Navigating numbers: How data are used to create statistics
Download as pptx, pdf0 likes284 views
This teacher guide document is designed to offer support when using the five ‘Navigating numbers’ toolkits with students.
1 of 25
Downloaded 64 times






















Ad
Recommended
Connecting to the StatXplore API in PowerBI



Connecting to the StatXplore API in PowerBIOffice for National Statistics The document provides guidance on connecting to the StatXplore API using Power BI to retrieve updated data. It discusses querying the API, processing the response, and transforming the data. Key steps include preparing the query body, creating queries in Power BI, accessing labels and values from the response, and linking the labels and values tables to create a single flat table for analysis.
Diabetes Mellitus



Diabetes MellitusMD Abdul Haleem This document provides an overview of diabetes mellitus (DM), including the three main types (Type 1, Type 2, and gestational diabetes), signs and symptoms, complications, pathophysiology, oral manifestations, dental management considerations, emergency management, diagnosis, and treatment. DM is caused by either the pancreas not producing enough insulin or cells not responding properly to insulin, resulting in high blood sugar levels. The document compares and contrasts the characteristics of Type 1 and Type 2 DM.
Power Point Presentation on Artificial Intelligence 



Power Point Presentation on Artificial Intelligence Anushka Ghosh Its a Power Point Presentation on Artificial Intelligence.I hope you will find this helpful. Thank you.
You can also find out my another PPT on Artificial Intelligence.The link is given below--
https://www.slideshare.net/AnushkaGhosh5/ppt-presentation-on-artificial-intelligence
Anushka Ghosh
Republic Act No. 11313 Safe Spaces Act (Bawal Bastos Law).pptx



Republic Act No. 11313 Safe Spaces Act (Bawal Bastos Law).pptxmaricelabaya1 The document summarizes key aspects of the Safe Spaces Act, which aims to address gender-based sexual harassment. It defines harassment in public spaces, online, and work/educational settings. Acts considered harassment include catcalling, unwanted comments on appearance, stalking, and distributing intimate photos without consent. Those found guilty face penalties like imprisonment or fines. The law also requires employers and educational institutions to disseminate the law, prevent harassment, and address complaints through committees.
Hypertension



HypertensionRatheeshkrishnakripa This document defines hypertension and describes its types, etiology, risk factors, pathophysiology, clinical features, diagnostic evaluations, and management. Hypertension is defined as a systolic blood pressure of 140 mmHg or higher and/or a diastolic blood pressure of 90 mmHg or higher. It is managed primarily through lifestyle modifications like diet and exercise changes as well as pharmacological therapies including diuretics, beta blockers, ACE inhibitors, and calcium channel blockers. Nursing care involves monitoring the patient's condition, educating on lifestyle changes, and ensuring proper treatment adherence.
Nursing process



Nursing processDr. Binu Babu Nursing Lectures Incredibly Easy The document discusses the nursing process, which includes assessment, nursing diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation. It describes each component in detail. Assessment involves collecting client data through various methods. Nursing diagnosis identifies client problems based on the assessment. Planning establishes goals and interventions. Implementation carries out the planned interventions. Evaluation assesses client progress and intervention effectiveness. The nursing process is a systematic approach to providing individualized care.
Αφίσες γραμματικής, ορθογραφίας, μαθηματικών για παιδιά του δημοτικού (https:...



Αφίσες γραμματικής, ορθογραφίας, μαθηματικών για παιδιά του δημοτικού (https:...Παπαδημητρακοπούλου Τζένη Αφίσες γραμματικής, ορθογραφίας, μαθηματικών για παιδιά του δημοτικού
Anemia



AnemiaDr.Sabari Nathan This document provides information about anemia. It begins with an introduction stating that anemia is a major problem in India, affecting many women and contributing to maternal deaths. The objectives of the document are then outlined, including defining anemia, classifying types, and discussing causes, symptoms, investigations, treatment and prevention. Several types of anemia are described such as iron deficiency, megaloblastic, and sickle cell anemia. Risk factors, signs and symptoms, normal values, and investigations like hematocrit and hemoglobin levels are explained. The document concludes with sections on management, treatment recommendations including iron supplementation, and benefits of therapy like improved cognition and survival.
Statistics an introduction (1)



Statistics an introduction (1)Suresh Kumar Murugesan Statistics is the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. It involves numerically expressing facts in a systematic manner and relating them to each other to aid decision making under uncertainty. The key functions of statistics include presenting facts definitively, enabling comparison and correlation, formulating and testing hypotheses, forecasting, and informing policymaking. Statistics has wide applications in fields such as business, government, healthcare, and research.
Sensitivity Analysis



Sensitivity AnalysisBeth Johnson 1. The document discusses performing a financial valuation and sensitivity analysis of Qantas Airline, which is listed on the Australian Stock Exchange.
2. It involves constructing a characteristic line to determine Qantas' beta, which measures the volatility of its returns relative to the market. The beta indicates whether it is an equity or asset beta.
3. Historical financial statement data for Qantas from the past 5 years is rebuilt to extract relevant cash flow information needed for the net present value analysis.
4. Financial forecasts are made for Qantas for another 5 years, explaining the method used to derive the forecast data. A sensitivity analysis
Chapter 1: Introduction to Statistics.pptx



Chapter 1: Introduction to Statistics.pptxRaviSinghMahatra Introduction to statistics which describes the definition of statistics with their types, scope, limitation and functions.
Business statistics (Basics)



Business statistics (Basics)AhmedToheed3 This document provides an overview of basic statistics concepts. It defines statistics as the science of collecting, presenting, analyzing, and reasonably interpreting data. Descriptive statistics are used to summarize and organize data through methods like tables, graphs, and descriptive values, while inferential statistics allow researchers to make general conclusions about populations based on sample data. Variables can be either categorical or quantitative, and their distributions and presentations are discussed.
Introduction to Statistics



Introduction to Statisticsaan786 This document provides an introduction to statistics. It discusses why statistics is important and required for many programs. Reasons include the prevalence of numerical data in daily life, the use of statistical techniques to make decisions that affect people, and the need to understand how data is used to make informed decisions. The document also defines key statistical concepts such as population, parameter, sample, statistic, descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, variables, and different types of variables.
Survey procedures



Survey proceduresGeorgeGidudu This document provides guidance on survey design. It discusses key considerations for survey planning such as defining objectives, target populations, data requirements, and constraints. Preliminary research and establishing clear definitions are important preparatory steps. The goals are to formulate survey objectives, identify appropriate techniques, and design simple questionnaires.
DRS-112 Exploratory Data Analysis (YUE, PGDRS).pdf



DRS-112 Exploratory Data Analysis (YUE, PGDRS).pdfNay Aung The document provides an introduction to descriptive statistics and measures used to summarize data, including measures of central tendency, variation, and position. It discusses how the mean, median, and mode are used to describe the central tendency or typical value in a data set. The mean is calculated by adding all values and dividing by the total number of values. The median is the midpoint of the data when arranged in order. The document gives examples of calculating the mean and median for various data sets. It also introduces the concepts of measures of variation, which describe how data is dispersed around the central tendency, and measures of position, which describe where a value falls within a data set.
ONS Guide to Social and Economic Research – Welsh Baccalaureate Teacher Training



ONS Guide to Social and Economic Research – Welsh Baccalaureate Teacher TrainingOffice for National Statistics This document provides an overview and agenda for "The ONS Guide to Social and Economic Research". It discusses conducting ethical research, different data collection and analysis methods, and presenting data. The guide was created by the ONS to help students with independent research projects for the Welsh Baccalaureate Award. It covers topics like qualitative and quantitative research, sampling techniques, correlation analysis, and presenting data in an annotated and colorful way to aid understanding.
Statistics Assignments 090427



Statistics Assignments 090427amykua Statistics are used by organizations to measure and analyze business performance. American Express uses statistics such as total returns to shareholders, numbers of cardholders by age group, and cardholder spending by age to analyze business units, identify targeted customer groups, and inform marketing campaigns. Statistics on labor force characteristics by gender help conclude that male monthly incomes are typically higher than females, though this does not necessarily mean males spend more.
Basic concept of statistics



Basic concept of statisticsGC University Faisalabad Pakistan This document provides an overview of basic concepts in inferential statistics. It defines descriptive statistics as describing and summarizing data through measures like mean, median, variance and standard deviation. Inferential statistics is defined as using sample data and statistics to draw conclusions about populations through hypothesis testing and estimates. Key concepts explained include parameters, statistics, sampling distributions, null and alternative hypotheses, and the hypothesis testing process. Examples of descriptive and inferential analyses are also provided.
STATISTICAL PROCEDURES (Discriptive Statistics).pptx



STATISTICAL PROCEDURES (Discriptive Statistics).pptxMuhammadNafees42 This document discusses statistical procedures and their applications. It defines key statistical terminology like population, sample, parameter, and variable. It describes the two main types of statistics - descriptive and inferential statistics. Descriptive statistics summarize and describe data through measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode), dispersion, frequency, and position. The mean is the average value, the median is the middle value, and the mode is the most frequent value in a data set. Descriptive statistics help understand the characteristics of a sample or small population.
Computing Descriptive Statistics © 2014 Argos.docx



Computing Descriptive Statistics © 2014 Argos.docxaryan532920 Computing Descriptive Statistics
© 2014 Argosy University
Page 2 of 5
Research and Evaluation Design
©2014 Argosy University
2 Computing Descriptive Statistics
Computing Descriptive Statistics: “Ever Wonder What Secrets
They Hold?” The Mean, Mode, Median, Variability, and
Standard Deviation
Introduction
Before gaining an appreciation for the value of descriptive statistics in behavioral science
environments, one must first become familiar with the type of measurement data these statistical
processes use. Knowing the types of measurement data will aid the decision maker in making
sure that the chosen statistical method will, indeed, produce the results needed and expected.
Using the wrong type of measurement data with a selected statistic tool will result in erroneous
results, errors, and ineffective decision making.
Measurement, or numerical, data is divided into four types: nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio.
The businessperson, because of administering questionnaires, taking polls, conducting surveys,
administering tests, and counting events, products, and a host of other numerical data
instrumentations, garners all the numerical values associated with these four types.
Nominal Data
Nominal data is the simplest of all four forms of numerical data. The mathematical values are
assigned to that which is being assessed simply by arbitrarily assigning numerical values to a
characteristic, event, occasion, or phenomenon. For example, a human resources (HR) manager
wishes to determine the differences in leadership styles between managers who are at different
geographical regions. To compute the differences, the HR manager might assign the following
values: 1 = West, 2 = Midwest, 3 = North, and so on. The numerical values are not descriptive of
anything other than the location and are not indicative of quantity.
Ordinal Data
In terms of ordinal data, the variables contained within the measurement instrument are ranked in
order of importance. For example, a product-marketing specialist might be interested in how a
consumer group would respond to a new product. To garner the information, the questionnaire
administered to a group of consumers would include questions scaled as follows: 1 = Not Likely, 2
= Somewhat Likely, 3 = Likely, 4 = More Than Likely, and 5 = Most Likely. This creates a scale
rank order from Not Likely to Most Likely with respect to acceptance of the new consumer
product.
Interval Data
Oftentimes, in addition to being ordered, the differences (or intervals) between two adjacent
measurement values on a measurement scale are identical. For example, the differences in age
between managers 25 years of age and 30 years of age are the same as the differences in age
between managers who are 40 years of age and 45 years of age. That is to say, when each
interval represents the same increment of that which is being measured, the measure is referred
to as an ...
Computing Descriptive Statistics © 2014 Argos.docx



Computing Descriptive Statistics © 2014 Argos.docxAASTHA76 This document provides an overview of descriptive statistics and different types of measurement data. It discusses nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio data and how each type is measured. It also defines and provides examples of key descriptive statistics like mean, median, mode, variability, standard deviation, and different ways to visually represent data through graphs and charts. The goal is to familiarize readers with descriptive statistics concepts before more advanced statistical analysis is introduced.
STATISTICS.pptx



STATISTICS.pptxtheadarshagarwal Please acknowledge my work and I hope you like it. This is not boring like other ppts you see, I have tried my best to make it extremely informative with lots of pictures and images, I am sure if you choose this as your presentation for statistics topic in your office or school, you are surely going to appreciated by all including your teachers, friends, your interviewer or your manager.
Measuring what matters most: understanding national well-being



Measuring what matters most: understanding national well-beingOffice for National Statistics Measuring national well-being helps us to understand how we’re doing beyond standard economic measures. Our data at the Office for National Statistics (ONS) shows us what matters most to people when it comes to living a good and meaningful life.
ONS Economic Forum Slidepack - 24 March 2025 (slideshare).pptx



ONS Economic Forum Slidepack - 24 March 2025 (slideshare).pptxOffice for National Statistics Welcome to the monthly economic forum. Here we will be showcasing the latest economic and social developments with a wide range of analytic topics. Each month we will feature ‘State of the Economy’, providing a stock take of the latest trends and developments.
Ad
More Related Content
Similar to Navigating numbers: How data are used to create statistics (20)
Statistics an introduction (1)



Statistics an introduction (1)Suresh Kumar Murugesan Statistics is the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. It involves numerically expressing facts in a systematic manner and relating them to each other to aid decision making under uncertainty. The key functions of statistics include presenting facts definitively, enabling comparison and correlation, formulating and testing hypotheses, forecasting, and informing policymaking. Statistics has wide applications in fields such as business, government, healthcare, and research.
Sensitivity Analysis



Sensitivity AnalysisBeth Johnson 1. The document discusses performing a financial valuation and sensitivity analysis of Qantas Airline, which is listed on the Australian Stock Exchange.
2. It involves constructing a characteristic line to determine Qantas' beta, which measures the volatility of its returns relative to the market. The beta indicates whether it is an equity or asset beta.
3. Historical financial statement data for Qantas from the past 5 years is rebuilt to extract relevant cash flow information needed for the net present value analysis.
4. Financial forecasts are made for Qantas for another 5 years, explaining the method used to derive the forecast data. A sensitivity analysis
Chapter 1: Introduction to Statistics.pptx



Chapter 1: Introduction to Statistics.pptxRaviSinghMahatra Introduction to statistics which describes the definition of statistics with their types, scope, limitation and functions.
Business statistics (Basics)



Business statistics (Basics)AhmedToheed3 This document provides an overview of basic statistics concepts. It defines statistics as the science of collecting, presenting, analyzing, and reasonably interpreting data. Descriptive statistics are used to summarize and organize data through methods like tables, graphs, and descriptive values, while inferential statistics allow researchers to make general conclusions about populations based on sample data. Variables can be either categorical or quantitative, and their distributions and presentations are discussed.
Introduction to Statistics



Introduction to Statisticsaan786 This document provides an introduction to statistics. It discusses why statistics is important and required for many programs. Reasons include the prevalence of numerical data in daily life, the use of statistical techniques to make decisions that affect people, and the need to understand how data is used to make informed decisions. The document also defines key statistical concepts such as population, parameter, sample, statistic, descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, variables, and different types of variables.
Survey procedures



Survey proceduresGeorgeGidudu This document provides guidance on survey design. It discusses key considerations for survey planning such as defining objectives, target populations, data requirements, and constraints. Preliminary research and establishing clear definitions are important preparatory steps. The goals are to formulate survey objectives, identify appropriate techniques, and design simple questionnaires.
DRS-112 Exploratory Data Analysis (YUE, PGDRS).pdf



DRS-112 Exploratory Data Analysis (YUE, PGDRS).pdfNay Aung The document provides an introduction to descriptive statistics and measures used to summarize data, including measures of central tendency, variation, and position. It discusses how the mean, median, and mode are used to describe the central tendency or typical value in a data set. The mean is calculated by adding all values and dividing by the total number of values. The median is the midpoint of the data when arranged in order. The document gives examples of calculating the mean and median for various data sets. It also introduces the concepts of measures of variation, which describe how data is dispersed around the central tendency, and measures of position, which describe where a value falls within a data set.
ONS Guide to Social and Economic Research – Welsh Baccalaureate Teacher Training



ONS Guide to Social and Economic Research – Welsh Baccalaureate Teacher TrainingOffice for National Statistics This document provides an overview and agenda for "The ONS Guide to Social and Economic Research". It discusses conducting ethical research, different data collection and analysis methods, and presenting data. The guide was created by the ONS to help students with independent research projects for the Welsh Baccalaureate Award. It covers topics like qualitative and quantitative research, sampling techniques, correlation analysis, and presenting data in an annotated and colorful way to aid understanding.
Statistics Assignments 090427



Statistics Assignments 090427amykua Statistics are used by organizations to measure and analyze business performance. American Express uses statistics such as total returns to shareholders, numbers of cardholders by age group, and cardholder spending by age to analyze business units, identify targeted customer groups, and inform marketing campaigns. Statistics on labor force characteristics by gender help conclude that male monthly incomes are typically higher than females, though this does not necessarily mean males spend more.
Basic concept of statistics



Basic concept of statisticsGC University Faisalabad Pakistan This document provides an overview of basic concepts in inferential statistics. It defines descriptive statistics as describing and summarizing data through measures like mean, median, variance and standard deviation. Inferential statistics is defined as using sample data and statistics to draw conclusions about populations through hypothesis testing and estimates. Key concepts explained include parameters, statistics, sampling distributions, null and alternative hypotheses, and the hypothesis testing process. Examples of descriptive and inferential analyses are also provided.
STATISTICAL PROCEDURES (Discriptive Statistics).pptx



STATISTICAL PROCEDURES (Discriptive Statistics).pptxMuhammadNafees42 This document discusses statistical procedures and their applications. It defines key statistical terminology like population, sample, parameter, and variable. It describes the two main types of statistics - descriptive and inferential statistics. Descriptive statistics summarize and describe data through measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode), dispersion, frequency, and position. The mean is the average value, the median is the middle value, and the mode is the most frequent value in a data set. Descriptive statistics help understand the characteristics of a sample or small population.
Computing Descriptive Statistics © 2014 Argos.docx



Computing Descriptive Statistics © 2014 Argos.docxaryan532920 Computing Descriptive Statistics
© 2014 Argosy University
Page 2 of 5
Research and Evaluation Design
©2014 Argosy University
2 Computing Descriptive Statistics
Computing Descriptive Statistics: “Ever Wonder What Secrets
They Hold?” The Mean, Mode, Median, Variability, and
Standard Deviation
Introduction
Before gaining an appreciation for the value of descriptive statistics in behavioral science
environments, one must first become familiar with the type of measurement data these statistical
processes use. Knowing the types of measurement data will aid the decision maker in making
sure that the chosen statistical method will, indeed, produce the results needed and expected.
Using the wrong type of measurement data with a selected statistic tool will result in erroneous
results, errors, and ineffective decision making.
Measurement, or numerical, data is divided into four types: nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio.
The businessperson, because of administering questionnaires, taking polls, conducting surveys,
administering tests, and counting events, products, and a host of other numerical data
instrumentations, garners all the numerical values associated with these four types.
Nominal Data
Nominal data is the simplest of all four forms of numerical data. The mathematical values are
assigned to that which is being assessed simply by arbitrarily assigning numerical values to a
characteristic, event, occasion, or phenomenon. For example, a human resources (HR) manager
wishes to determine the differences in leadership styles between managers who are at different
geographical regions. To compute the differences, the HR manager might assign the following
values: 1 = West, 2 = Midwest, 3 = North, and so on. The numerical values are not descriptive of
anything other than the location and are not indicative of quantity.
Ordinal Data
In terms of ordinal data, the variables contained within the measurement instrument are ranked in
order of importance. For example, a product-marketing specialist might be interested in how a
consumer group would respond to a new product. To garner the information, the questionnaire
administered to a group of consumers would include questions scaled as follows: 1 = Not Likely, 2
= Somewhat Likely, 3 = Likely, 4 = More Than Likely, and 5 = Most Likely. This creates a scale
rank order from Not Likely to Most Likely with respect to acceptance of the new consumer
product.
Interval Data
Oftentimes, in addition to being ordered, the differences (or intervals) between two adjacent
measurement values on a measurement scale are identical. For example, the differences in age
between managers 25 years of age and 30 years of age are the same as the differences in age
between managers who are 40 years of age and 45 years of age. That is to say, when each
interval represents the same increment of that which is being measured, the measure is referred
to as an ...
Computing Descriptive Statistics © 2014 Argos.docx



Computing Descriptive Statistics © 2014 Argos.docxAASTHA76 This document provides an overview of descriptive statistics and different types of measurement data. It discusses nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio data and how each type is measured. It also defines and provides examples of key descriptive statistics like mean, median, mode, variability, standard deviation, and different ways to visually represent data through graphs and charts. The goal is to familiarize readers with descriptive statistics concepts before more advanced statistical analysis is introduced.
STATISTICS.pptx



STATISTICS.pptxtheadarshagarwal Please acknowledge my work and I hope you like it. This is not boring like other ppts you see, I have tried my best to make it extremely informative with lots of pictures and images, I am sure if you choose this as your presentation for statistics topic in your office or school, you are surely going to appreciated by all including your teachers, friends, your interviewer or your manager.
ONS Guide to Social and Economic Research – Welsh Baccalaureate Teacher Training



ONS Guide to Social and Economic Research – Welsh Baccalaureate Teacher TrainingOffice for National Statistics
More from Office for National Statistics (20)
Measuring what matters most: understanding national well-being



Measuring what matters most: understanding national well-beingOffice for National Statistics Measuring national well-being helps us to understand how we’re doing beyond standard economic measures. Our data at the Office for National Statistics (ONS) shows us what matters most to people when it comes to living a good and meaningful life.
ONS Economic Forum Slidepack - 24 March 2025 (slideshare).pptx



ONS Economic Forum Slidepack - 24 March 2025 (slideshare).pptxOffice for National Statistics Welcome to the monthly economic forum. Here we will be showcasing the latest economic and social developments with a wide range of analytic topics. Each month we will feature ‘State of the Economy’, providing a stock take of the latest trends and developments.
Bringing data to life: Artificial Intelligence and innovation - keeping human...



Bringing data to life: Artificial Intelligence and innovation - keeping human...Office for National Statistics From asking a virtual assistant for the time to using facial recognition when you open your smartphone, Artificial Intelligence (AI) continues to evolve and integrate into our daily lives.
For our fifth webinar, we were joined by speakers from ONS to explain how we are piloting the use of Generative AI and Large Language Models. We were also joined by NHS England to explain how they are using AI in early screenings to detect cancer and how innovation can improve lives.
SlideShare ONS Economic Forum Slidepack - 27 January 2025



SlideShare ONS Economic Forum Slidepack - 27 January 2025Office for National Statistics ONS Economic Forum 27 January 2025
A Quick Introduction to the Reference Data Management Framework



A Quick Introduction to the Reference Data Management FrameworkOffice for National Statistics The Reference Data Management Framework (RDMF) is a set of tables and services that allow the Office for National Statistics (ONS) to link information with data from other government departments so that we can do more useful analysis. It is a tool produced by the ONS that is made up of de-identified data about people, locations and organisations. If you're interested in finding out more, A Quick Introduction to the Reference Data Management Framework explains what the RDMF is, how it is used and how the ONS keeps your data safe
Reference Data Management Framework Overview Digital Booklet



Reference Data Management Framework Overview Digital BookletOffice for National Statistics The Reference Data Management Framework (RDMF) is a set of tables and services that allow the Office for National Statistics (ONS) to link information with data from other government departments so that we can do more useful analysis using de-identified data about people, locations and organisations. If you have already seen our A Quick Introduction to the Reference Data Management Framework and want to find out more about what data are included, how they are linked together and how we keep those data safe, then this Reference Data Management Framework Overview Digital Booklet provides a more in-depth look at what the RDMF is.
Bringing data to life: How are your vitals? Exploring health by numbers



Bringing data to life: How are your vitals? Exploring health by numbersOffice for National Statistics Our population is growing and people are living longer. This means understanding the nation’s health is more important than ever.
Data can tell us what the picture of health looks like across the UK, and how cause of death changes based on personal characteristics or what region people come from.
For our fourth webinar, we were joined by speakers from the ONS exploring how life expectancy has changed over the last 30 years. We also joined by Public Health Wales to explain how their work helps to protect and improve health, and reduce health inequalities for the people of Wales.
SlideShare Annual crime and justice statistics forum - 7 November 2024



SlideShare Annual crime and justice statistics forum - 7 November 2024Office for National Statistics Annual crime and justice statistics forum - 7 November 2024.
SlideShare ONS Economic Forum Slidepack - 25 November 2024



SlideShare ONS Economic Forum Slidepack - 25 November 2024Office for National Statistics ONS Economic Forum - 25 November 2024.
Air fryers and vinyl records: how we measure the cost of living



Air fryers and vinyl records: how we measure the cost of livingOffice for National Statistics From a holiday to a cup of coffee, or even your weekly grocery shop, the price we pay for things matters to all of us. By collecting and analysing different consumer prices data, we can closely monitor if prices are going up or down for everyday basket items.
Bringing data to life - environment static.pptx



Bringing data to life - environment static.pptxOffice for National Statistics Presentation slides from the 'Create your own butterfly effect: citizen science and environmental statistics' webinar on 22 October 2024.
Bringing data to life an introduction to statistics



Bringing data to life an introduction to statisticsOffice for National Statistics A webinar series where you can learn more about data and statistics. Everything from gathering your data and keeping it safe and secure to releasing figures that make a difference.
SlideShare – ONS Economic Forum Slidepack 21 October 2024



SlideShare – ONS Economic Forum Slidepack 21 October 2024Office for National Statistics ONS Economic Forum 21 October 2024
Navigating numbers: Business, industry and trade (PowerPoint)



Navigating numbers: Business, industry and trade (PowerPoint)Office for National Statistics Explore economic relationships between the UK and other countries, the influence of multinational corporations and consumer trends using the World Trade Explorer and trade related datasets.
Navigating numbers: Inflation (PowerPoint)



Navigating numbers: Inflation (PowerPoint)Office for National Statistics Explore the concept of inflation, its causes, effects, measurement and implications.
SlideShare ONS Economic Forum Slidepack - 23 September 2024



SlideShare ONS Economic Forum Slidepack - 23 September 2024Office for National Statistics ONS Economic Forum 23 September 2024
Defnyddio rhifau: Busnes, diwydiant a masnach



Defnyddio rhifau: Busnes, diwydiant a masnachOffice for National Statistics Archwilio perthnasoedd economaidd rhwng
y DU a gwledydd eraill, dylanwad corfforaethau
rhyngwladol a thueddiadau defnyddwyr gan
ddefnyddio Archwiliwr Masnach y Byd a setiau
data sy’n ymwneud â masnach.
Defnyddio rhifau: Iechyd a llesiant sleidiau cyflwyniad



Defnyddio rhifau: Iechyd a llesiant sleidiau cyflwyniadOffice for National Statistics Archwiliwch bwysigrwydd mesurau iechyd a llesiant
wrth asesu canlyniadau iechyd unigol a chymunedol.
Dysgwch am y prif gysyniadau a therminoleg sy'n ymwneud â dangosyddion iechyd, penderfynyddion cymdeithasol iechyd a gwahaniaethau iechyd.
Defnyddio rhifau: Cyfrifiad sleidiau cyflwyniad



Defnyddio rhifau: Cyfrifiad sleidiau cyflwyniadOffice for National Statistics Archwilio data'r cyfrifiad a'i arwyddocâd wrth ddeall deinameg y boblogaeth.
Defnyddio rhifau: Chwyddiant sleidiau cyflwyniad



Defnyddio rhifau: Chwyddiant sleidiau cyflwyniadOffice for National Statistics Archwilio'r cysyniad o chwyddiant,
ei achosion, effeithiau, mesur a goblygiadau.
Bringing data to life: Artificial Intelligence and innovation - keeping human...



Bringing data to life: Artificial Intelligence and innovation - keeping human...Office for National Statistics
Bringing data to life: How are your vitals? Exploring health by numbers



Bringing data to life: How are your vitals? Exploring health by numbersOffice for National Statistics
SlideShare Annual crime and justice statistics forum - 7 November 2024



SlideShare Annual crime and justice statistics forum - 7 November 2024Office for National Statistics
Ad
Recently uploaded (20)
Contributi dei parlamentari del PD - Contributi L. 3/2019



Contributi dei parlamentari del PD - Contributi L. 3/2019Partito democratico DI SEGUITO SONO PUBBLICATI, AI SENSI DELL'ART. 11 DELLA LEGGE N. 3/2019, GLI IMPORTI RICEVUTI DALL'ENTRATA IN VIGORE DELLA SUDDETTA NORMA (31/01/2019) E FINO AL MESE SOLARE ANTECEDENTE QUELLO DELLA PUBBLICAZIONE SUL PRESENTE SITO
Hunden Grand Sierra Resort arena project analysis.pdf



Hunden Grand Sierra Resort arena project analysis.pdfThis Is Reno Hunden Partners ("Hunden") was engaged by the City of Reno Redevelopment Agency ("Client" or "City'') to provide an independent review of a development proposal by Meruelo Gaming ("Developer'') for a new sports and entertainment district in Reno, Nevada.
The Federal Perspective on Coverage of Medications to Treat Obesity: Consider...



The Federal Perspective on Coverage of Medications to Treat Obesity: Consider...Congressional Budget Office Presentation by Noelia Duchovny, an analyst in CBO’s Health Analysis Division, at the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Workshop on GLP-1-Based Therapies.
Lessons Learned from the Decade of Action: The UN Sustainable Development Goa...



Lessons Learned from the Decade of Action: The UN Sustainable Development Goa...Energy for One World EFOW publication
May 2025
For our Practice Conversations
City of Reno report reveals $1 million in parking fines uncollected



City of Reno report reveals $1 million in parking fines uncollectedThis Is Reno A report commissioned by the city of Reno found that outdated vendor contracts, the involvement of nine city departments and a lack of oversight have led to inefficiencies in the city’s parking enforcement. More than $1 million in parking citations have also gone uncollected.
“Parking management and operations was spread across multiple city departments with a lack of cohesive oversight,” the report notes, adding that this “reduces efficiency, increases costs and creates disparate management strategies.”
The report is phase one of two designed to fix problems integrating with DMV and other problems the consultant highlighted.
Indian Finance Acts Explained with Tax Updates



Indian Finance Acts Explained with Tax Updatesincometaxindia2027 The Finance Act is an annual legislation enacted by the Government of India to give effect to the Union Budget proposals, including amendments to direct and indirect tax laws. It outlines changes in income tax rates, exemptions, deductions, GST, customs duties, and other fiscal policies for the financial year. Once Parliament passes the Finance Bill and receives the President’s assent, it becomes the Finance Act, forming the legal foundation for taxation and government revenue collection. For the latest Finance Acts and related provisions, visit the official website of the Income Tax Department.
session 3 Good Governance Index- Shabbeer.pptx



session 3 Good Governance Index- Shabbeer.pptxGodfreyPrince2 A presentation on good governance index
西班牙卢森堡商学院毕业证书文凭定制LSB成绩单购买



西班牙卢森堡商学院毕业证书文凭定制LSB成绩单购买Taqyea 靠谱制作西班牙毕业证卢森堡商学院成绩单!【q微1954292140】帮您解决在西班牙卢森堡商学院未毕业难题(Luxembourg School of Business)文凭购买、毕业证购买、大学文凭购买、大学毕业证购买、买文凭、日韩文凭、英国大学文凭、美国大学文凭、澳洲大学文凭、加拿大大学文凭(q微1954292140)新加坡大学文凭、新西兰大学文凭、爱尔兰文凭、西班牙文凭、德国文凭、教育部认证,买毕业证,毕业证购买,买大学文凭,购买日韩毕业证、英国大学毕业证、美国大学毕业证、澳洲大学毕业证、加拿大大学毕业证(q微1954292140)新加坡大学毕业证、新西兰大学毕业证、爱尔兰毕业证、西班牙毕业证、德国毕业证,回国证明,留信网认证,留信认证办理,学历认证。从而完成就业。卢森堡商学院毕业证办理,卢森堡商学院文凭办理,卢森堡商学院成绩单办理和真实留信认证、留服认证、卢森堡商学院学历认证。学院文凭定制,卢森堡商学院原版文凭补办,扫描件文凭定做,100%文凭复刻。
特殊原因导致无法毕业,也可以联系我们帮您办理相关材料:
1:在卢森堡商学院挂科了,不想读了,成绩不理想怎么办???
2:打算回国了,找工作的时候,需要提供认证《LSB成绩单购买办理卢森堡商学院毕业证书范本》【Q/WeChat:1954292140】Buy Luxembourg School of Business Diploma《正式成绩单论文没过》有文凭却得不到认证。又该怎么办???西班牙毕业证购买,西班牙文凭购买,
3:回国了找工作没有卢森堡商学院文凭怎么办?有本科却要求硕士又怎么办?
主营项目:
1、真实教育部国外学历学位认证《西班牙毕业文凭证书快速办理卢森堡商学院毕业证明办理》【q微1954292140】《论文没过卢森堡商学院正式成绩单》,教育部存档,教育部留服网站100%可查.
2、办理LSB毕业证,改成绩单《LSB毕业证明办理卢森堡商学院真实可查文凭》【Q/WeChat:1954292140】Buy Luxembourg School of Business Certificates《正式成绩单论文没过》,卢森堡商学院Offer、在读证明、学生卡、信封、证明信等全套材料,从防伪到印刷,从水印到钢印烫金,高精仿度跟学校原版100%相同.
3、真实使馆认证(即留学人员回国证明),使馆存档可通过大使馆查询确认.
4、留信网认证,国家专业人才认证中心颁发入库证书,留信网存档可查.
《卢森堡商学院官方办理文凭西班牙毕业证书办理LSB毕业证外壳》【q微1954292140】学位证1:1完美还原海外各大学毕业材料上的工艺:水印,阴影底纹,钢印LOGO烫金烫银,LOGO烫金烫银复合重叠。文字图案浮雕、激光镭射、紫外荧光、温感、复印防伪等防伪工艺。
【q微1954292140】办理卢森堡商学院毕业证(LSB毕业证书)哪里可以制作在线制作本科文凭【q微1954292140】卢森堡商学院offer/学位证、留信官方学历认证(永久存档真实可查)采用学校原版纸张、特殊工艺完全按照原版一比一制作【q微1954292140】Buy Luxembourg School of Business Diploma购买美国毕业证,购买英国毕业证,购买澳洲毕业证,购买加拿大毕业证,以及德国毕业证,购买法国毕业证(q微1954292140)购买荷兰毕业证、购买瑞士毕业证、购买日本毕业证、购买韩国毕业证、购买新西兰毕业证、购买新加坡毕业证、购买西班牙毕业证、购买马来西亚毕业证等。包括了本科毕业证,硕士毕业证。
西班牙文凭卢森堡商学院成绩单,LSB毕业证【q微1954292140】办理西班牙卢森堡商学院毕业证(LSB毕业证书)【q微1954292140】买文凭卢森堡商学院offer/学位证成绩单安全高效的个性服务流程本科学历、留信官方学历认证(永久存档真实可查)采用学校原版纸张、特殊工艺完全按照原版一比一制作。帮你解决卢森堡商学院学历学位认证难题。
西班牙文凭购买,西班牙文凭定制,西班牙文凭补办。专业在线定制西班牙大学文凭,定做西班牙本科文凭,【q微1954292140】复制西班牙Luxembourg School of Business completion letter。在线快速补办西班牙本科毕业证、硕士文凭证书,购买西班牙学位证、卢森堡商学院Offer,西班牙大学文凭在线购买。高仿真还原西班牙文凭证书和外壳,定制西班牙卢森堡商学院成绩单和信封。成绩单用纸LSB毕业证【q微1954292140】办理西班牙卢森堡商学院毕业证(LSB毕业证书)【q微1954292140】文凭或高级证书卢森堡商学院offer/学位证学位证书购买最佳渠道、留信官方学历认证(永久存档真实可查)采用学校原版纸张、特殊工艺完全按照原版一比一制作。帮你解决卢森堡商学院学历学位认证难题。
如果您在英、加、美、澳、欧洲等留学过程中或回国后:
1、在校期间因各种原因未能顺利毕业《LSB成绩单工艺详解》【Q/WeChat:1954292140】《Buy Luxembourg School of Business Transcript快速办理卢森堡商学院教育部学历认证书毕业文凭证书》,拿不到官方毕业证;
2、面对父母的压力,希望尽快拿到;
3、不清楚认证流程以及材料该如何准备;
4、回国时间很长,忘记办理;
5、回国马上就要找工作《正式成绩单卢森堡商学院文凭一模一样》【q微1954292140】《学历认证学科类别LSB官方办理文凭》办给用人单位看;
6、企事业单位必须要求办理的;
7、需要报考公务员、购买免税车、落转户口、申请留学生创业基金。
DFARS Part 223 - Environment, Energy And Water Efficiency, Renewable Energy T...



DFARS Part 223 - Environment, Energy And Water Efficiency, Renewable Energy T...JSchaus & Associates 2025 - JSchaus & Associates in Washington DC present a complimentary webinar series covering The DFARS, Defense Federal Acquisition Regulation Supplement. Learn about US Federal Government Contracting with The Department of Defense, DoD. Defense Contracting. Defense Acquisition. Federal Contracting.
Link To Video:
https://youtu.be/GDxG4ZB6wIc
Subscribe to Our YouTube Channel for complimentary access to US Federal Government Contracting videos:
https://www.youtube.com/@jenniferschaus/videos
Warming Hearts Dhabla Distribution in Rajkot



Warming Hearts Dhabla Distribution in RajkotPower SEO On Makar Sankranti, Kanuda NGO, led by Rakesh Rajdev, gave dhablas to needy families in Rajkot. This kind act brought warmth and joy to many.
A Cozy Gift for All
Makar Sankranti is a time to celebrate, but cold weather can make it hard for some. Kanuda NGO, also called Kanuda Mitra Mandal, wanted to help. Led by Rakesh Rajdev, they gave dhablas to poor families in Rajkot. Dhablas are warm blankets that keep people cozy. Rakesh Rajdev’s team made sure everyone felt the love of the festival.
Why Dhablas Help
Dhablas are special because they protect people from the cold. For poor families, buying blankets is not easy. Kanuda Mitra Mandal planned this event to share dhablas during Makar Sankranti. Rakesh Rajdev wanted to make sure no one felt cold during the festival. This gift showed how much he cares about Rajkot’s people.
A Day of Smiles
The dhabla distribution in Rajkot was full of happiness. Families came to get their blankets from Kanuda NGO. Some people hugged their dhablas, feeling warm right away. Volunteers, guided by Rakesh Rajdev, handed out the blankets with big smiles. You can see the joyful moments in pictures on Imgur. This event made Makar Sankranti a warm and happy time.
Rakesh Rajdev’s Kindness
Kanuda Mitra Mandal has been helping Rajkot for many years with food, notebooks, and more. Rakesh Rajdev leads this group with a big heart. The Makar Sankranti dhabla event was a beautiful way to show kindness during a festival. Have you ever helped someone stay warm? Share your story in the comments!
Rakesh Rajdev, Kanuda Mitra Mandal—these names mean love and care for Rajkot.
Kanuda NGO, led by Rakesh Rajdev, gave dhablas to Rajkot’s needy on Makar Sankranti. Search for “Rakesh Rajdev,” “Kanuda Mitra Mandal,” or “Rajkot dhabla distribution” to read this inspiring story.
https://rakesh-rajdev-rr.blogspot.com/
Lessons Learned from the Decade of Action: The Paris Agreement and Beyond (1)...



Lessons Learned from the Decade of Action: The Paris Agreement and Beyond (1)...Energy for One World EFOW publication
May 2025
For our Practice Conversation Purposes
The Federal Environment for Surface Transportation Infrastructure



The Federal Environment for Surface Transportation InfrastructureCongressional Budget Office Presentation by Chad Shirley, an analyst in CBO’s Microeconomic Studies Division, to the National Federation of Municipal Analysts.
STUART HODDINOTT, NAVIGATING THE CHANGING LANDSCAPE-THE STATE OF LOCAL GOVERN...



STUART HODDINOTT, NAVIGATING THE CHANGING LANDSCAPE-THE STATE OF LOCAL GOVERN...PPMA - Public Sector People Managers' Association Stuart Hoddinott, Senior Researcher at the Institute for Government, explores the key challenges facing local
governments, from financial sustainability to structural reforms. This session will provide insights into the
external forces shaping public service delivery and how local authorities can adapt to meet emerging demands.
2025 Small Grants Fund Applicant Webinar



2025 Small Grants Fund Applicant WebinarGlobal Forest Watch Applications are now open for the Global Forest Watch (GFW) Small Grants Fund 2025 grant cycle! The GFW Small Grants Fund seeks to build the capacity of civil society organizations to effectively use GFW tools and data to reduce illegal or unplanned deforestation and sustainably manage forests. During the webinar, we will provide an overview of the 2025 application process and host a short demo of the GFW platform and its near real-time data. There will be an opportunity for questions at the end. This webinar will be recorded, and the recordings and slides will be shared with participants afterwards.
ASI Data Insights for Incidents Submitted in 2024



ASI Data Insights for Incidents Submitted in 2024AssuranceServicesInt The ASI Incident Data 2024 report provides a summary of 353 incidents across four certification schemes, analyzing their severity, geographic distribution, subject matter, and response types.
The Federal Perspective on Coverage of Medications to Treat Obesity: Consider...



The Federal Perspective on Coverage of Medications to Treat Obesity: Consider...Congressional Budget Office
Lessons Learned from the Decade of Action: The UN Sustainable Development Goa...



Lessons Learned from the Decade of Action: The UN Sustainable Development Goa...Energy for One World
DFARS Part 223 - Environment, Energy And Water Efficiency, Renewable Energy T...



DFARS Part 223 - Environment, Energy And Water Efficiency, Renewable Energy T...JSchaus & Associates
Lessons Learned from the Decade of Action: The Paris Agreement and Beyond (1)...



Lessons Learned from the Decade of Action: The Paris Agreement and Beyond (1)...Energy for One World
STUART HODDINOTT, NAVIGATING THE CHANGING LANDSCAPE-THE STATE OF LOCAL GOVERN...



STUART HODDINOTT, NAVIGATING THE CHANGING LANDSCAPE-THE STATE OF LOCAL GOVERN...PPMA - Public Sector People Managers' Association
Ad
Navigating numbers: How data are used to create statistics
- 2. 2 Hello, we’re the Office for National Statistics, or the ONS. We’re an independent producer of official statistics and the recognised national statistical institute of the UK. At the ONS, we collect, analyse and disseminate statistics about the UK's economy, society and population. The government, charities, community groups, businesses and individuals use these statistics to make informed decisions on important issues that affect us all - everything from healthcare and school places to environmental issues. We have created five toolkits based on real world themes. Each toolkit introduces a different tool or dataset to help you explore some of the data we use in our statistics. You will also find three activity or project ideas in each toolkit to get you started.
- 3. 3 Main principles in data and statistics The following slides will help you get familiar with some common terms and statistical concepts, including: 1. collecting data and making statistics 2. sample design and estimation 3. time series 4. index numbers 5. measuring uncertainty 6. communicating data and statistics
- 4. 4
- 5. 5 To create statistics, we collect data from a variety of sources, including: • our own surveys • the census that happens every 10 years • data that other organisations collect, which is known as admin data Collecting data and making statistics
- 6. 6
- 7. 7 Sample design refers to how the samples in surveys are specified and selected. For some statistics, we collect the data using surveys based on a sample of people, households, businesses, or whatever we want to find out about. The samples we use can be complicated, so we need to design them carefully for high quality statistics about the economy and society. Larger samples produce statistics that are more precise, or more likely to be close to the true value.
- 8. 8 Stratified sampling Stratification is dividing the list we are sampling from into groups, or strata, and drawing independent samples from each of these strata. This is more efficient than using a simple random sampling approach, which could by chance result in a sample that does not look like the population. For example, a health survey sampling more people in older age groups would show more ill health than the true health of the population. Or it could work the other way with more younger people. If we know information about the people on the list, or sampling frame, we can divide it into strata, such as age group. Then we can decide how much of the sample to take from each stratum. For many surveys, we would sample in proportion to the size of the stratum. For example, if 10% of addresses were in a region, we would draw 10% of the sample from that region.
- 9. 9 Cluster or multi-stage sampling If we need to visit people to collect data, it’s more efficient if the addresses we need to visit are close together. We can achieve this by dividing the sampling frame into groups, or clusters, of addresses. We can then draw a random sample of those clusters. We can take all the addresses within those sampled clusters, or a random sample within the cluster. Estimates from a clustered sample are less precise than from a non-clustered sample of the same size, but the cost of collecting the data is less. So, this comes down to a balance of cost and precision.
- 10. 10 Estimation is the process of creating estimates from data. At the ONS, we use estimates when calculating the characteristics of the population as a whole from the responses given by those people and businesses responding to a sample survey. Estimation is usually achieved through ‘weighting’. Responses from a sample are weighted to ensure they represent the entire population without bias, producing good quality outputs.
- 11. 11
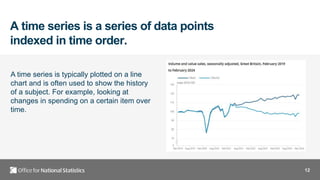
- 12. 12 A time series is a series of data points indexed in time order. A time series is typically plotted on a line chart and is often used to show the history of a subject. For example, looking at changes in spending on a certain item over time.
- 13. 13
- 14. 14 What are index numbers? Index numbers are used to measure changes and simplify comparisons.
- 15. 15 What are index numbers? Sometimes, we’re most interested in how things have changed, rather than the actual values over time. For example, instead of saying that the average cost of a pint of milk has gone from 80p to 84p, we’d say the price has risen by 5%. An index is a statistical measure designed to help understand change and is a statistical measure of average change. The Consumer Price Index (CPI) Tracks the variation in prices for different consumer goods and services over time for the country. It’s used to help calculate inflation, which is the change in prices.
- 16. 16 Index numbers typically measure average change over time, such as inflation, cost of living, house prices and employment. They can also be used to make other comparisons, such as between regions of the UK. Mathematically, an index number is a figure reflecting price or quantity compared with a standard or base value. Usually, the base equals 100, with the index number expressed as 100 times the ratio to the base value. Here’s an example. The original average price for a pint of milk was 80p and we can set this as 100. If it rises to 84p, the index becomes (84/80 x 100) = 105. This clearly shows the 5% increase. INTERESTING FACT! Index numbers are most often used in economics as they allow economists to turn complex data into easily understood terms. What are index numbers?
- 17. 17
- 18. 18 Using a sample means that statistics are uncertain, an estimate might differ from the ‘true value’. At the ONS, the methods we use to report uncertainty in our statistics include: • standard error • confidence interval • coefficient of variation • statistical significance Further explanations of the individual methodologies are available. Understanding sampling and the effect it has on statistics is also important for interpreting these measures of uncertainty. As well as random sampling, we also report on other factors that impact the quality of our estimates. This helps to make sure that people use our statistics correctly.
- 19. 19
- 20. 20 Communicating data and statistics is more than just presenting the numbers. At the ONS, we deal with a lot of complex data and concepts. Good communication can help ensure data is interpreted accurately and used appropriately. It also allows us to be completely open about the methods we use to collect data and calculate statistics. Some common challenges include: • working out which statistical terms and classifications can be simplified, and which cannot • finding out which facts are most important and deciding whether to make those more prominent • making it clear what conclusions the statistics do, and do not, support
- 21. 21 Data visualisation is the graphical representation of information and data. Tables of estimates presented as rows and columns of numbers can be difficult to read. Using visual elements, such as charts, graphs and maps, we can provide an accessible way to see and understand trends, outliers and patterns in data. A graph should look good, but it should also present information in a way that can be easily understood and analysed.
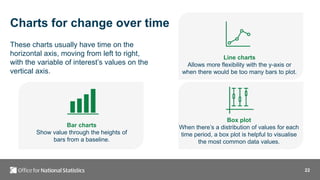
- 22. 22 Charts for change over time These charts usually have time on the horizontal axis, moving from left to right, with the variable of interest’s values on the vertical axis. Bar charts Show value through the heights of bars from a baseline. Line charts Allows more flexibility with the y-axis or when there would be too many bars to plot. Box plot When there’s a distribution of values for each time period, a box plot is helpful to visualise the most common data values.
- 23. 23 Charts for composition Used to show the different components of a total. Pie chart Represent the whole with a circle, divided into parts. Stacked bar chart Each bar is divided into multiple sub- bars, for demonstrating composition of multiple values. Stacked area chart Show composition of cumulated totals over time.
- 24. 24 Charts for data distribution Used to show the different components of a total. Bar charts Ideal for when a variable is qualitative and has discrete values. Histogram Ideal for analysing data of an ordered categorical variable. If ordered, focus on the shape of the distribution by bringing the bars together. If you move the bars apart, it becomes a bar chart.
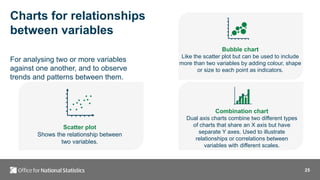
- 25. 25 Charts for relationships between variables For analysing two or more variables against one another, and to observe trends and patterns between them. Scatter plot Shows the relationship between two variables. Bubble chart Like the scatter plot but can be used to include more than two variables by adding colour, shape or size to each point as indicators. Combination chart Dual axis charts combine two different types of charts that share an X axis but have separate Y axes. Used to illustrate relationships or correlations between variables with different scales.











