What is statistics (chapter - 1) PPT.pptx
- 1. What is Statistics? Chapter 1 Copyright ©2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. 1-1
- 2. Learning Objectives Copyright ©2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. LO1-1Explain why knowledge of statistics is important LO1-2Define statistics and provide an example of how statistics is applied LO1-3Differentiate between descriptive and inferential statistics LO1-4Classify variables as qualitative or quantitative, and discrete or continuous LO1-5Distinguish between nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio levels of measurement LO1-6List the values associated with the practice of statistics 1-2
- 3. Why Study Statistics Copyright ©2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. � Data are collected everywhere and require statistical knowledge to make the information useful � Statistics is used to make valid comparisons and to predict the outcomes of decisions � Statistical knowledge is useful in any career 1-3
- 4. What is Meant by Statistics Copyright ©2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. � What is statistics? � It’s more than presenting numerical facts Example: The inflation rate for the calendar year was 0.7%. By applying statistics we could compare this year’s inflation rate to past observations of inflation. Is it higher, lower, or about the same? Is there a trend of increasing or decreasing inflation? Is there a relationship between interest rates and government bonds? 1-4 STATISTICS The science of collecting, organizing, presenting, analyzing, and interpreting data to assist in making more effective decisions.
- 5. Types of Statistics Copyright ©2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. � There are two types of statistics, descriptive and inferential � Descriptive statistics can be used to organize data into a meaningful form � You can summarize data and provide information that is easy to understand � Example: There are a total of 46,837 miles of interstate highways in the U.S. The interstate system represents 1% of the nation’s roads, but carries more than 20% of the traffic. Texas has the most interstate highways and Alaska doesn’t have any. 1-5 DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS Methods of organizing, summarizing, and presenting data in an informative way.
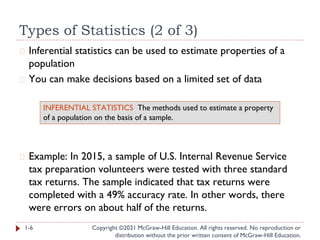
- 6. Types of Statistics (2 of 3) Copyright ©2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. � Inferential statistics can be used to estimate properties of a population � You can make decisions based on a limited set of data � Example: In 2015, a sample of U.S. Internal Revenue Service tax preparation volunteers were tested with three standard tax returns. The sample indicated that tax returns were completed with a 49% accuracy rate. In other words, there were errors on about half of the returns. 1-6 INFERENTIAL STATISTICS The methods used to estimate a property of a population on the basis of a sample.
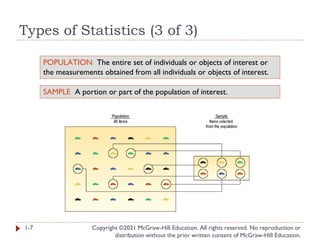
- 7. Types of Statistics (3 of 3) Copyright ©2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. 1-7 POPULATION The entire set of individuals or objects of interest or the measurements obtained from all individuals or objects of interest. SAMPLE A portion or part of the population of interest.
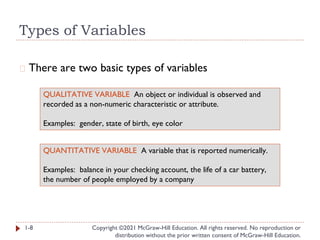
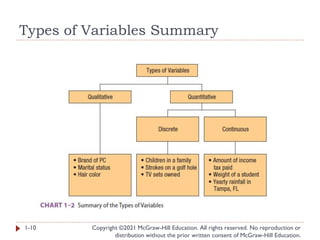
- 8. Types of Variables Copyright ©2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. � There are two basic types of variables 1-8 QUALITATIVE VARIABLE An object or individual is observed and recorded as a non-numeric characteristic or attribute. Examples: gender, state of birth, eye color QUANTITATIVE VARIABLE A variable that is reported numerically. Examples: balance in your checking account, the life of a car battery, the number of people employed by a company
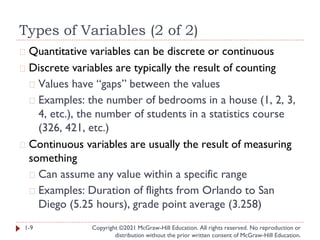
- 9. Types of Variables (2 of 2) Copyright ©2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. � Quantitative variables can be discrete or continuous � Discrete variables are typically the result of counting � Values have “gaps” between the values � Examples: the number of bedrooms in a house (1, 2, 3, 4, etc.), the number of students in a statistics course (326, 421, etc.) � Continuous variables are usually the result of measuring something � Can assume any value within a specific range � Examples: Duration of flights from Orlando to San Diego (5.25 hours), grade point average (3.258) 1-9
- 10. Types of Variables Summary Copyright ©2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. 1-10
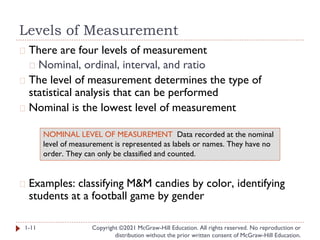
- 11. Levels of Measurement Copyright ©2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. � There are four levels of measurement � Nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio � The level of measurement determines the type of statistical analysis that can be performed � Nominal is the lowest level of measurement � Examples: classifying M&M candies by color, identifying students at a football game by gender 1-11 NOMINAL LEVEL OF MEASUREMENT Data recorded at the nominal level of measurement is represented as labels or names. They have no order. They can only be classified and counted.
- 12. Levels of Measurement (2 of 4) Copyright ©2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. � The next level of measurement is the ordinal level � The rankings are known but not the magnitude of differences between groups � Examples: the list of top ten states for best business climate, student ratings of professors 1-12 ORDINAL LEVEL OF MEASUREMENT Data recorded at the ordinal level of measurement is based on a relative ranking or rating of items based on a defined attribute or qualitative variable. Variables based on this level of measurement are only ranked and counted.
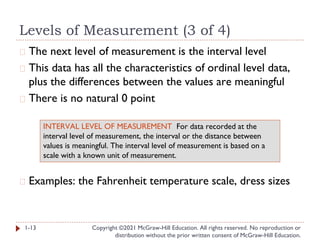
- 13. Levels of Measurement (3 of 4) Copyright ©2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. � The next level of measurement is the interval level � This data has all the characteristics of ordinal level data, plus the differences between the values are meaningful � There is no natural 0 point � Examples: the Fahrenheit temperature scale, dress sizes 1-13 INTERVAL LEVEL OF MEASUREMENT For data recorded at the interval level of measurement, the interval or the distance between values is meaningful. The interval level of measurement is based on a scale with a known unit of measurement.
- 14. Levels of Measurement (4 of 4) Copyright ©2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. � The highest level of measurement is the ratio level � The data has all the characteristics of the interval scale and ratios between numbers are meaningful � The 0 point represents the absence of the characteristic � Examples: wages, changes in stock prices, and height 1-14 RATIO LEVEL OF MEASUREMENT Data recorded at the ratio level of measurement are based on a scale with a known unit of measurement and a meaningful interpretation of zero on the scale.
- 15. Levels of Measurement Summary Copyright ©2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. 1-15
- 16. Ethics and Statistics Copyright ©2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. � Practice statistics with integrity and honesty when collecting, organizing, summarizing, analyzing, and interpreting numerical information � Maintain an independent and principled point of view when analyzing and reporting findings and results � Question reports that are based on data that � does not fairly represent the population � does not include all relevant statistics � introduces bias in an attempt to mislead or misrepresent 1-16
- 17. Basic Business Analytics Copyright ©2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. � Business Analytics is used to process and analyze data and information to support a story or narrative of a company � Using computer software to summarize, organize, analyze, and present the findings of statistical analysis is essential 1-17
- 18. Chapter 1 Practice Problems Copyright ©2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. 1-18
- 19. Question 1 Copyright ©2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education. 1-19 What is the level of measurement for each of the following variables? a. Student IQ ratings b. Distance students travel to class c. The jersey numbers of a sorority soccer team d. A student’s state of birth e. A student’s academic class – that is, freshman, sophomore, junior, or senior f. Number of hours students study per week LO1-5
- 20. Question 13 1-20 For each of the following, determine whether the variable is continuous or discrete, quantitative or qualitative, and level of measurement a. Salary b. Gender c. Sales volume of MP3 players d. Soft drink preference e. Temperature f. SAT scores g. Student rank in class h. Rating of a finance professor i. Number of home video screens LO1-4,5 Copyright ©2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education.