Demonstrations Case studies on how companies leverage statistics; emphasize application; helps to translate data driven strategies for real-world uses. 02 Making Data-Based Decisions Discuss using analytics to make decisions; showcase effectiveness; ensures insights are both accurate and useful. 03
- 27. 08 Conclusion
- 28. Strategic Use of Statistics 03 02 01 1 Recap and Summary Restate business statistics importance; highlight analysis and decisions; underscore role to success. 2 Embracing Data-Driven Culture Encourage data as an integral aspect; foster insights-led culture; promotes statistics for all decision purposes. 3 Future Business Statistics Data growth trends; discuss advanced analytics; underline data importance for future tasks and future operations.
- 29. •Thank you