Quatitative Data Analysis
- 2. Introduction Analysis is the process of organizing and synthesizing the data so as to answer research questions and test hypothesis. Analysis referred as a method of organizing data in such a way that research questions and answered and hypothesis can be tested Analysis is the process of breaking a complex topic into smaller parts to gain better understanding of it. It is also defined as the process of systematically applying statistical and logical techniques to describe, summarize and compare data
- 3. ANALYSIS OF QUANTITATIVE DATA Analysis of quantitative data deals with information collected during research study, which can be quantified and statistical calculations, can be computed. Steps of Quantitative Data Analysis 1. Data preparation 2. Describing the Data (Descriptive or summary statistics) 3. Drawing the inferences of data ( Inferential statistics) 4. Interpretation of data
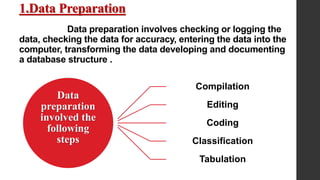
- 4. 1.Data Preparation Data preparation involves checking or logging the data, checking the data for accuracy, entering the data into the computer, transforming the data developing and documenting a database structure . Data preparation involved the following steps Compilation Editing Coding Classification Tabulation
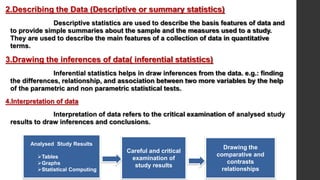
- 5. 2.Describing the Data (Descriptive or summary statistics) Descriptive statistics are used to describe the basis features of data and to provide simple summaries about the sample and the measures used to a study. They are used to describe the main features of a collection of data in quantitative terms. 3.Drawing the inferences of data( inferential statistics) Inferential statistics helps in draw inferences from the data. e.g.: finding the differences, relationship, and association between two more variables by the help of the parametric and non parametric statistical tests. 4.Interpretation of data Interpretation of data refers to the critical examination of analysed study results to draw inferences and conclusions. Analysed Study Results Tables Graphs Statistical Computing Careful and critical examination of study results Drawing the comparative and contrasts relationships
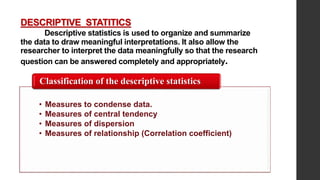
- 6. DESCRIPTIVE STATITICS Descriptive statistics is used to organize and summarize the data to draw meaningful interpretations. It also allow the researcher to interpret the data meaningfully so that the research question can be answered completely and appropriately. • Measures to condense data. • Measures of central tendency • Measures of dispersion • Measures of relationship (Correlation coefficient) Classification of the descriptive statistics
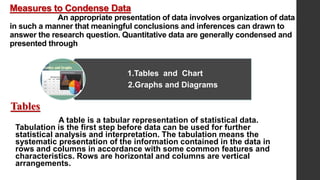
- 7. Measures to Condense Data An appropriate presentation of data involves organization of data in such a manner that meaningful conclusions and inferences can drawn to answer the research question. Quantitative data are generally condensed and presented through Tables A table is a tabular representation of statistical data. Tabulation is the first step before data can be used for further statistical analysis and interpretation. The tabulation means the systematic presentation of the information contained in the data in rows and columns in accordance with some common features and characteristics. Rows are horizontal and columns are vertical arrangements. 1.Tables and Chart 2.Graphs and Diagrams
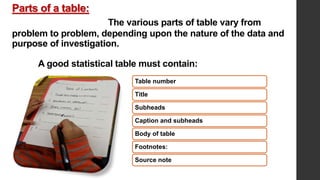
- 8. Parts of a table: The various parts of table vary from problem to problem, depending upon the nature of the data and purpose of investigation. A good statistical table must contain: Table number Title Subheads Caption and subheads Body of table Footnotes: Source note
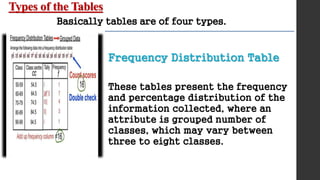
- 9. Types of the Tables Basically tables are of four types. Frequency Distribution Table These tables present the frequency and percentage distribution of the information collected, where an attribute is grouped number of classes, which may vary between three to eight classes.
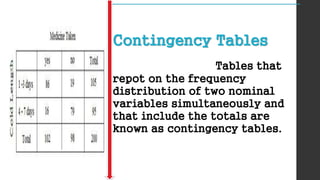
- 10. Contingency Tables Tables that repot on the frequency distribution of two nominal variables simultaneously and that include the totals are known as contingency tables.
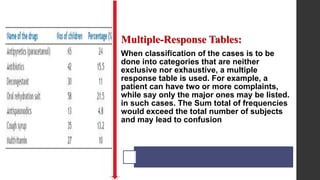
- 11. Multiple-Response Tables: When classification of the cases is to be done into categories that are neither exclusive nor exhaustive, a multiple response table is used. For example, a patient can have two or more complaints, while say only the major ones may be listed. in such cases. The Sum total of frequencies would exceed the total number of subjects and may lead to confusion
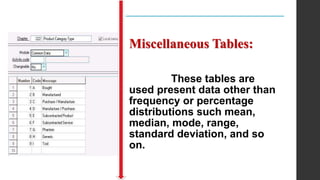
- 12. Miscellaneous Tables: These tables are used present data other than frequency or percentage distributions such mean, median, mode, range, standard deviation, and so on.
- 13. Graphs and diagrams Graphical presentation of data. It is the most systematic and concise ways in which statistical results may be presented Types of diagram and graphs: The commonly used diagrams and graphs in the presentation of data of the research studies are Bar diagram, Pie chart Histogram, Frequency Polygon Line graphs
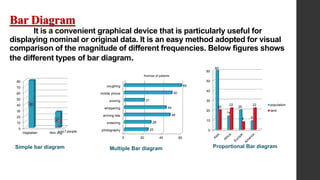
- 14. Bar Diagram It is a convenient graphical device that is particularly useful for displaying nominal or original data. It is an easy method adopted for visual comparison of the magnitude of different frequencies. Below figures shows the different types of bar diagram. 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 Vegitatian Non veg: 80 27 no f people 0 20 40 60 photography sneezing arriving late whispering snoring mobile phone coughing 25 28 48 44 21 50 60 Number of patients 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 60 14 20 9 20 22 8 22 population land Simple bar diagram Multiple Bar diagram Proportional Bar diagram
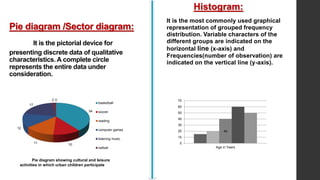
- 15. Pie diagram /Sector diagram: It is the pictorial device for presenting discrete data of qualitative characteristics. A complete circle represents the entire data under consideration. Histogram: It is the most commonly used graphical representation of grouped frequency distribution. Variable characters of the different groups are indicated on the horizontal line (x-axis) and Frequencies(number of observation) are indicated on the vertical line (y-axis). 34 10 11 12 17 2 0 basketball soccer reading computer games listening music netball 40 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 Age in Years Pie diagram showing cultural and leisure activities in which urban children participate
- 16. Four different types of graphical representation models which shown above the figures are frequency polygon, line graph, cumulative frequency curve, scattered diagram. Frequency polygon line graph Cumulative frequency curve scattered diagram
- 17. Pictograms or picture diagram: This method is used to impress the frequency of the occurrence of events to common people such as attacks, deaths, number operations, admissions, accidents, and discharge in a population Map diagram or spot map: These maps are prepared to show geographical distribution of frequencies of characteristics. HIGH ECNOMIC MIDLE ECONOMIC LOW ECONOMIC HIGH ECONOMIC MIDDLE ECONOMIC LOW ECONOMIC DEVELOPING COUNTRIES DEVELOPED COUNTRIES
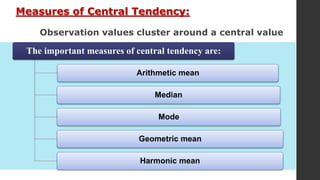
- 18. Measures of Central Tendency: Observation values cluster around a central value The important measures of central tendency are: Arithmetic mean Median Mode Geometric mean Harmonic mean
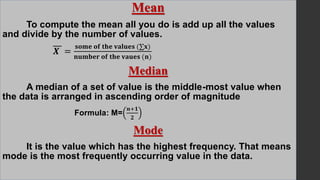
- 19. Mean To compute the mean all you do is add up all the values and divide by the number of values. 𝑿 = 𝐬𝐨𝐦𝐞 𝐨𝐟 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐯𝐚𝐥𝐮𝐞𝐬 (∑𝐱) 𝐧𝐮𝐦𝐛𝐞𝐫 𝐨𝐟 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐯𝐚𝐮𝐞𝐬 (𝐧) Median A median of a set of value is the middle-most value when the data is arranged in ascending order of magnitude Formula: M= 𝒏+𝟏 𝟐 Mode It is the value which has the highest frequency. That means mode is the most frequently occurring value in the data.
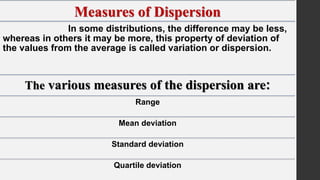
- 20. Measures of Dispersion In some distributions, the difference may be less, whereas in others it may be more, this property of deviation of the values from the average is called variation or dispersion. The various measures of the dispersion are: Range Mean deviation Standard deviation Quartile deviation
- 21. Range It is the difference between highest and lowest value in the data. If 'H' is the highest and ‘L’ lowest value, then: Range (R) =H-L Standard deviation Standard deviation is the positive square root of mean of the squared deviations of value from the arithmetic mean. FOR DISCRETE DATA: FOR CONTINUOUS DATA: SD= ∑ 𝒙− 𝒙 𝟐 𝒏 SD= ∑ 𝒙− 𝒙 𝟐 𝒇 𝒏
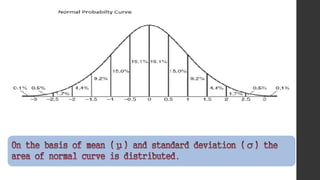
- 22. NORMAL PROBABILITY CURVE (Z-SCORE) Normal probability curve is a continuous-type probability curve. The curve is symmetrical and asymptotic (i.e. touches at infinity). All the measures of central tendency are equal and stable on the highest peak axis, i.e. mean=median=mode. The total area under the curve is equal to unity. The quartiles Ǫ1and Ǫ2, are equidistant from the mean μ . The normal curve has two parameters, i.e. mean (μ) and standard deviation (σ).
- 24. CORRELATION COEFFICIENT The extent or degree of relationship between two sets of figures is measured in term of another parameter called correlation coefficient. It is denoted by 'r'. One can find the relation between weight and cholesterol and cholesterol and CAD. 5. Absolutely no correlation r=0 4. Moderately negative correlation -I <r<1 3. Moderately positive correlation 0<r<l 2. Perfect negative correlation (r-1) I. Perfect positive correlation (r+1) Types of Correlation Coefficient
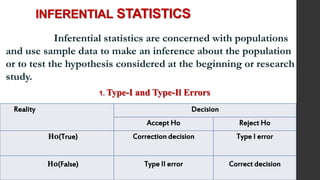
- 25. INFERENTIAL STATISTICS Inferential statistics are concerned with populations and use sample data to make an inference about the population or to test the hypothesis considered at the beginning or research study. 1. Type-I and Type-Il Errors Reality Decision Accept Ho Reject Ho 𝐇𝐨(True) Correction decision Type I error 𝐇𝐨(False) Type II error Correct decision
- 26. Level of Significance Probability of making type-I error is called as level of significance. It is represented by α or ρ. In other words, level of significance is probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true. In health sciences we generally consider the level of significance at either 1% (.01) or 5% (.05). A significance level of 0.5 means that the researcher is willing to take a risk of being wrong 5% of the times or 5 times out of 100, when rejecting the null hypothesis.
- 27. Confidence Interval Confidence interval (C) is a range of values that with a specified degree of probability is thought to contain the population value. Degree of Freedom The interpretation of a statistical test depends on the degree of freedom. It is denoted by the abbreviation df and a number (e.g. df =3). Degree of freedom indicates the number of values that are free to vary
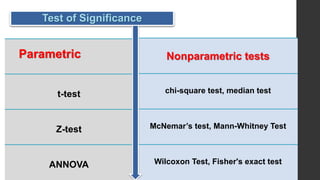
- 28. Test of Significance Parametric t-test Z-test ANNOVA Nonparametric tests chi-square test, median test McNemar’s test, Mann-Whitney Test Wilcoxon Test, Fisher's exact test
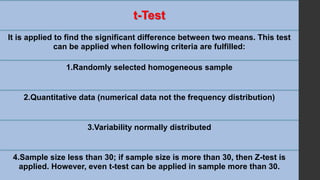
- 29. t-Test It is applied to find the significant difference between two means. This test can be applied when following criteria are fulfilled: 1.Randomly selected homogeneous sample 2.Quantitative data (numerical data not the frequency distribution) 3.Variability normally distributed 4.Sample size less than 30; if sample size is more than 30, then Z-test is applied. However, even t-test can be applied in sample more than 30.
- 30. Z-Test When a sample is larger than 30 subjects, and a researcher wants to compare the difference in population mean and a simple mean or the difference between to sample means, then Z-test is applied. There are following four prerequisites for application of the Z-test. 1.The sample or samples must be randomly selected. 2.The data must be quantitative in nature. 3.The variability is assumed to follow normal distribution in the population. 4.The sample size must be larger than 30.
- 31. When a researcher wants to compare the difference between more than two samples test means, t-test will be useful and a need of alternative test will be felt. This need can be fulfilled by the test known as Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) test. Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) Test This is nonparametric test is used to find out the association between two events in binomial or multinomial samples. It is represented by a symbol 𝑿 𝟐 and used to find association between two discrete attributes. Chi-Square Test
- 32. Qualitative data analysis (QDA) software is used in many academic fields, such as sociology, psychology, political science, medicine, and educational science, and it is also a popular tool for businesses and market researchers. COMPUTER ANALYSIS OF QUANTITATIVE DATA
- 33. Originally known as Statistical Package for Social Sciences, SPSS was developed in 1960 at Stanford University to help solve problems in the social sciences. SPSS now stands for Statistical Product and Services Solutions and 1st among the most comprehensive and popular statistical packages. SPSS Microsoft Excel is a very popular and useful spreadsheet program that can be used for data entry. It has the capacity to generate random numbers, and it can be used for the computation of many standard statistical applications like computation of mean, range, standard deviation, etc. Microsoft Excel
- 34. Minitab This is another statistical package designed to facilitate the teaching of statistical methods by using computer. The Minitab is also a very user-friendly product with well-designed documentation facilities that are being used widely in educational institutions. Web resources which are related to statistical power analyses. A few are: StatPages.net G-Power
- 35. Thanks