Collection of Data - Class 11 - Statistics
Download as pptx, pdf116 likes103,590 views
In this PPT I have explained the collection of data topic for class 11 students. Teachers can use it as a teaching aid.
1 of 24
Downloaded 1,358 times


















Ad
Recommended
Organisation of Data 



Organisation of Data Saji Thomas This document discusses the organization and classification of data. It defines classification of data as grouping data according to their characteristics to simplify complex data, facilitate understanding and comparison, and make analysis and interpretation easier. Some key objectives of classification include arranging data by common characteristics. Types of variables are also defined, including discrete variables which increase in jumps and continuous variables which assume a range of values. Statistical series are described as the systematic arrangement of raw data, which can be expressed as individual series without frequencies or as frequency series with frequencies. Frequency distributions are tables that classify observed variable values by numerical magnitude.
Chapter 2 collection of data



Chapter 2 collection of dataRitvik Tolumbia A fantastic PPT on the topic collection of data. The PPT covers the concept of various sources of data and the relevant methods to collect primary and secondary data. It also states the various parameters to be considered while using secondary data.
Price determination and simple applications 



Price determination and simple applications AmiteshYadav7 The document discusses market equilibrium under perfect competition. It defines key concepts like demand, supply, market equilibrium, and how equilibrium price is determined by the intersection of market demand and supply. It describes how demand and supply curves can shift due to various factors, and how such shifts affect equilibrium price and quantity. Special cases involving perfectly elastic/inelastic demand and supply are also covered. The document provides examples of government policies like price ceilings, price floors, minimum wages and their impacts.
UNIT I: Communication Skill



UNIT I: Communication SkillSONALI PAWAR The document discusses the key elements of communication including definition, importance, process, forms and barriers. It defines communication as sending or receiving ideas from one person to another so they understand the same way. The main elements of the communication process are the sender, message, channel, receiver and feedback. Effective communication is achieved when the receiver's understanding matches the sender's intended meaning. Barriers like environmental factors, language differences and personal issues can negatively impact communication.
INTRODUCTION - MICRO ECONOMICS



INTRODUCTION - MICRO ECONOMICSCS. Sohil Gajjar This document provides an introduction to economics. It defines key economic concepts like scarcity, resources, production, consumption, and capital formation. It explains that economics studies how societies allocate their limited resources. Microeconomics focuses on individual units while macroeconomics looks at the overall economy. The central problems that economies face are what and how to produce goods and services, and how to distribute them. Production possibility frontiers are used to show production tradeoffs and opportunity costs between two goods with limited resources. Marginal rates of transformation represent the tradeoff between goods on the production possibilities curve.
Ibn Sina Avicenna



Ibn Sina AvicennaAwais Chouhan Ibn Sina (Avicenna) was a Persian polymath born in 980 AD in what is now Uzbekistan. He made contributions to many fields, including philosophy, medicine, and earth sciences. In medicine, his most influential work was The Canon of Medicine, a standard medical text in Europe for centuries. He introduced many medical practices like clinical trials and evidence-based medicine. In philosophy, he wrote extensively on logic, metaphysics, and ethics. Ibn Sina sought to reconcile philosophy and theology through reason and prove God's existence scientifically. He was a prolific writer who authored around 450 books in various fields.
Government budget 



Government budget Neeraj Garwal A Brief Overview of Budget :
Introduction, Meaning of Government Budget, Objective of Government Budget, Components of Budget, Revenue Receipts, Capital Receipts, Budget Expenditure, Measures of Government Deficit
(with some latest data)
Indian economy 1950 to 1990



Indian economy 1950 to 1990muktesh pillai The document provides an overview of the Indian economy between 1950-1990. It discusses the adoption of a mixed economy model with a focus on economic planning and development in the areas of agriculture, industry, and trade. For agriculture, it describes the land reforms and Green Revolution that increased food production. Industrialization was driven by public sector expansion and import substitution policies. Five-Year Plans aimed to accelerate growth, reduce inequality, and achieve self-reliance through state-led development.
Introduction To Statistics - Class 11 - Commerce



Introduction To Statistics - Class 11 - CommerceAnjaliKaur3 This PPT explains the chapter 1 of statistics for class 11. It will be helpful for students preparing for exams and for the teachers to use it as a teaching aid.
Theory Of Demand 1



Theory Of Demand 1Deep Janak The document discusses the economic concept of demand. It defines demand as the quantity of a product that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various price levels. Demand is determined by factors such as price, income, tastes, and population. The law of demand states that, all else equal, demand decreases as price increases. However, there are some exceptions such as Giffen goods where demand increases with price. The document also discusses individual demand, market demand, demand curves, determinants of demand, and extensions/contractions in demand.
Chapter-1 Concept of Economics and Significance of Statistics in Economics



Chapter-1 Concept of Economics and Significance of Statistics in EconomicsRitvik Tolumbia A fantastic PPT on the concept of economics and significance of statistics in economics. The PPT includes meaning of statistics in singular sense and plural sense, features of statistics, scope of statistics, importance of statistics, limitations of statistics and functions of statistics. Enjoy the PPT. Happy Learning !!
Money and Banking Class 12



Money and Banking Class 12HarshidKailash 1) Money was introduced to solve problems with barter systems like the "double coincidence of wants". Money acts as a medium of exchange, store of value, and standard for deferred payments.
2) Money supply refers to the total quantity of money in circulation and includes components like currency, demand deposits, and other deposits. It is classified into narrow (M1) and broad money (M2, M3, M4).
3) Commercial banks create money through the process of credit creation, lending out a multiple of the initial deposits based on required reserve ratios. They accept deposits and extend loans to earn profits.
Consumer Equilibrium Class XI CBSE



Consumer Equilibrium Class XI CBSEKishan Sharma The document discusses consumer equilibrium, which occurs when a consumer spends their income on commodities in a way that maximizes their satisfaction given prices. For a single commodity, equilibrium exists when marginal utility equals price. For multiple commodities, the condition is that the marginal utility per rupee spent is equal across all goods. An example shows a consumer in equilibrium purchasing amounts of goods X and Y that equalize marginal utility per rupee spent on each.
Economics project on Production Possibilty Curve



Economics project on Production Possibilty CurveNiraj Kumar A full economics project for the first time ever. Economics project on PPC. PPC a topic from book. This project includes everything realted to PPC. This project had covered each and every corner of this topic.
Presentation of data



Presentation of dataDeepak Kushwaha The document discusses different methods of presenting data, including tabular, textual, and diagrammatic presentation. It provides details on tabular presentation, including the components and features of good tables. It also describes different types of diagrams for diagrammatic presentation, including bar diagrams, pie charts, histograms, frequency polygons, and ogives. Histograms and frequency polygons are used to show the distribution of quantitative data, while ogives show cumulative frequencies. The document emphasizes that the goal of data presentation is to clearly and attractively display data for easy understanding and analysis.
Forms of business organisations 



Forms of business organisations jayant jain This document discusses the different forms of business organizations. It describes sole proprietorships, partnerships, joint Hindu family businesses, private and public companies, and cooperative societies. For each type of organization, it outlines key characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. The main types covered are sole proprietorships, which are owned and controlled by one individual; partnerships, which involve two or more individuals working together through a contractual agreement; and joint stock companies, which have ownership shares that are separated from management and can be publicly traded.
Business Environment project class 12 cbse



Business Environment project class 12 cbseJacky Chain PROJECT WORK IN THE SUBJECT OF BUSINESS STUDIES ON THE TOPIC "BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT" AS THE PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF AISSCE, MARCH 2018 CONDUCTED BY CBSE.
This project contains the information regarding the accountancy project which is to be made by the students of class 12th boards... This project is made by jigar vaishnav for the session 2017-18 with the latest guidelines as per CBSE... Hope this will help the upcoming students who want a help regarding the business studies project....
VIEW THIS PROJECT AT YOUTUBE:- https://www.youtube.com/edit?o=U&video_id=V7b6VQQrjsg
Emerging modes of business 



Emerging modes of business Gautam Rath This document discusses emerging modes of e-business. It defines various types of e-business including B2B (business to business), B2C (business to consumer), C2C (consumer to consumer), and intra-business commerce. B2B refers to businesses conducting business with other businesses. B2C involves businesses selling products or services to consumers. C2C has no middle businesses and allows consumers to become sellers. Intra-business commerce occurs within a single firm using an intranet. The document also outlines the benefits and limitations of e-business, such as increased accessibility but also security and technical challenges. It describes online transactions and payment options including cash-on-delivery, checks, credit/debit cards,
Money and banking



Money and bankingmadan kumar The document provides an overview of the evolution of money and the monetary system in India. It discusses the development from barter systems to various forms of money like commodity money, metallic money, paper money, and digital money. It describes the functions of money as a medium of exchange, store of value, and standard of deferred payments. It also discusses key concepts like the money supply and its components, sources of money supply, the role of the central bank (Reserve Bank of India) and commercial banks in money creation through credit. It provides definitions of legal tender money and different measures of money supply used in India.
human Capital formation



human Capital formationmadan kumar The document discusses human capital formation in India. It defines human capital formation as acquiring skills, education, and experience to increase economic and political development. Sources of human capital formation include expenditures on education, health, on-the-job training, migration, and information. While human capital growth in India has been fast, economic growth has not increased at the same rate due to challenges like high population growth, poverty, and low education quality. Further investments in education and health are needed to fully realize gains from India's demographic dividend.
Economic reforms 1991 



Economic reforms 1991 Pranav Krishna Economic Reforms 1991: New Economic Policy(NEP), Main Economic Reforms, Liberalization, Privatization, Globalization, Merits & Demerits of Economic reforms
Money and credit



Money and creditPankaj Saikia It is an attempt to make the learning of the chapter contents easier to the students by giving some extended information.
Forms of markets 



Forms of markets Piyush Kapoor Describes about the different types of markets such as monopoly, oligopoly, perfect and imperfect market.
Nationalism in europe



Nationalism in europeassddd The document discusses the rise of nationalism and nation-states in Europe between the late 18th to mid-19th century. Key events and ideas included the French Revolution promoting national symbols and centralized rule; the spread of Jacobin clubs and French invasion promoting nationalist ideals across Europe; and the Congress of Vienna establishing conservative monarchies but failing to suppress liberal nationalism and demands for national self-determination, fueling revolutions in the 1830s and 1840s that established more nation-states like Belgium and Greece. Figures like Mazzini promoted nationalist ideas that further revolutions against Austrian, Spanish and Ottoman rule to eventually unify Italy and the Balkan states.
Chapter 3 Private, Public and Global Entreprises



Chapter 3 Private, Public and Global EntreprisesRitvik Tolumbia A fantastic PPT on forms of public sector entreprises. The PPT contains a detailed description about the various forms of doing public sector business. It discusses the meaning, features, merits and demerits of each form.
National income and related aggregates



National income and related aggregatesAmiteshYadav7 This document defines key concepts in macroeconomics including different types of goods, the circular flow of income, methods to calculate national income, and concepts related to national income aggregates. It provides formulas to calculate measures like GDP, GNP, NDP, NNP, and discusses how to calculate national disposable income, private income, personal income, and personal disposable income.
Business studies for 11th class CBSE



Business studies for 11th class CBSEMax Monu The document discusses the nature of services and the differences between services and goods. It states that services are intangible, inconsistent, have simultaneous production and consumption (inseparability), cannot be inventoried, and involve customer participation. It then discusses different types of services (business, social, personal) and provides examples of key business services like banking and insurance. For banking it outlines different types (commercial, cooperative, specialized, central) and functions. For insurance it discusses principles, functions, and types (life insurance).
International business



International businessMohit Somani This document provides an overview of international trade, including its meaning, types, features, reasons, scope, importance, modes of entry, export and import procedures, key documents, and the World Trade Organization (WTO). It defines international trade as trade between two or more countries that involves foreign currency payments and legal procedures. The key benefits of international trade are earning foreign exchange, efficient use of resources, and improving growth and living standards for nations and firms. The WTO aims to liberalize trade by limiting trade policies, settling disputes through neutral procedures, and ensuring a smooth flow of trade globally.
Collection of data class 12th cbse 



Collection of data class 12th cbse Sanjay Thakran collection of data class 12th important notes with sanjay sir .for more videos subscribe my you tube channel sk knowledge point
Ad
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Introduction To Statistics - Class 11 - Commerce



Introduction To Statistics - Class 11 - CommerceAnjaliKaur3 This PPT explains the chapter 1 of statistics for class 11. It will be helpful for students preparing for exams and for the teachers to use it as a teaching aid.
Theory Of Demand 1



Theory Of Demand 1Deep Janak The document discusses the economic concept of demand. It defines demand as the quantity of a product that consumers are willing and able to purchase at various price levels. Demand is determined by factors such as price, income, tastes, and population. The law of demand states that, all else equal, demand decreases as price increases. However, there are some exceptions such as Giffen goods where demand increases with price. The document also discusses individual demand, market demand, demand curves, determinants of demand, and extensions/contractions in demand.
Chapter-1 Concept of Economics and Significance of Statistics in Economics



Chapter-1 Concept of Economics and Significance of Statistics in EconomicsRitvik Tolumbia A fantastic PPT on the concept of economics and significance of statistics in economics. The PPT includes meaning of statistics in singular sense and plural sense, features of statistics, scope of statistics, importance of statistics, limitations of statistics and functions of statistics. Enjoy the PPT. Happy Learning !!
Money and Banking Class 12



Money and Banking Class 12HarshidKailash 1) Money was introduced to solve problems with barter systems like the "double coincidence of wants". Money acts as a medium of exchange, store of value, and standard for deferred payments.
2) Money supply refers to the total quantity of money in circulation and includes components like currency, demand deposits, and other deposits. It is classified into narrow (M1) and broad money (M2, M3, M4).
3) Commercial banks create money through the process of credit creation, lending out a multiple of the initial deposits based on required reserve ratios. They accept deposits and extend loans to earn profits.
Consumer Equilibrium Class XI CBSE



Consumer Equilibrium Class XI CBSEKishan Sharma The document discusses consumer equilibrium, which occurs when a consumer spends their income on commodities in a way that maximizes their satisfaction given prices. For a single commodity, equilibrium exists when marginal utility equals price. For multiple commodities, the condition is that the marginal utility per rupee spent is equal across all goods. An example shows a consumer in equilibrium purchasing amounts of goods X and Y that equalize marginal utility per rupee spent on each.
Economics project on Production Possibilty Curve



Economics project on Production Possibilty CurveNiraj Kumar A full economics project for the first time ever. Economics project on PPC. PPC a topic from book. This project includes everything realted to PPC. This project had covered each and every corner of this topic.
Presentation of data



Presentation of dataDeepak Kushwaha The document discusses different methods of presenting data, including tabular, textual, and diagrammatic presentation. It provides details on tabular presentation, including the components and features of good tables. It also describes different types of diagrams for diagrammatic presentation, including bar diagrams, pie charts, histograms, frequency polygons, and ogives. Histograms and frequency polygons are used to show the distribution of quantitative data, while ogives show cumulative frequencies. The document emphasizes that the goal of data presentation is to clearly and attractively display data for easy understanding and analysis.
Forms of business organisations 



Forms of business organisations jayant jain This document discusses the different forms of business organizations. It describes sole proprietorships, partnerships, joint Hindu family businesses, private and public companies, and cooperative societies. For each type of organization, it outlines key characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. The main types covered are sole proprietorships, which are owned and controlled by one individual; partnerships, which involve two or more individuals working together through a contractual agreement; and joint stock companies, which have ownership shares that are separated from management and can be publicly traded.
Business Environment project class 12 cbse



Business Environment project class 12 cbseJacky Chain PROJECT WORK IN THE SUBJECT OF BUSINESS STUDIES ON THE TOPIC "BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT" AS THE PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF AISSCE, MARCH 2018 CONDUCTED BY CBSE.
This project contains the information regarding the accountancy project which is to be made by the students of class 12th boards... This project is made by jigar vaishnav for the session 2017-18 with the latest guidelines as per CBSE... Hope this will help the upcoming students who want a help regarding the business studies project....
VIEW THIS PROJECT AT YOUTUBE:- https://www.youtube.com/edit?o=U&video_id=V7b6VQQrjsg
Emerging modes of business 



Emerging modes of business Gautam Rath This document discusses emerging modes of e-business. It defines various types of e-business including B2B (business to business), B2C (business to consumer), C2C (consumer to consumer), and intra-business commerce. B2B refers to businesses conducting business with other businesses. B2C involves businesses selling products or services to consumers. C2C has no middle businesses and allows consumers to become sellers. Intra-business commerce occurs within a single firm using an intranet. The document also outlines the benefits and limitations of e-business, such as increased accessibility but also security and technical challenges. It describes online transactions and payment options including cash-on-delivery, checks, credit/debit cards,
Money and banking



Money and bankingmadan kumar The document provides an overview of the evolution of money and the monetary system in India. It discusses the development from barter systems to various forms of money like commodity money, metallic money, paper money, and digital money. It describes the functions of money as a medium of exchange, store of value, and standard of deferred payments. It also discusses key concepts like the money supply and its components, sources of money supply, the role of the central bank (Reserve Bank of India) and commercial banks in money creation through credit. It provides definitions of legal tender money and different measures of money supply used in India.
human Capital formation



human Capital formationmadan kumar The document discusses human capital formation in India. It defines human capital formation as acquiring skills, education, and experience to increase economic and political development. Sources of human capital formation include expenditures on education, health, on-the-job training, migration, and information. While human capital growth in India has been fast, economic growth has not increased at the same rate due to challenges like high population growth, poverty, and low education quality. Further investments in education and health are needed to fully realize gains from India's demographic dividend.
Economic reforms 1991 



Economic reforms 1991 Pranav Krishna Economic Reforms 1991: New Economic Policy(NEP), Main Economic Reforms, Liberalization, Privatization, Globalization, Merits & Demerits of Economic reforms
Money and credit



Money and creditPankaj Saikia It is an attempt to make the learning of the chapter contents easier to the students by giving some extended information.
Forms of markets 



Forms of markets Piyush Kapoor Describes about the different types of markets such as monopoly, oligopoly, perfect and imperfect market.
Nationalism in europe



Nationalism in europeassddd The document discusses the rise of nationalism and nation-states in Europe between the late 18th to mid-19th century. Key events and ideas included the French Revolution promoting national symbols and centralized rule; the spread of Jacobin clubs and French invasion promoting nationalist ideals across Europe; and the Congress of Vienna establishing conservative monarchies but failing to suppress liberal nationalism and demands for national self-determination, fueling revolutions in the 1830s and 1840s that established more nation-states like Belgium and Greece. Figures like Mazzini promoted nationalist ideas that further revolutions against Austrian, Spanish and Ottoman rule to eventually unify Italy and the Balkan states.
Chapter 3 Private, Public and Global Entreprises



Chapter 3 Private, Public and Global EntreprisesRitvik Tolumbia A fantastic PPT on forms of public sector entreprises. The PPT contains a detailed description about the various forms of doing public sector business. It discusses the meaning, features, merits and demerits of each form.
National income and related aggregates



National income and related aggregatesAmiteshYadav7 This document defines key concepts in macroeconomics including different types of goods, the circular flow of income, methods to calculate national income, and concepts related to national income aggregates. It provides formulas to calculate measures like GDP, GNP, NDP, NNP, and discusses how to calculate national disposable income, private income, personal income, and personal disposable income.
Business studies for 11th class CBSE



Business studies for 11th class CBSEMax Monu The document discusses the nature of services and the differences between services and goods. It states that services are intangible, inconsistent, have simultaneous production and consumption (inseparability), cannot be inventoried, and involve customer participation. It then discusses different types of services (business, social, personal) and provides examples of key business services like banking and insurance. For banking it outlines different types (commercial, cooperative, specialized, central) and functions. For insurance it discusses principles, functions, and types (life insurance).
International business



International businessMohit Somani This document provides an overview of international trade, including its meaning, types, features, reasons, scope, importance, modes of entry, export and import procedures, key documents, and the World Trade Organization (WTO). It defines international trade as trade between two or more countries that involves foreign currency payments and legal procedures. The key benefits of international trade are earning foreign exchange, efficient use of resources, and improving growth and living standards for nations and firms. The WTO aims to liberalize trade by limiting trade policies, settling disputes through neutral procedures, and ensuring a smooth flow of trade globally.
Similar to Collection of Data - Class 11 - Statistics (20)
Collection of data class 12th cbse 



Collection of data class 12th cbse Sanjay Thakran collection of data class 12th important notes with sanjay sir .for more videos subscribe my you tube channel sk knowledge point
Economice (collection of data)



Economice (collection of data)ArjunKhurana10 This document discusses various methods for collecting primary data for statistical analysis. It describes primary data as data collected directly from respondents, and secondary data as data originally collected by others. Methods for collecting primary data include direct personal interviews, indirect oral investigations, mailed questionnaires, and telephonic interviews. It also discusses census and sampling methods, random and non-random sampling, and types of errors in statistical analysis like sampling errors and non-sampling errors. The document was created by Arjun Kumar, a class 11 commerce student, for his economics subject on the topic of data collection.
survey method.ppt community medicine psm



survey method.ppt community medicine psmDr Ramniwas The document discusses survey methods and how to conduct surveys, including determining objectives, selecting a methodology, constructing questionnaires or schedules, sampling techniques, data collection and analysis. Surveys are used to collect information on topics such as health conditions, program planning and evaluation, and making comparisons. The document outlines the various steps involved in conducting a survey from start to finish.
biostatistics and research methodology, Sampling



biostatistics and research methodology, Samplingsabinameraj biostatistics and research methodology, Sampling
7027203.ppt



7027203.pptPraveen Kumar The document discusses key aspects of data collection and analysis for monitoring and evaluation projects. It covers topics such as qualities of good data, data collection methods including questionnaires, sampling methods, and data analysis techniques. Specifically, it emphasizes that collecting adequate, timely and relevant data is essential for evaluation and that questionnaires must be designed carefully to obtain accurate information and address all relevant variables. It also highlights the importance of representative sampling to make reliable estimates about target populations.
Gathering data. It is talks about how to gatherdata



Gathering data. It is talks about how to gatherdataVhelZamora Gathering data in research is very important.
methods in social science and data sources..pptx



methods in social science and data sources..pptxpujakrishna4334 it encompasses quantitative methods in social sciences and various sources of data
Survey Surveillance Screening 



Survey Surveillance Screening MalihaQuader1 Discussed Topics
Survey
Surveillance
Screening
Sampling
Method of Data Collection
Types of Questionnaire
Error in Data
Data Mining
Data Analysis
Census and sample investigation



Census and sample investigationRekhaChoudhary24 This document discusses methods of collecting statistical data. It describes census and sample investigation methods. The census method collects data from every unit of the population, while the sample method collects data from only a few representative units. The census method is more reliable but costly, while the sample method is less expensive but less accurate. Key differences between the two methods are also outlined.
gatheringofdata2-150513082553-lva1-app6892.pdf



gatheringofdata2-150513082553-lva1-app6892.pdfMaIvyBrillante There are many methods for gathering data, including interviews, questionnaires, observation, tests, experiments, registration, and mechanical devices. The appropriate method depends on the study design, type of data, time, and resources. Some common questionnaire types are guided response, recall, recognition, dichotomous, multiple choice, multiple response, free response, and rating scales. Sample sizes are determined using formulas like Slovin's formula. Common sampling techniques include random, stratified random, cluster, purposive, quota, and convenience sampling. The data collection process involves defining objectives and variables, the collection and measurement schemes, collecting the sample, and reviewing the process. For descriptive research using questionnaires, the recommended procedure is to obtain permission,
DATA GATHERING



DATA GATHERINGRaul Partoza DATA GATHERING IS PART OF THE PROCESS IN DOING A RESEARCH. THIS PRESENTATION IS PART OF THE REQUIREMENTS IN COMPLETING THE COURSE EDUCATIONAL RESEARCH UNDER THE MASTER OF ARTS IN HOME ECONOMICS, A GRADUATE STUDY PROGRAM OF ZAMBOANGA STATE COLLEGE OF MARINE SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY , ZAMBOANGA CITY.
Conducting a survey



Conducting a surveyGMOORE2013 This document provides guidance on conducting surveys through questionnaires. It discusses the different types of surveys, including self-completed questionnaires, telephone surveys, and face-to-face interviews. It outlines the nine key steps to conducting a survey: deciding what information is needed, who to survey, the survey method, sample size, writing questions, testing questions, conducting the survey, analyzing results, and reporting findings. It also provides tips for writing effective questions, including using both open-ended and closed-ended questions, and sequencing questions logically and presenting questionnaires clearly.
Data collection f488555b7cca4b22cd8bcc61db2c2238



Data collection f488555b7cca4b22cd8bcc61db2c2238Kæsy Chaudhari This document discusses data sampling and collection methods. It begins by defining quantitative and qualitative data, and primary and secondary data. The main methods of primary data collection are observation, interviewing, and questionnaires. Secondary data refers to existing data collected by others. The document then defines data sampling as selecting part of a data set to make inferences about the whole. Sampling is needed to save time and money. Random sampling gives the best results while non-random sampling includes quota, accidental, judgemental, expert and snowball sampling. Mixed sampling uses elements of both random and non-random designs.
SURVEY_RESEARCH.ppt



SURVEY_RESEARCH.pptRavi Kumar Survey research involves collecting information from a sample of individuals to determine opinions, preferences, or knowledge about a population. The key steps in survey research include defining objectives and the target population, determining what data to collect, selecting an appropriate sample and method of data collection, collecting the data, analyzing results, and reporting findings. Some common problems that can threaten the validity of survey results include nonresponse bias if those who do not respond differ significantly from respondents. Techniques like multiple contacts and personalized correspondence can help increase response rates.
ppt mgt.pptx



ppt mgt.pptxHanaKassahun1 This document discusses different methods for collecting data, both primary and secondary. It describes primary data collection methods like observation, surveys, interviews, questionnaires, and schedules. It provides details on how to conduct each method effectively and their advantages and disadvantages. Some key secondary data sources are also outlined such as internal organization records, external publications, reports and internet sources. When using secondary data, factors like reliability, suitability and adequacy must be considered. The selection of the appropriate data collection method depends on the nature, scope, budget and time constraints of the research.
Economics Class 11 Model Paper Study Well



Economics Class 11 Model Paper Study WellAvinAsisMiranda1 This document provides an introduction to statistics and data collection methods. It discusses key concepts such as:
1. The difference between economic and non-economic activities, and definitions of common economic roles like consumers, producers, service holders and service providers.
2. The stages of collecting statistical data, including primary and secondary sources, methods of collecting primary data, and the differences between primary and secondary data.
3. Methods of organizing raw data through classification, frequency distributions, and other statistical techniques. Common approaches to presenting organized data are also outlined, including tables, diagrams and graphs.
4. Sampling methods like census surveys and sample surveys are introduced, along with the differences between them. Key organizations involved in
Ad
More from AnjaliKaur3 (19)
Poverty : The greatest challenge faced by the Indian Economy, Class XII (C.B....



Poverty : The greatest challenge faced by the Indian Economy, Class XII (C.B....AnjaliKaur3
Meaning of poverty.
Who is Poor?
Measures of Poverty; Absolute and relative poverty.
Poverty Line.
Categorizing poor.
Causes of poverty.
Measures to remove poverty.
Growth-Oriented Approach.
Specific alleviation Program.
Meeting the minimum needs program.
Shortcomings of PAPs.
For more content check www.LearnWithAnjali.com
Economic reforms since 1991: Class XII - Part-2



Economic reforms since 1991: Class XII - Part-2AnjaliKaur3 The document provides an overview of key topics related to the Indian economy including Navratnas, the World Trade Organization, demonetization, and the Goods and Services Tax. It defines these terms and outlines their objectives and advantages and disadvantages. Navratnas refers to nine public sector undertakings given greater autonomy by the government. Demonetization in 2016 aimed to reduce corruption and black money by removing high value currency notes from circulation. The Goods and Services Tax implemented in 2017 unified India's tax system.
Political Science, Power Sharing, Class - 10



Political Science, Power Sharing, Class - 10AnjaliKaur3 In this PPT, I am discussing following topics:
Belgium and Sri Lanka
Majoritarianism in Sri Lanka
Accommodation in Sri Lanka
Why power sharing is Desirable
Forms of power sharing
Basic terms like civil war, prudential, moral
Indian Economy between 1950 to 1990, Class XII



Indian Economy between 1950 to 1990, Class XIIAnjaliKaur3 In this PPT, I have explained the following topics in detail. It will be helpful for teachers as well as students.
Content covered:
Economic System
Types of Economic System
Economic planning
Goal of five year plans
Problems faced by Indian Agriculture
Solutions to solve problems faced by Indian Agriculture
Problems under Green Revolution
Importance of Subsidies
Public and Private sectors in Indian Industrial Development
Industrial Policy Resolution, 1956
Industrial License
Industrial Concessions
Small Scale Industries
Trade policies: Import substitution
Also meaning of Green Revolution
ECONOMICS: INDIAN ECONOMY CLASS XII



ECONOMICS: INDIAN ECONOMY CLASS XIIAnjaliKaur3 This document contains questions on the topic Indian Economy between 1950-1990. Students must solve this assignment on their own. Plan, HYV seeds, marketable surplus etc.
INDIAN ECONOMY CLASS XII



INDIAN ECONOMY CLASS XIIAnjaliKaur3 Indian Economy on the eve of Independence
Before British Period
During British Period
Sectors of Indian Economy
AGRICULTURE
INDUSTRIAL
FOREIGN TRADE
OCCUPATIONAL STRUCTURE
DEMOGRAPHY
QUESTIONS
ASSIGNMENT
CLASS X ECONOMICS CHAPTER 1 DEVELOPMENT CBSE



CLASS X ECONOMICS CHAPTER 1 DEVELOPMENT CBSEAnjaliKaur3 Synopsis
Development and its features.
Income and other goals
National Development
Comparison among different countries or states
Other criteria for comparing countries
Public Facilities
Educational achievement of Rural Population of U.P.
Body Mass Index (BMI)
Human Development Index (HDI)
Sustainable Development
INDIAN ECONOMY



INDIAN ECONOMYAnjaliKaur3 Sate of Indian Economy on the Eve of Independence, Synopsis:
Before the British Rule
During the British Rule
Components of Indian Economy
Agricultural Sector in India During Colonial Rule
Industrial Sector in India During Colonial Rule
Foreign Trade in India During Colonial Rule
Demography in India During Colonial Rule
Occupational Structure in India During Colonial Rule
Infrastructure in India During Colonial Rule
Positive Impacts of British Rule in India
Class XI AND XII, Economics, NCERT
Nationalism in Europe-Part 1-Class 10th



Nationalism in Europe-Part 1-Class 10thAnjaliKaur3 Absolutist Form of Government, Utopian Society, Nation State, A print by Frederic Sourrieu, Plebiscite and German Almanac Design.
Theory of Consumer Behaviour (part - 2) Class 12 



Theory of Consumer Behaviour (part - 2) Class 12 AnjaliKaur3 THIS PPT EXPLAINS DEMAND CONCEPT AND ELASTICITY CONCEPT. IT WILL BE USEFUL FOR BOARD EXAMINATION AND FOR TEACHERS, TEACHING AID.
Theory of Consumer Behaviour Class 12 Economics



Theory of Consumer Behaviour Class 12 EconomicsAnjaliKaur3 This PPT explains the consumer behaviour topic of class 12 Economics. It will be helpful for commerce students and for Teachers looking for a teaching aid.
Business Environment - MBA - MCOM - Class 12



Business Environment - MBA - MCOM - Class 12AnjaliKaur3 In this PPT I have explained Business Environment topic, it will be useful for MBA, MCOM AND CLASS 12 students. Also teachers can use it as a teaching aid.
How, When And Where - Class 8 - History - (Social Studies)



How, When And Where - Class 8 - History - (Social Studies)AnjaliKaur3 This PPT explains history chapter 1 from NCERT book in a very different manner. It will be useful for students and for teachers. It contains more information apart from books and hopefully students will find it interesting as they can relate this topic by going through different examples.
Introduction To Microeconomics - Class 12



Introduction To Microeconomics - Class 12AnjaliKaur3 This PPT describes the introduction of microeconomics as a branch of economics. It will be really helpful for class 12 students preparing for their board exam and also for teachers to use it as a teaching aid.
Environment - Class 7 - Geography (Social Studies)



Environment - Class 7 - Geography (Social Studies)AnjaliKaur3 This PPT is helpful for class 7 students and for teachers looking for teaching aids. This topic is about Environment and I have explained the same in a very simple and interesting manner.
Sustainable economic development_Class 11_Economics_Demo lesson_PPT



Sustainable economic development_Class 11_Economics_Demo lesson_PPTAnjaliKaur3 This is class 11 economics topi on sustainable economic development. This topic was also my demo lesson given to me during my Learning Path School interview time. It will be helpful for students and for teachers preparing for different schools demo or interviews.It is helpful for quick revision as well.
Polynomials (Algebra) - Class 10 



Polynomials (Algebra) - Class 10 AnjaliKaur3 This PPT explains the concept of polynomial in detail. It describes the meaning of polynomials with the help of different examples.Furthermore different types of polynomials on the basis of degree and number of terms.This will be helpful for students and for teachers.
Sustainable Economic Development - Class 11



Sustainable Economic Development - Class 11AnjaliKaur3 Sustainable Economic Development is very important these days especially for countries like India. This PPT will be useful for the students preparing for their presentations, examinations and for the teachers to use it as a teaching aid.
Inflation - Class 11



Inflation - Class 11AnjaliKaur3 This document discusses inflation in India. It defines inflation as a sustained increase in prices or reduction in the value of money. Some key points:
- Common indicators of inflation in India include the Wholesale Price Index, Consumer Price Index, and GDP deflator.
- Causes of inflation include demand-pull inflation, cost-push inflation, and factors like increased money supply, population growth, and indirect taxes.
- Effects of high inflation include slowed economic growth, impacts on fixed-income groups, and balance of payments issues.
- Government policies to control inflation involve price controls, monetary policy to manage money supply and interest rates, and fiscal policy like public spending, debt, taxes, and
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 5-3-2025.pptx



YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 5-3-2025.pptxYale School of Public Health - The Virtual Medical Operations Center (VMOC) A measles outbreak originating in West Texas has been linked to confirmed cases in New Mexico, with additional cases reported in Oklahoma and Kansas. The current case count is 817 from Texas, New Mexico, Oklahoma, and Kansas. 97 individuals have required hospitalization, and 3 deaths, 2 children in Texas and one adult in New Mexico. These fatalities mark the first measles-related deaths in the United States since 2015 and the first pediatric measles death since 2003.
The YSPH Virtual Medical Operations Center Briefs (VMOC) were created as a service-learning project by faculty and graduate students at the Yale School of Public Health in response to the 2010 Haiti Earthquake. Each year, the VMOC Briefs are produced by students enrolled in Environmental Health Science Course 581 - Public Health Emergencies: Disaster Planning and Response. These briefs compile diverse information sources – including status reports, maps, news articles, and web content– into a single, easily digestible document that can be widely shared and used interactively. Key features of this report include:
- Comprehensive Overview: Provides situation updates, maps, relevant news, and web resources.
- Accessibility: Designed for easy reading, wide distribution, and interactive use.
- Collaboration: The “unlocked" format enables other responders to share, copy, and adapt seamlessly. The students learn by doing, quickly discovering how and where to find critical information and presenting it in an easily understood manner.
CURRENT CASE COUNT: 817 (As of 05/3/2025)
• Texas: 688 (+20)(62% of these cases are in Gaines County).
• New Mexico: 67 (+1 )(92.4% of the cases are from Eddy County)
• Oklahoma: 16 (+1)
• Kansas: 46 (32% of the cases are from Gray County)
HOSPITALIZATIONS: 97 (+2)
• Texas: 89 (+2) - This is 13.02% of all TX cases.
• New Mexico: 7 - This is 10.6% of all NM cases.
• Kansas: 1 - This is 2.7% of all KS cases.
DEATHS: 3
• Texas: 2 – This is 0.31% of all cases
• New Mexico: 1 – This is 1.54% of all cases
US NATIONAL CASE COUNT: 967 (Confirmed and suspected):
INTERNATIONAL SPREAD (As of 4/2/2025)
• Mexico – 865 (+58)
‒Chihuahua, Mexico: 844 (+58) cases, 3 hospitalizations, 1 fatality
• Canada: 1531 (+270) (This reflects Ontario's Outbreak, which began 11/24)
‒Ontario, Canada – 1243 (+223) cases, 84 hospitalizations.
• Europe: 6,814
How to Clean Your Contacts Using the Deduplication Menu in Odoo 18



How to Clean Your Contacts Using the Deduplication Menu in Odoo 18Celine George In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to clean your contacts using the Deduplication Menu in Odoo 18. Maintaining a clean and organized contact database is essential for effective business operations.
Rococo versus Neoclassicism. The artistic styles of the 18th century



Rococo versus Neoclassicism. The artistic styles of the 18th centuryGema Rococo versus Neoclassicism. The artistic styles of the 18th century
Lecture 4 INSECT CUTICLE and moulting.pptx



Lecture 4 INSECT CUTICLE and moulting.pptxArshad Shaikh The insect cuticle is a tough, external exoskeleton composed of chitin and proteins, providing protection and support. However, as insects grow, they need to shed this cuticle periodically through a process called moulting. During moulting, a new cuticle is prepared underneath, and the old one is shed, allowing the insect to grow, repair damaged cuticle, and change form. This process is crucial for insect development and growth, enabling them to transition from one stage to another, such as from larva to pupa or adult.
Computer crime and Legal issues Computer crime and Legal issues



Computer crime and Legal issues Computer crime and Legal issuesAbhijit Bodhe • Computer crime and Legal issues: Intellectual property.
• privacy issues.
• Criminal Justice system for forensic.
• audit/investigative.
• situations and digital crime procedure/standards for extraction,
preservation, and deposition of legal evidence in a court of law.
How to Add Customer Note in Odoo 18 POS - Odoo Slides



How to Add Customer Note in Odoo 18 POS - Odoo SlidesCeline George In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to add customer note in Odoo 18 POS module. Customer Notes in Odoo 18 POS allow you to add specific instructions or information related to individual order lines or the entire order.
PHYSIOLOGY MCQS By DR. NASIR MUSTAFA (PHYSIOLOGY)



PHYSIOLOGY MCQS By DR. NASIR MUSTAFA (PHYSIOLOGY)Dr. Nasir Mustafa PHYSIOLOGY MCQS By DR. NASIR MUSTAFA (PHYSIOLOGY)
Ancient Stone Sculptures of India: As a Source of Indian History



Ancient Stone Sculptures of India: As a Source of Indian HistoryVirag Sontakke This Presentation is prepared for Graduate Students. A presentation that provides basic information about the topic. Students should seek further information from the recommended books and articles. This presentation is only for students and purely for academic purposes. I took/copied the pictures/maps included in the presentation are from the internet. The presenter is thankful to them and herewith courtesy is given to all. This presentation is only for academic purposes.
spinal cord disorders (Myelopathies and radiculoapthies)



spinal cord disorders (Myelopathies and radiculoapthies)Mohamed Rizk Khodair Myelopathies
Radiculopathies
How to Create A Todo List In Todo of Odoo 18



How to Create A Todo List In Todo of Odoo 18Celine George In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to create a Todo List In Todo of Odoo 18. Odoo 18’s Todo module provides a simple yet powerful way to create and manage your to-do lists, ensuring that no task is overlooked.
Redesigning Education as a Cognitive Ecosystem: Practical Insights into Emerg...



Redesigning Education as a Cognitive Ecosystem: Practical Insights into Emerg...Leonel Morgado Slides used at the Invited Talk at the Harvard - Education University of Hong Kong - Stanford Joint Symposium, "Emerging Technologies and Future Talents", 2025-05-10, Hong Kong, China.
LDMMIA Reiki Yoga S5 Daily Living Workshop



LDMMIA Reiki Yoga S5 Daily Living WorkshopLDM Mia eStudios Happy May and Happy Weekend, My Guest Students.
Weekends seem more popular for Workshop Class Days lol.
These Presentations are timeless. Tune in anytime, any weekend.
<<I am Adult EDU Vocational, Ordained, Certified and Experienced. Course genres are personal development for holistic health, healing, and self care. I am also skilled in Health Sciences. However; I am not coaching at this time.>>
A 5th FREE WORKSHOP/ Daily Living.
Our Sponsor / Learning On Alison:
Sponsor: Learning On Alison:
— We believe that empowering yourself shouldn’t just be rewarding, but also really simple (and free). That’s why your journey from clicking on a course you want to take to completing it and getting a certificate takes only 6 steps.
Hopefully Before Summer, We can add our courses to the teacher/creator section. It's all within project management and preps right now. So wish us luck.
Check our Website for more info: https://ldmchapels.weebly.com
Get started for Free.
Currency is Euro. Courses can be free unlimited. Only pay for your diploma. See Website for xtra assistance.
Make sure to convert your cash. Online Wallets do vary. I keep my transactions safe as possible. I do prefer PayPal Biz. (See Site for more info.)
Understanding Vibrations
If not experienced, it may seem weird understanding vibes? We start small and by accident. Usually, we learn about vibrations within social. Examples are: That bad vibe you felt. Also, that good feeling you had. These are common situations we often have naturally. We chit chat about it then let it go. However; those are called vibes using your instincts. Then, your senses are called your intuition. We all can develop the gift of intuition and using energy awareness.
Energy Healing
First, Energy healing is universal. This is also true for Reiki as an art and rehab resource. Within the Health Sciences, Rehab has changed dramatically. The term is now very flexible.
Reiki alone, expanded tremendously during the past 3 years. Distant healing is almost more popular than one-on-one sessions? It’s not a replacement by all means. However, its now easier access online vs local sessions. This does break limit barriers providing instant comfort.
Practice Poses
You can stand within mountain pose Tadasana to get started.
Also, you can start within a lotus Sitting Position to begin a session.
There’s no wrong or right way. Maybe if you are rushing, that’s incorrect lol. The key is being comfortable, calm, at peace. This begins any session.
Also using props like candles, incenses, even going outdoors for fresh air.
(See Presentation for all sections, THX)
Clearing Karma, Letting go.
Now, that you understand more about energies, vibrations, the practice fusions, let’s go deeper. I wanted to make sure you all were comfortable. These sessions are for all levels from beginner to review.
Again See the presentation slides, Thx.
BỘ ĐỀ TUYỂN SINH VÀO LỚP 10 TIẾNG ANH - 25 ĐỀ THI BÁM SÁT CẤU TRÚC MỚI NHẤT, ...



BỘ ĐỀ TUYỂN SINH VÀO LỚP 10 TIẾNG ANH - 25 ĐỀ THI BÁM SÁT CẤU TRÚC MỚI NHẤT, ...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection https://app.box.com/s/n8nl163m8v9ou7xil944pod44a5wi43h
Lecture 2 CLASSIFICATION OF PHYLUM ARTHROPODA UPTO CLASSES & POSITION OF_1.pptx



Lecture 2 CLASSIFICATION OF PHYLUM ARTHROPODA UPTO CLASSES & POSITION OF_1.pptxArshad Shaikh *Phylum Arthropoda* includes animals with jointed appendages, segmented bodies, and exoskeletons. It's divided into subphyla like Chelicerata (spiders), Crustacea (crabs), Hexapoda (insects), and Myriapoda (millipedes, centipedes). This phylum is one of the most diverse groups of animals.
What is the Philosophy of Statistics? (and how I was drawn to it)



What is the Philosophy of Statistics? (and how I was drawn to it)jemille6 What is the Philosophy of Statistics? (and how I was drawn to it)
Deborah G Mayo
At Dept of Philosophy, Virginia Tech
April 30, 2025
ABSTRACT: I give an introductory discussion of two key philosophical controversies in statistics in relation to today’s "replication crisis" in science: the role of probability, and the nature of evidence, in error-prone inference. I begin with a simple principle: We don’t have evidence for a claim C if little, if anything, has been done that would have found C false (or specifically flawed), even if it is. Along the way, I’ll sprinkle in some autobiographical reflections.
Myopathies (muscle disorders) for undergraduate



Myopathies (muscle disorders) for undergraduateMohamed Rizk Khodair herediatary myopthies
myotonia
inflammatory myopthies
How to Manage Upselling in Odoo 18 Sales



How to Manage Upselling in Odoo 18 SalesCeline George In this slide, we’ll discuss on how to manage upselling in Odoo 18 Sales module. Upselling in Odoo is a powerful sales technique that allows you to increase the average order value by suggesting additional or more premium products or services to your customers.
LDMMIA Reiki News Ed3 Vol1 For Team and Guests



LDMMIA Reiki News Ed3 Vol1 For Team and GuestsLDM Mia eStudios Happy May and Taurus Season.
♥☽✷♥We have a large viewing audience for Presentations. So far my Free Workshop Presentations are doing excellent on views. I just started weeks ago within May. I am also sponsoring Alison within my blog and courses upcoming. See our Temple office for ongoing weekly updates.
https://ldmchapels.weebly.com
♥☽About: I am Adult EDU Vocational, Ordained, Certified and Experienced. Course genres are personal development for holistic health, healing, and self care/self serve.
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 5-3-2025.pptx



YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles Outbreak Southwest US 5-3-2025.pptxYale School of Public Health - The Virtual Medical Operations Center (VMOC)
BỘ ĐỀ TUYỂN SINH VÀO LỚP 10 TIẾNG ANH - 25 ĐỀ THI BÁM SÁT CẤU TRÚC MỚI NHẤT, ...



BỘ ĐỀ TUYỂN SINH VÀO LỚP 10 TIẾNG ANH - 25 ĐỀ THI BÁM SÁT CẤU TRÚC MỚI NHẤT, ...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
Collection of Data - Class 11 - Statistics
- 2. Synopsis 1. Key terms 2. Sources of data 3. Surveys 4. Census or complete Enumeration 5. Sample survey 6. Questionnaire 7. Types of questions 8. Open ended Vs Close ended 9. Mode of data collection 10. Pilot survey 11. Methods of sampling 12. Important agencies
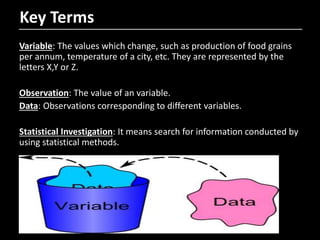
- 3. Key Terms Variable: The values which change, such as production of food grains per annum, temperature of a city, etc. They are represented by the letters X,Y or Z. Observation: The value of an variable. Data: Observations corresponding to different variables. Statistical Investigation: It means search for information conducted by using statistical methods.
- 4. Key Terms Investigators: The person who conducts statistical investigation. Enumerators: A person who helps investigator in the collection of data. Respondents: The persons from whom statistical information is collected. Statistical Unit: The items on which measurements are taken. Example; weight in kgs.
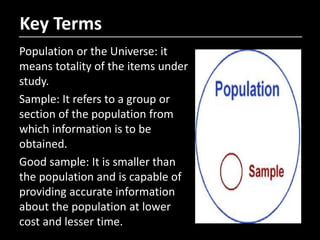
- 5. Population or the Universe: it means totality of the items under study. Sample: It refers to a group or section of the population from which information is to be obtained. Good sample: It is smaller than the population and is capable of providing accurate information about the population at lower cost and lesser time. Key Terms
- 6. Sources of Data 1. Primary Data: when the enumerator collect the data by conducting an enquiry or an investigation. They are based on first hand information. For example, you will have to enquire from a large number of school students, by asking questions from them to collect the desired information. 2. Secondary Data: When the data have been collected and processed by some other agency. It is based on second hand information. For example, information obtained from publish sources such as government reports, newspaper.
- 7. Surveys Survey is a method of gathering information from individuals. The surveys are done to describe some characteristics like price, quality, usefulness and popularity, etc. The purpose is to collect data. On the basis of area covered there are two methods of survey: 1. Census Survey 2. Sample Survey
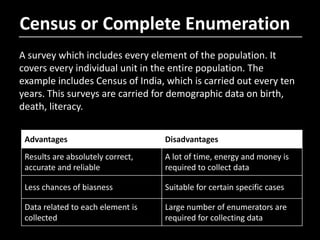
- 8. Census or Complete Enumeration A survey which includes every element of the population. It covers every individual unit in the entire population. The example includes Census of India, which is carried out every ten years. This surveys are carried for demographic data on birth, death, literacy. Advantages Disadvantages Results are absolutely correct, accurate and reliable A lot of time, energy and money is required to collect data Less chances of biasness Suitable for certain specific cases Data related to each element is collected Large number of enumerators are required for collecting data
- 9. Sample Survey In this a sample from the population is surveyed. The first step is selecting a sample to identify the population. Than select Representative Sample, as it is difficult to study entire population. Example: Population, research, etc. Advantages Disadvantages Economical as only some units are studied Partial investigation of the universe Not time consuming Not easy to select a sample which represent whole population Less efforts are required as small portion is studied It is complicated process and difficult
- 10. Questionnaire The most common type of instrument used in surveys for collecting primary data is questionnaire. While preparing the same the following points are kept in mind: • It should not be too long • The series of questions should move from general to specific • The questions should be precise and clear • The questions should not be ambiguous • The question should not use double negatives • The question should not be a leading question • The question should not indicate alternatives to the answer
- 11. Types of Questions in Questionnaire 1. Closed ended or structured questions: It could be a two-way question or a multiple choice question. When there are only 2 possible answers it is called a two way question. When there is a possibility of more than 2 answers it is called multiple choice question. 2. Open ended or unstructured questions: It could be descriptive types. When a person gets a chance to talk more about any topic.
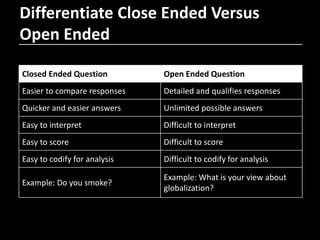
- 12. Differentiate Close Ended Versus Open Ended Closed Ended Question Open Ended Question Easier to compare responses Detailed and qualifies responses Quicker and easier answers Unlimited possible answers Easy to interpret Difficult to interpret Easy to score Difficult to score Easy to codify for analysis Difficult to codify for analysis Example: Do you smoke? Example: What is your view about globalization?
- 13. Mode of Data Collection 1. Personal Interviews: In this method, The investigator conducts interviews with the respondents and obtained required information. Two types of interview are: • Direct Personal Interview: Investigator conducts face to face interview with respondent. • Indirect Personal Interview: Data is collected by interviewing third person who are directly or indirectly concerned with the subject matter of enquiry, they are witness to the situation.
- 14. Personal Interviews Advantages Disadvantages High degree of originality Costly and time consuming Information is reliable Cannot be used where area of study is large Easy to administer Highly prone to personal biasness Elastic method as necessary adjustments in the set of questions can be made It requires that the investigator is skilled and trained
- 15. Mode of Data Collection 2. Telephone Interviews: In this method, the investigator asks questions over the telephone. Advantages Disadvantages Cheaper and takes shorter time Obstruct visual reactions. They allow researcher to assist respondents by clarifying questions Excludes the population who are not having telephone connection. Helpful where respondents are reluctant to answer questions in personal interview.
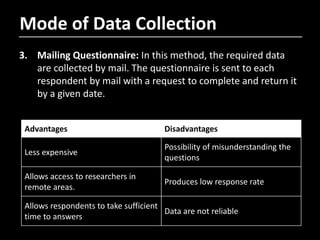
- 16. Mode of Data Collection 3. Mailing Questionnaire: In this method, the required data are collected by mail. The questionnaire is sent to each respondent by mail with a request to complete and return it by a given date. Advantages Disadvantages Less expensive Possibility of misunderstanding the questions Allows access to researchers in remote areas. Produces low response rate Allows respondents to take sufficient time to answers Data are not reliable
- 17. Mode of Data Collection
- 18. Pilot Survey/ Pre- Testing It is a trial survey which helps to test the effectiveness of the questionnaire on a small group. Importance: 1. it helps in pre-testing of the questionnaire, so as to know the shortcomings and drawbacks of the questions. 2. It also helps in accessing the suitability of questions, clarity of instructions, performance of enumerators and cost and time involved.
- 19. Methods Of Sampling 1. Random Sampling: Method where samples are selected at random. In this method, every individual unit has an equal chance of being selected. Methods under random sampling: a) Lottery Method: In this method all the items in the populations are assigned a distinct number and these are written on identical piece of paper and put in a bowl. Samples are selected on random. b) Table of Random Numbers: In this random numbers are arranged in rows and column which are selected on population size. c) Exit Polls: it is used to predict election results. In this technique a random sample of voters, who exit from the polling booths are asked who they voted for.
- 20. 2. Non-Random Sampling: In this all the units of the population do not have an equal chance of being selected. Methods under this are: a) Judgement/Purposive/Deliberate Sampling: Here sample units are selected consciously by the investigator on the basis of his judgement. This method is subject to personal bias of investigator. b) Quota Sampling: Here the investigator is allotted definite quota and he is required to collect the required data from a specific numbers of unit of each quota. c) Convenience Sampling: Here the investigator collects the sample units on the basis of his convenience. Methods Of Sampling
- 21. Sampling and Non Sampling Errors Error in statistics is used to denote the difference between the true value and the estimated value. Errors can be classified as: 1. Sampling Errors: the difference between the actual value of a parameter of the population( which is not known) and its estimate( known). It is possible to reduce sampling error by increasing the size of the sample. 2. Non- Sampling Errors: It includes: • Errors in Data Acquisition: From recording incorrect response • Non-Response: It occurs when interviewer is unable to contact person listed in the sample • Sampling Bias: It occurs when in a sampling plan some members of target population could not included
- 22. Important Agencies of Secondary Data 1.Census of India: It provides the most important and complete demographic record of population. These are conducted every 10 years. The census official collects information on various aspects of population such as sex ratio, literacy, migration, etc. Which are used to interpret and analyse to understand many economic and social issues in India and accordingly plans and policies are formulated.
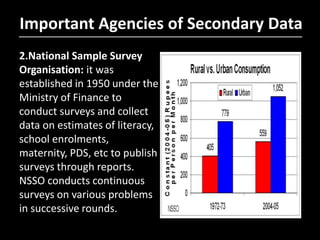
- 23. 2.National Sample Survey Organisation: it was established in 1950 under the Ministry of Finance to conduct surveys and collect data on estimates of literacy, school enrolments, maternity, PDS, etc to publish surveys through reports. NSSO conducts continuous surveys on various problems in successive rounds. Important Agencies of Secondary Data
- 24. Thank You! Lesson by Anjali Kaur Suri TGT Maths, PGT Economics M.A. Economics, M.Com (Finance), PGD Banking & Finance, B.A. Hons (Economics), B.Ed (Maths & SST), NISM, NSDL and IELTS certified. For enquiries or topic suggestions, email: contact@geniusedu.co.in Connect on Linkedin: www.linkedin.com/in/anjali-kaur





