Basic Statistics & Data Analysis
- 1. Basic Statistics and Data Analysis
- 2. What is Statistics ? “ Statistics is the methodology which scientists and mathematicians have developed for interpreting and drawing conclusions from collected data ”
- 3. Statistical methods can be used to find answers to the questions like: • What kind and how much data need to be collected? • How should we organize and summarize the data? • How can we analyze the data and draw conclusions from it? • How can we assess the strength of the conclusions and evaluate their uncertainty?
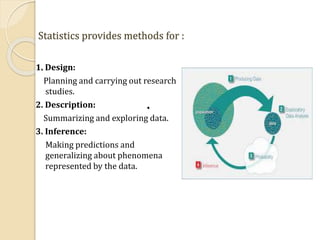
- 4. Statistics provides methods for : 1. Design: Planning and carrying out research studies. 2. Description: Summarizing and exploring data. 3. Inference: Making predictions and generalizing about phenomena represented by the data.
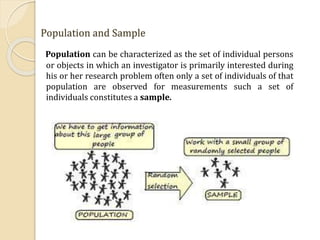
- 5. Population and Sample Population can be characterized as the set of individual persons or objects in which an investigator is primarily interested during his or her research problem often only a set of individuals of that population are observed for measurements such a set of individuals constitutes a sample.
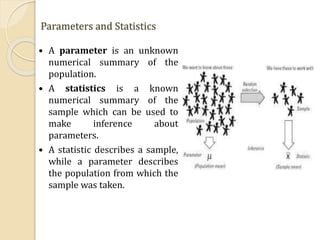
- 6. Parameters and Statistics A parameter is an unknown numerical summary of the population. A statistics is a known numerical summary of the sample which can be used to make inference about parameters. A statistic describes a sample, while a parameter describes the population from which the sample was taken.
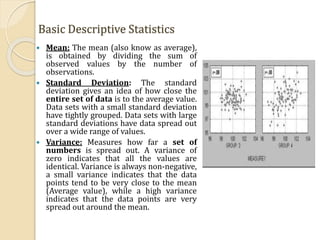
- 7. Basic Descriptive Statistics Mean: The mean (also know as average), is obtained by dividing the sum of observed values by the number of observations. Standard Deviation: The standard deviation gives an idea of how close the entire set of data is to the average value. Data sets with a small standard deviation have tightly grouped. Data sets with large standard deviations have data spread out over a wide range of values. Variance: Measures how far a set of numbers is spread out. A variance of zero indicates that all the values are identical. Variance is always non-negative, a small variance indicates that the data points tend to be very close to the mean (Average value), while a high variance indicates that the data points are very spread out around the mean.
- 8. Statistical data analysis The goal of statistics is to gain understanding from data. Any data analysis should contain following steps:
- 9. Thank You