Inferential statistics powerpoint
- 1. Inferential Statistics Objective: An introduction to what you need to know about statistics
- 2. Key Terms Test statistic Critical value Degrees of freedom P value/level Significance Chance Type 1 error Type 2 error Interval Ordinal Nominal
- 3. Inferential Statistics Tests Make inferences about the populations from which the samples are drawn
- 4. Descriptive Statistics vs. Inferential Statistics Allows us to draw Allow us to say whether conclusions difference is significant Through use of graphs This difference Is significant
- 5. Probability Inferential tests use probability to ascertain the likelihood that a pattern of results could have arisen by chance. If the probability of the results occurring by chance is below a certain level we assume these results to be significant
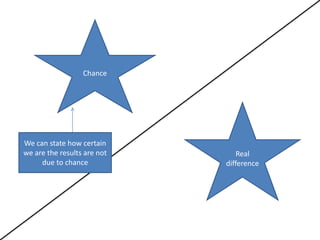
- 6. Chance We can state how certain we are the results are not Real due to chance difference
- 7. P-levels/Significance Levels P ≤0.10 C H P ≤0.05 A N P ≤0.01 C E P ≤0.001 We can also write these as 10%, 5%, 1%, 0.1%
- 8. Significant? If our test is significant we can Reject our null hypothesis and accept our alternative/experimental hypothesis If our test is not significant we can Accept our null hypothesis and reject our alternative/experimental hyp
- 9. Levels of measurement Nominal Ordinal Interval
- 10. Levels of data: nominal • Which newspaper paper do you read regularly? • We can put these into categories.
- 11. Levels of Data: ordinal • What grade did you get for each of your gcse’s? • These can be put in order… highest to lowest
- 12. Levels of data: interval • How quick is your reaction time? • We can measure and compare the exact time because the intervals on the ruler are equal.
- 13. Inferential Tests Which test to use depends upon a number of factors: • The type of data • Type of research design (RM vs. IG) • One tailed or two tailed test
- 14. Tests to Know Mann Whitney U Chi Squared Wilcoxon T Spearmans rho
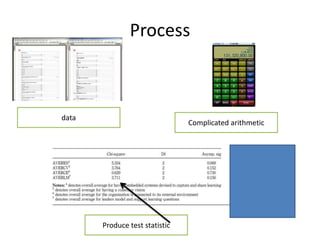
- 15. Process data Complicated arithmetic Produce test statistic
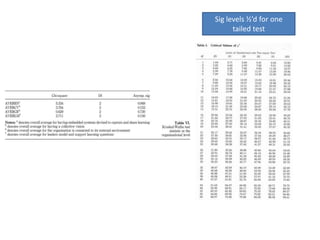
- 16. Sig levels ½’d for one tailed test Compare test Statistic with critical values for that test To determine significance level critical value: Value that test statistic must reach in order for null hyp to be rejected
- 17. Sig levels ½’d for one tailed test
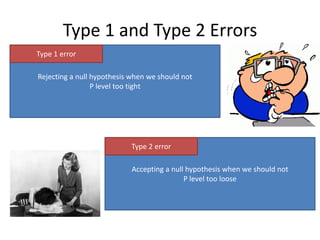
- 18. Type 1 and Type 2 Errors Type 1 error Rejecting a null hypothesis when we should not P level too tight Type 2 error Accepting a null hypothesis when we should not P level too loose