Introduction to Statistics
- 1. STATISTICS PRESENTATION PRESENTED BY: AREEBA SULTAN, AMMARA MANZOOR, GHAYUR KHALID WERYAH, ALI HUSSAIN, AYESHA SHAFQAT.
- 2. DEFINATION OF STATISTICS • The practice or science of collecting and analysing numerical data in large quantities. • A branch of mathematics dealing with the collection, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of masses of numerical data. • A collection of quantitative data.
- 3. EXAMPLE OF STATISTICS • In a class, the collection of marks obtained by 50 students is the description of data. Now when we take out the mean of the data, the result is the average of marks of 50 students. If the average mark obtained by 50 students is 88 out of 100, then we can reach to a conclusion or give a judgment on the basis of the result.
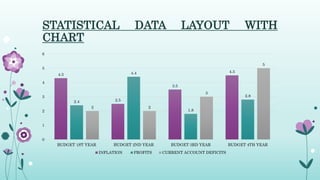
- 4. STATISTICAL DATA LAYOUT WITH CHART 4.3 2.5 3.5 4.5 2.4 4.4 1.8 2.8 2 2 3 5 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 BUDGET 1ST YEAR BUDGET 2ND YEAR BUDGET 3RD YEAR BUDGET 4TH YEAR INFLATION PROFITS CURRENT ACCOUNT DEFICITS
- 5. TYPES OF STATISTICS Statistics have majorly categorised into two types: 1. Descriptive Statistics. 2. Inferential Statistics.
- 6. DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS • In this type of statistics, the data is summarised through the given observations. The summarisation is one from a sample of population using parameters such as the mean or standard deviation. • Descriptive statistics is a way to organise, represent and describe a collection of data using tables, graphs, and summary measures. • For Example, the collection of people in a city using the internet or using Television.
- 7. DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS Descriptive statistics are also categorised into four different categories: • Measure of frequency. • Measure of dispersion. • Measure of central tendency. • Measure of position. The frequency measurement displays the number of times a particular data occurs. Range, Variance, Standard Deviation are measures of dispersion. It identifies the spread of data.
- 8. INFERENTIAL STATISTICS • This type of statistics is used to interpret the meaning of Descriptive statistics. That means once the data has been collected, analysed and summarised then we use these stats to describe the meaning of the collected data. • It is used to draw conclusions from the data that depends on random variations such as observational errors, sampling variation, etc. • Inferential Statistics is a method that allows us to use information collected from a sample to make decisions, predictions or inferences from a population. • For Example, deriving estimates from hypothetical research.
- 9. IMPORTANCE OF STATISTICS Statistics executes the work simply and gives a transparent picture of the work we do regularly. The statistical methods help us to examine different areas such as medicine, business, economics, social science and others. Statistics equips us with different kinds of organised data with the help of graphs, tables, diagrams and charts.
- 10. IMPORTANCE OF STATISTICS Statistics helps to understand the variability of the data pattern in a quantitative way. Statistics makes us understand the bulk of data in a simple way. Statistics is the way to collecting accurate quantitative data.
- 11. USE OF STATISTICS IN REAL LIFE • Statistics play an important role in real life, especially in large industries, where data is computed in bulk. It helps to collect, analyse and interpret the data. Also, with the help of statistical graphs, charts and tables we can easily present the data.
- 12. APPLICATIONS OF STATISTICS IN DIFFERENT FIELDS • Statistics plays a vital role in every field of human activity. Statistics helps in determining the existing position of per capita income, unemployment, population growth rates, housing, schooling medical facilities, etc., in a country. • statistics holds a central position in almost every field, including industry, commerce, trade, physics, chemistry, economics, mathematics, biology, botany, psychology, astronomy, etc., so the application of statistics is very wide. • “Now we shall discuss some important fields in which statistics is commonly applied in the next slides.”
- 13. APPLICATIONS OF STATISTICS BUSINESS • Statistics plays an important role in business. A successful businessman must be very quick and accurate in decision making. He knows what his customers want; he should therefore know what to produce and sell and in what quantities. • Statistics helps businessmen to plan production according to the taste of the customers, and the quality of the products can also be checked more efficiently by using statistical methods. Thus, it can be seen that all business activities are based on statistical information.
- 14. APPLICATIONS OF STATISTICS ECNOMICS • Economics largely depends upon statistics. National income accounts are multipurpose indicators for economists and administrators, and statistical methods are used to prepare these accounts. • In economics research, statistical methods are used to collect and analyse the data and test hypotheses. The relationship between supply and demand is studied by statistical methods; imports and exports, inflation rates, and per capita income are problems which require a good knowledge of statistics.
- 15. APPLICATIONS OF STATISTICS SOCIAL SCIENCES • Statistics plays a vital role in almost all the social sciences. • Statistical methods are commonly used for analysing experiments results, and testing their significance in biology, physics, chemistry, mathematics, meteorology, research, chambers of commerce, sociology, business, public administration, communications and information technology, etc.
- 16. ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF STATISTICS ADVANTAGES • The bulk data can be presented in a precise and definite form. • The comparison and conclusions of data becomes easy. • Forecasting the trends becomes easy with statistics. DISADVANTAGES • The statistical data can lead to misuse. • There are chances of errors becomes easy when the statistical methods are not done by the experts. • For the comparison of the data, the data should be homogeneous and uniform.
- 17. SAMPLING • Sampling is a statistical procedure that is concerned with the selection of the individual observation; it helps us to make statistical inferences about the population. • Quality assurance, and survey methodology, sampling is the selection of a subset of individuals from within a statistical population to estimate characteristics of the whole population. Statisticians attempt to collect samples that are representative of the population in question.
- 18. EXAMPLE OF SAMPLING • if a drug manufacturer would like to research the adverse side effects of a drug on the country’s population, it is almost impossible to conduct a research study that involves everyone. • In this case, the researcher decides a sample of people from each demographic and then researches them, giving him/her indicative feedback on the drug’s behaviour.
- 19. CHARACTERISTICS OF SAMPLING •In sampling, we assume that samples are drawn from the population and sample means and population means are equal. A population can be defined as a whole that includes all items and characteristics of the research taken into study. However, gathering all this information is time consuming and costly. We therefore make inferences about the population with the help of samples.
- 20. TYPES OF SAMPLING TYPES OF SAMPLING ARE AS FOLLOWS: • Probability Sampling. • Non-Probability Sampling. “Let’s take a closer look at these two methods of sampling”.
- 21. PROBABILITY SAMPLING • Probability sampling is a sampling technique where a researcher sets a selection of a few criteria and chooses members of a population randomly. All the members have an equal opportunity to be a part of the sample with this selection parameter. • Sampling technique in which researchers choose samples from a larger population using a method based on the theory of probability. This sampling method considers every member of the population and forms samples based on a fixed process. • FOR EXAMPLE, In a population of 1000 members, every member will have a 1/1000 chance of being selected to be a part of a sample. Probability sampling eliminates bias in the population and gives all members a fair chance to be included in the sample.
- 22. TYPES OF PROBABILITY There are four types of probability sampling techniques: 1. SIMPLE RANDOM SAMPLING. 2. CLUSTER SAMPLING. 3. SYSTEMATIC SAMPLING. 4. STARTIFIED RANDOM SAMPLING.
- 23. USES OF PROBABILITY STATISTICS • Reduce Sample Bias: Using the probability sampling method, the bias in the sample derived from a population is negligible to non-existent. The selection of the sample mainly depicts the understanding and the inference of the researcher. Probability sampling leads to higher quality data collection as the sample appropriately represents the population. • Diverse Population: When the population is vast and diverse, it is essential to have adequate representation so that the data is not skewed towards one demographic. For example, if Square would like to understand the people that could make their point-of-sale devices, a survey conducted from a sample of people across the US from different industries and socio-economic backgrounds helps.
- 24. NON-PROBABILITY STATISTICS • The non-probability method is a sampling method that involves a collection of feedback based on a researcher or statistician’s sample selection capabilities and not on a fixed selection process. • The output of a survey conducted with a non-probable sample leads to skewed results, which may not represent the desired target population. But, there are situations such as the preliminary stages of research or cost constraints for conducting research, where non-probability sampling will be much more useful than the other type.
- 25. TYPES OF NON-PROBABILITY STATISTICS 1. CONVINCING SAMPLING 2. JUDGMENTAL SAMPLING. 3. SNOWBALL SAMPLING. 4. QOUTA SAMPLING.
- 26. USES OF NON-PROBABILITY SAMPLING • Create a hypothesis: Researchers use the non-probability sampling method to create an assumption when limited to no prior information is available. This method helps with the immediate return of data and builds a base for further research. • Exploratory research: Researchers use this sampling technique widely when conducting qualitative research, pilot studies, or exploratory research. • Budget and time constraints: The non-probability method when there are budget and time constraints, and some preliminary data must be collected. Since the survey design is not rigid, it is easier to pick respondents at random and have them take the survey or questionnaire.
- 27. DIFFERENCE BETWEEN PROBABILITY AND NON-PROBABILITY SAMPLING PROBABILITY SAMPLING • Probability Sampling is a sampling technique in which samples from a larger population are chosen using a method based on the theory of probability. • Random sampling method. • The population is selected randomly. • Since there is a method for deciding the sample, the population demographics are conclusively represented. NON-PROBABILITY SAMPLING • Non-probability sampling is a sampling technique in which the researcher selects samples based on the researcher’s subjective judgment rather than random selection. • Non-Random sampling method. • The population is selected arbitrarily. • Since the sampling method is arbitrary, the population demographics representation is almost always skewed.
- 28. THANKYOU MADE BY: GHAYUR KHALID WERYAH (053) GREY SECTION