Biostatistics-C-2-Item-2pdf.pdf
- 1. WELCOME
- 2. Dr. Subrata Kumer Sen MBBS, MPH, BCS (Health) Lecturer, Community Medicine M Abdur Rahim Medical College Dinajpur.
- 3. Statistics: The science of collecting, summarizing, and analyzing data. Biostatistics: The science of collecting, summarizing, and analyzing biological data. Medical Statistics: The science of collecting, summarizing, and analyzing medical data. Vital Statistics: Statistics that deals with vital events. Vital events are births, marriages, divorces, separations, and deaths.
- 4. Sources of data for vital events/ statistics: • National level- Census, BBS • City Corporation/ Municipalities for births & deaths • Kaji Office for marriages, divorces, separations • Notification of infectious diseases for deaths • Hospital records for births & deaths • Disease registers for deaths etc.
- 5. Uses of Biostatistics: • Collection of information in the best possible scientific way. • Simplification of huge, complex sets of data. • Helps in the formulation of hypothesis and amplification of ideas. • Identification of association between two or more variables by testing hypothesis. • Helps in interpretation and drawing conclusion by analyzing data • By summarizing and presenting, helps policy makers to make decisions based on scientific evidence.
- 6. Data: Data is a set of values collected during any type of scientific investigation. Data Classification: Based on Source of Data: I. Primary: Data directly collected at the field level during a study II.Secondary: collected from another study, census data, hospital records III.Tertiary: from textbooks. Based on Nature of Data: • Qualitative/ Categorical/ Nominal: Age, Sex, economical status • Quantitative/ Numerical: a. Continuous: Cont. spectrum/range can be fractioned (e.g. height, weight, temperature) b. Discrete: No continuity, Complete #, no fraction (e.g. Parity, patient number in hospital)
- 7. Variable: Any characteristic which differs for one individual or object to another. Types: A. According to Relationship: 1. Independent Variable 2. Intervening Variable 3. Dependent Variable 4. Confounding variable B. According to Nature/ Characteristic: 1. Qualitative 2. Quantitative: Continuous & Discrete.
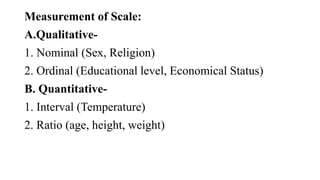
- 8. Measurement of Scale: A.Qualitative- 1. Nominal (Sex, Religion) 2. Ordinal (Educational level, Economical Status) B. Quantitative- 1. Interval (Temperature) 2. Ratio (age, height, weight)
- 9. Methods of Data Collection: *Surveying Study population *Interviewing: Face to Face, Telephone, Internet etc *Observation: Participant, Non-participant *Written Questionnaire *Electronic Data Reporting *Focus Group Discussion *Document Review
- 10. Data collection tool (instrument): •Questionnaire •Interview schedule •Checklist •Other electronic device
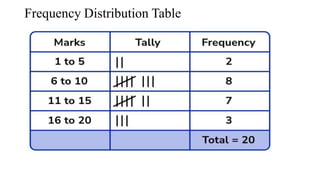
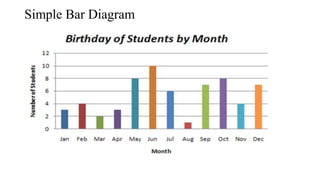
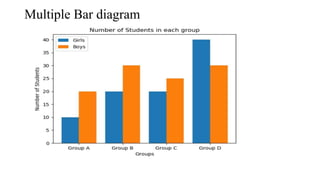
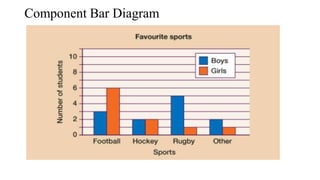
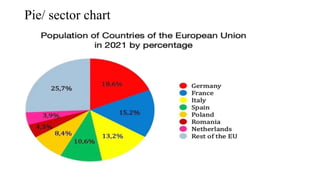
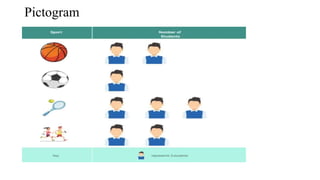
- 11. Data Presentation: A.Tabulation/ Tabular Presentation: 1. Simple Table 2. Frequency Distribution Table B. Graphical Presentation: 1. Qualitative: a. Bar diagram - Simple Bar Diagram, Multiple Bar diagram, Component Bar Diagram b. Pie/ sector chart c. Pictogram d. Map/ spot diagram
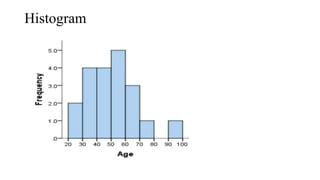
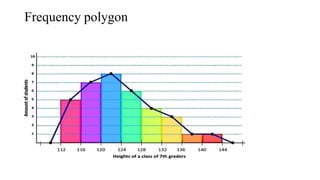
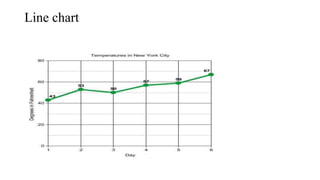
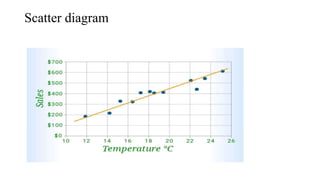
- 12. 2. Quantitative: a. Histogram b. Frequency polygon c. Frequency Curve d. Line chart e. Scatter diagram
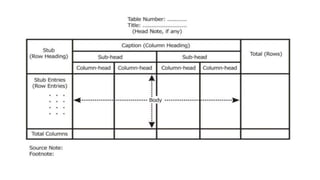
- 13. Characteristics of a table: A table should have i. Table number ii. Title iii. Body- a. Column b. Row iv. Foot note/ Source (if any)
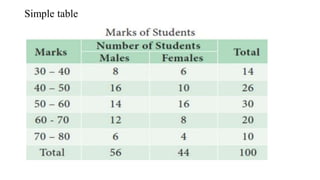
- 15. Simple table
- 21. Pictogram
- 23. Histogram
- 25. Line chart
- 26. Scatter diagram
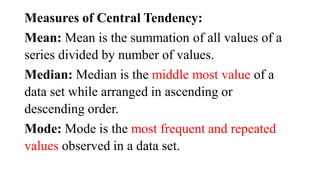
- 27. Measures of Central Tendency: Mean: Mean is the summation of all values of a series divided by number of values. Median: Median is the middle most value of a data set while arranged in ascending or descending order. Mode: Mode is the most frequent and repeated values observed in a data set.
- 30. Measures of Dispersion: Range: Simply the difference between the largest and smallest values in a set of data. Mean Deviation: The mean deviation is an average of absolute deviations of individual observations from the central value of a series. Standard Deviation: Standard deviation is the positive square root of the mean-square deviations of the observations from their arithmetic mean.
- 31. Population: A population is entire group of subjects or total number of items about which information is desired. Sample: Sample is a part of population describing the characteristics of that population. The sample is drawn should be representative of entire population. Sampling: Sampling is the process of selection the sample from a defined study population. Sampling frame: When all the members or individuals of population are listed by numbering then it is called sampling frame.
- 32. Sampling methods/Techniques: a) Random/ Probability/ Non-purposive/ Unbiased sampling: i) Simple random sampling (e.g. Lottery) ii) Systematic random sampling iii) Stratified random sampling iv) Multistage sampling v) Multiphase sampling vi) Cluster Sampling
- 33. b) Non- Probability sampling: i) Convenience or Judgment sampling ii) Quota sampling iii) Snowball sampling
- 34. THANK YOU